正在加载图片...
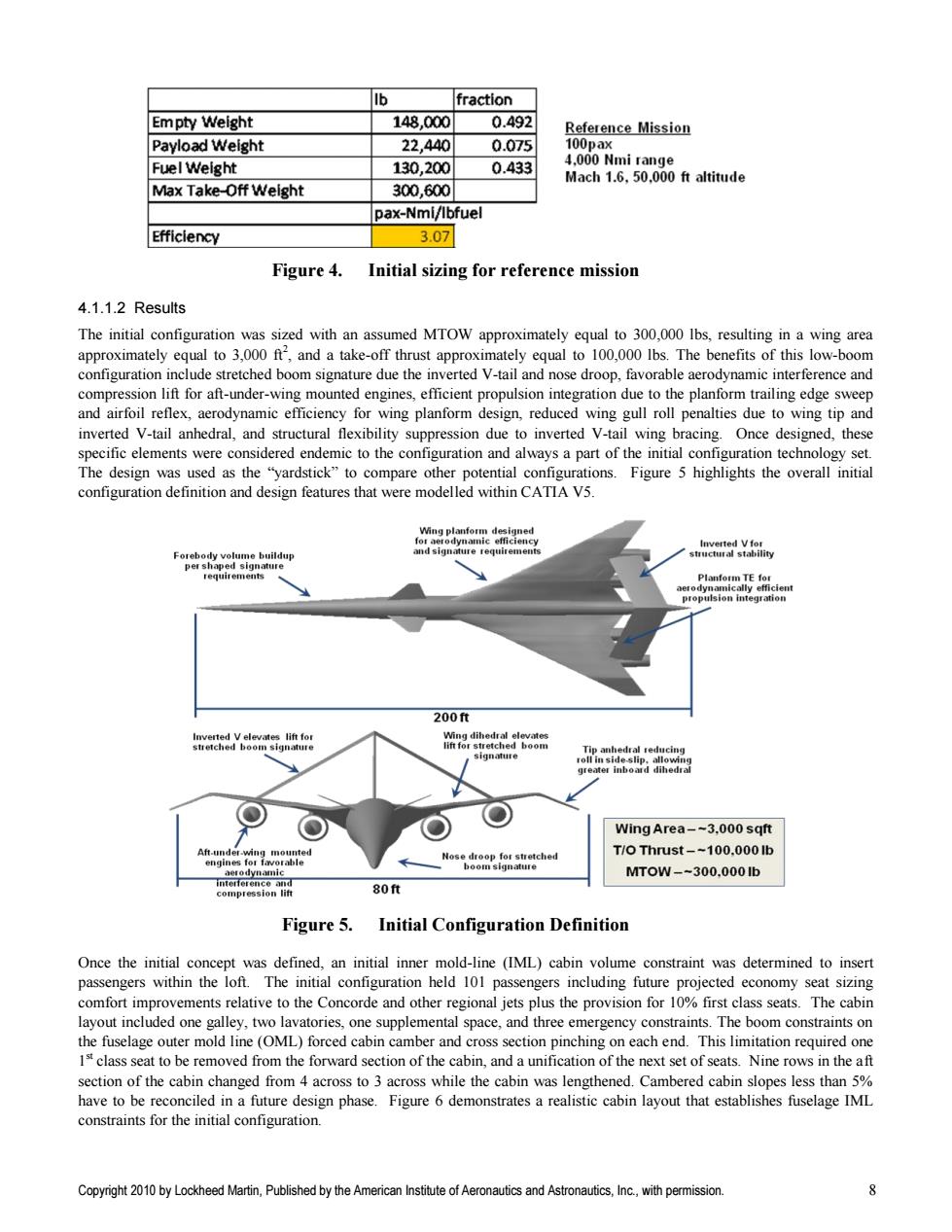
b fraction Empty Weight 148,000 0.492 Reference Mission Payload Weight 22,440 0.075 100pax Fuel Weight 130,200 0.433 4.000 Nmi range Mach 1.6.50.000 ft altitude Max Take-Off Weight 300,600 pax-Nmi/Ibfuel Efficiency 3.07 Figure 4. Initial sizing for reference mission 4.1.1.2 Results The initial configuration was sized with an assumed MTOW approximately equal to 300,000 Ibs,resulting in a wing area approximately equal to 3,000 ft,and a take-off thrust approximately equal to 100,000 Ibs.The benefits of this low-boom configuration include stretched boom signature due the inverted V-tail and nose droop,favorable aerodynamic interference and compression lift for aft-under-wing mounted engines,efficient propulsion integration due to the planform trailing edge sweep and airfoil reflex,aerodynamic efficiency for wing planform design,reduced wing gull roll penalties due to wing tip and inverted V-tail anhedral,and structural flexibility suppression due to inverted V-tail wing bracing.Once designed,these specific elements were considered endemic to the configuration and always a part of the initial configuration technology set. The design was used as the "yardstick"to compare other potential configurations.Figure 5 highlights the overall initial configuration definition and design features that were modelled within CATIA V5. Forebody volume buildup and signature requirements Inverted Vfor structural stability per shaped signature requirements Planform TE for 200ft Wing dihedral elevates lift for stretched boom Tip anhedral reducing signature roll in side-slip,allowing greater inboard dihedral Wing Area--3,000 sqft Aft-under-wing mounted T/O Thrust--100.000 lb engines for favorable Nose droop for stretched boom siqnature aerodynamic MToW--300.000b interference and compression lift 80ft Figure 5.Initial Configuration Definition Once the initial concept was defined,an initial inner mold-line(IML)cabin volume constraint was determined to insert passengers within the loft.The initial configuration held 101 passengers including future projected economy seat sizing comfort improvements relative to the Concorde and other regional jets plus the provision for 10%first class seats.The cabin layout included one galley,two lavatories,one supplemental space,and three emergency constraints.The boom constraints on the fuselage outer mold line(OML)forced cabin camber and cross section pinching on each end.This limitation required one 1s class seat to be removed from the forward section of the cabin,and a unification of the next set of seats.Nine rows in the aft section of the cabin changed from 4 across to 3 across while the cabin was lengthened.Cambered cabin slopes less than 5% have to be reconciled in a future design phase.Figure 6 demonstrates a realistic cabin layout that establishes fuselage IML constraints for the initial configuration. Copyright 2010 by Lockheed Martin,Published by the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Inc.,with permission.Copyright 2010 by Lockheed Martin, Published by the American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc., with permission. 8 Figure 4. Initial sizing for reference mission 4.1.1.2 Results The initial configuration was sized with an assumed MTOW approximately equal to 300,000 lbs, resulting in a wing area approximately equal to 3,000 ft2 , and a take-off thrust approximately equal to 100,000 lbs. The benefits of this low-boom configuration include stretched boom signature due the inverted V-tail and nose droop, favorable aerodynamic interference and compression lift for aft-under-wing mounted engines, efficient propulsion integration due to the planform trailing edge sweep and airfoil reflex, aerodynamic efficiency for wing planform design, reduced wing gull roll penalties due to wing tip and inverted V-tail anhedral, and structural flexibility suppression due to inverted V-tail wing bracing. Once designed, these specific elements were considered endemic to the configuration and always a part of the initial configuration technology set. The design was used as the ―yardstick‖ to compare other potential configurations. Figure 5 highlights the overall initial configuration definition and design features that were modelled within CATIA V5. Figure 5. Initial Configuration Definition Once the initial concept was defined, an initial inner mold-line (IML) cabin volume constraint was determined to insert passengers within the loft. The initial configuration held 101 passengers including future projected economy seat sizing comfort improvements relative to the Concorde and other regional jets plus the provision for 10% first class seats. The cabin layout included one galley, two lavatories, one supplemental space, and three emergency constraints. The boom constraints on the fuselage outer mold line (OML) forced cabin camber and cross section pinching on each end. This limitation required one 1 st class seat to be removed from the forward section of the cabin, and a unification of the next set of seats. Nine rows in the aft section of the cabin changed from 4 across to 3 across while the cabin was lengthened. Cambered cabin slopes less than 5% have to be reconciled in a future design phase. Figure 6 demonstrates a realistic cabin layout that establishes fuselage IML constraints for the initial configuration