正在加载图片...
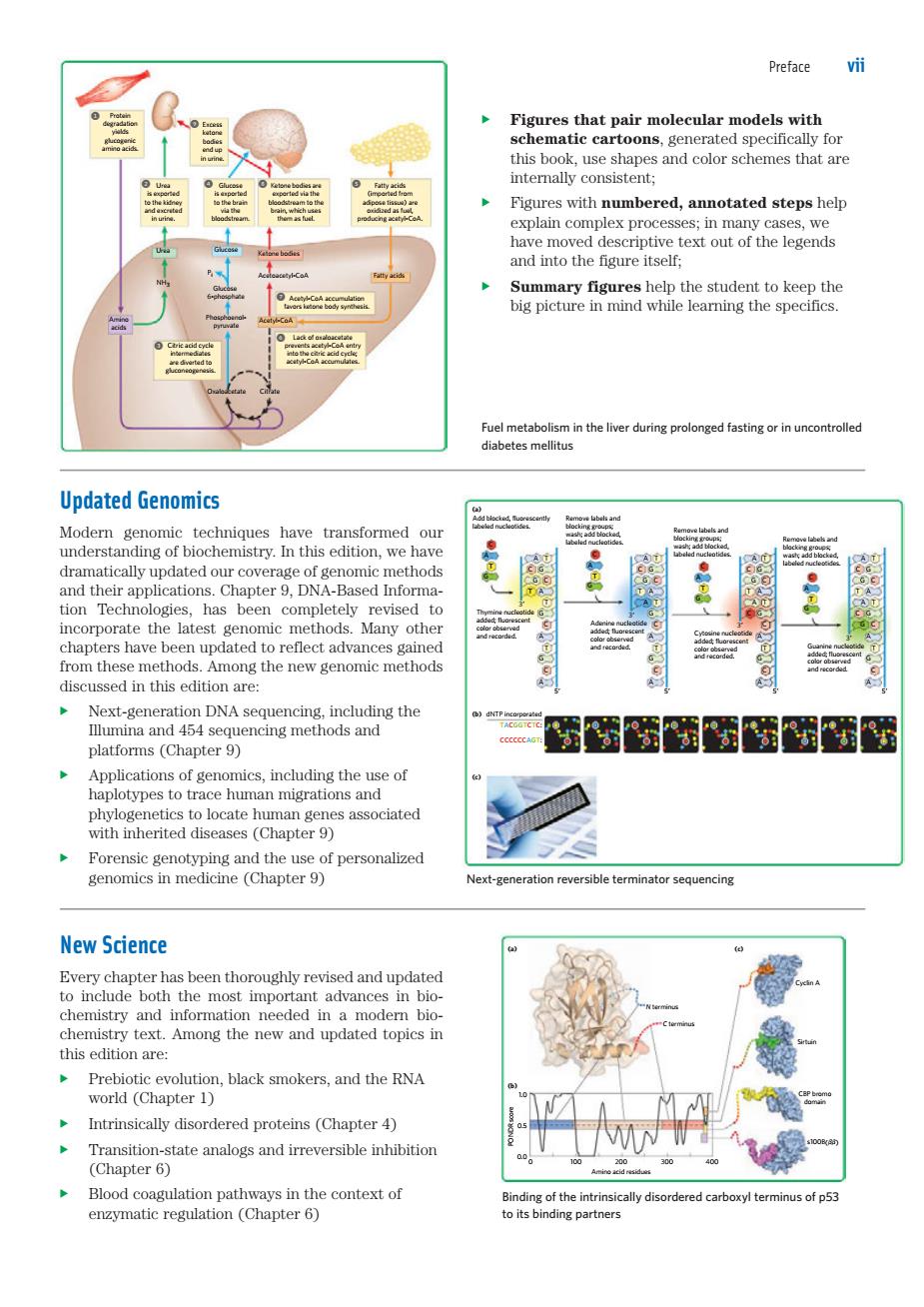
Prefare vii Figures that pair molecular models with c ca this ho interally consistent: A Figures with numbered,annotated steps help explain complex pro s:in many cases we text out of the legends Summary figures help the student to keep the big picture in mind while learning the specifics Updated Genomics Modern genomic techniques have transformed an thirpplicaChapterDNA-d tion Technologies has been completely revised neoporatethecaesteaenehok Many othe from these methods.Among the new genomic methods discussed in this edition are Next-generation DNA sequencing.including the Illumina and 454 sequencing methods and platforms (Chapter 9) Applications of genomics,including the use of migrations and with inherited diseases (Chapter ciated Forensic genoty Next-generation reversible terminator sequencing New Science Every chapter has been thoroughly revised and updatec to include both the most important advances in bio this edition are: Prebiotic evolution,black smokers,and the RNA world (Chapter 1) 4 Intrinsically disordered proteins(Chapter) (Chapter 6u Figures that pair molecular models with schematic cartoons, generated specifically for this book, use shapes and color schemes that are internally consistent; u Figures with numbered, annotated steps help explain complex processes; in many cases, we have moved descriptive text out of the legends and into the figure itself; u Summary figures help the student to keep the big picture in mind while learning the specifics. Updated Genomics Modern genomic techniques have transformed our understanding of biochemistry. In this edition, we have dramatically updated our coverage of genomic methods and their applications. Chapter 9, DNA-Based Information Technologies, has been completely revised to incorporate the latest genomic methods. Many other chapters have been updated to reflect advances gained from these methods. Among the new genomic methods discussed in this edition are: u Next-generation DNA sequencing, including the Illumina and 454 sequencing methods and platforms (Chapter 9) u Applications of genomics, including the use of haplotypes to trace human migrations and phylogenetics to locate human genes associated with inherited diseases (Chapter 9) u Forensic genotyping and the use of personalized genomics in medicine (Chapter 9) Next-generation reversible terminator sequencing New Science Every chapter has been thoroughly revised and updated to include both the most important advances in biochemistry and information needed in a modern biochemistry text. Among the new and updated topics in this edition are: u Prebiotic evolution, black smokers, and the RNA world (Chapter 1) u Intrinsically disordered proteins (Chapter 4) u Transition-state analogs and irreversible inhibition (Chapter 6) u Blood coagulation pathways in the context of enzymatic regulation (Chapter 6) Binding of the intrinsically disordered carboxyl terminus of p53 to its binding partners Preface vii Fuel metabolism in the liver during prolonged fasting or in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus FMTOC.indd Page vii 09/10/12 1:57 PM user-F408 /Users/user-F408/Desktop 1 7 3 6 2 48 9 5 Acetyl-CoA Pi Oxaloacetate Amino acids NH3 Glucose 6-phosphate Phosphoenolpyruvate Citrate Acetoacetyl-CoA Ketone bodies Urea Glucose Fatty acids Protein degradation yields glucogenic amino acids. Glucose is exported to the brain via the bloodstream. Excess ketone bodies end up in urine. Fatty acids (imported from adipose tissue) are oxidized as fuel, producing acetyl-CoA. Ketone bodies are exported via the bloodstream to the brain, which uses them as fuel. Urea is exported to the kidney and excreted in urine. Citric acid cycle intermediates are diverted to gluconeogenesis. Acetyl-CoA accumulation favors ketone body synthesis. Lack of oxaloacetate prevents acetyl-CoA entry into the citric acid cycle; acetyl-CoA accumulates. TACGGTCTC: CCCCCCAGT: dNTP incorporated T (b) (c) (a) 5 3 C T A A G C A G C T A A C C T G G T A C G T A C G T A C G T G C A G 5 3 C T A A G C A G C T A C T G T G C A 5 3 C T A A G C A G C T A C T G T G A 5 3 C T A A G C A G C T A C T G T G Guanine nucleotide added; fluorescent color observed and recorded. Cytosine nucleotide added; fluorescent color observed and recorded. Remove labels and blocking groups; wash; add blocked, labeled nucleotides. Remove labels and blocking groups; wash; add blocked, labeled nucleotides. Remove labels and blocking groups; wash; add blocked, labeled nucleotides. Add blocked, fluorescently labeled nucleotides. Adenine nucleotide added; fluorescent color observed and recorded. Thymine nucleotide added; fluorescent color observed and recorded. 300 Cyclin A Sirtuin s100B( ) bb 100 400 0.0 0.5 PONDR score 1.0 0 002 Amino acid residues C terminus N terminus CBP bromo domain (b) )a( )c(��������