正在加载图片...
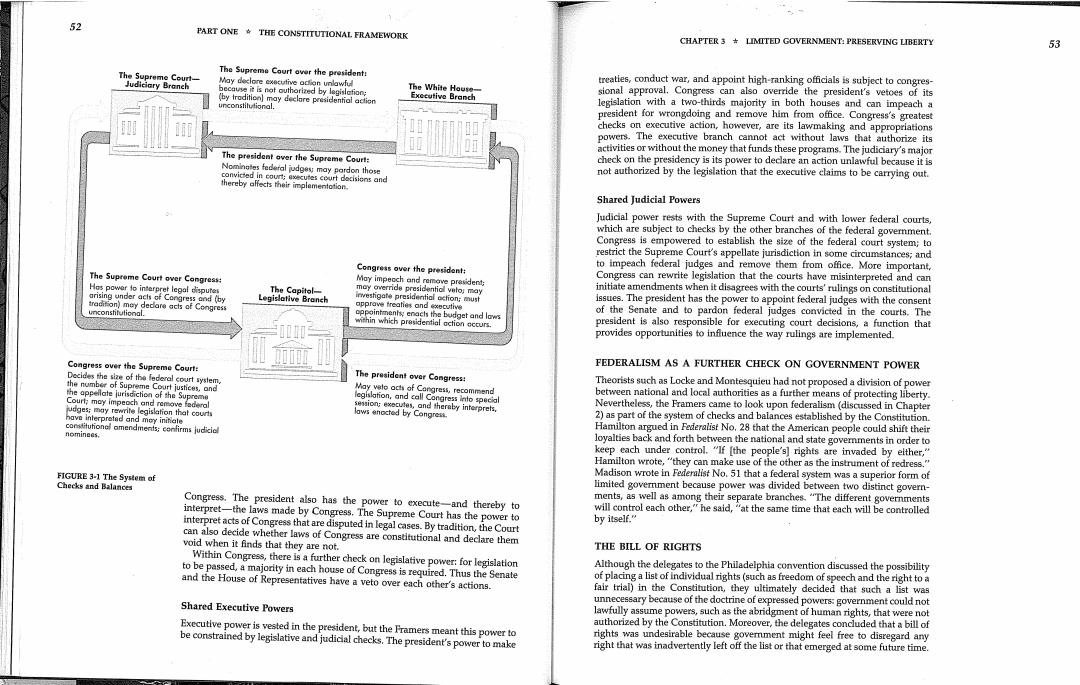
52 PART ONE THE CONSTITUTIONAL FRAMEWORK CHAPTER 3 LIMITED GOVERNMENT:PRESERVING LIBERTY 53 The Supreme Court over the president: treaties,conduct war,and appoint high-ranking officials is subject to congres- is not outhorized by sional approval.Congress can also override the president's vetoes of its may declare presidential acion legislation with a two-thirds majority in both houses and can impeach a president for wrongdoing and remove him from office.Congress's greatest checks on executive action,however,are its lawmaking and appropriations powers.The executive branch cannot act without laws that authorize its The president aver the Supreme Court: activities or without the money that funds these programs.The judiciary's major check on the presidency is its power to declare an action unlawful because it is nca地 not authorized by the legislation that the executive claims to be carrying out. isicns and Shared Judicial Powers Judicial power rests with the Supreme Court and with lower federal courts, which are subject to checks by the other branches of the federal government Congress is empowered to establish the size of the federal court system;to restrict the Supreme Court's appellate jurisdiction in some circumstances;and Congress over the president: to impeach federal judges and remove them from office.More important, The Supreme Court over Congress: Congress can rewrite legislation that the courts have misinterpreted and can Hospwronutes The Capitol- initiate amendments when it disagrees with the courts'rulings on constitutional r acls of Congress and (by s and e issues.The president has the power to appoint federal judges with the consent of the Senate and to pardon federal judges convicted in the courts.The president is also responsible for executing court decisions,a function that provides opportunities to infuence the way rulings are implemented. Congress over the Supreme Court: FEDERALISM AS A FURTHER CHECK ON GOVERNMENT POWER The president over Congress: Theorists such as Locke and Montesquieu had not proposed a division of power between national and local authorities as a further means of protecting liberty. Courl:moy impeoch a Nevertheless,the Framers came to look upon federalism(discussed in Chapter 2)as part of the system of checks and balances established by the Constitution. el amendmers;cenfirms judicicl Hamilton argued in Federalist No.28 that the American people could shift their loyalties back and forth between the national and state governments in order to keep each under control."If [the people's]rights are invaded by either," Hamilton wrote,"they can make use of the other as the instrument of redress." FIGURE 3-1 The Systom of Checks and Balances Madison wrote in Federlist No.51 that a federal system was a superior form of limited goverment because power was divided between two distinct govern- Congress.The president also has the power to execute-and thereby to ments,as well as among their separate branches."The different governments interpret-the laws made by Congress.The Supreme Court has the power to will control each other,"he said,"at the same time that each will be controlled interpret acts of Congress that are disputed in legal cases.By tradition,the Court by itself." can also decide whether laws of Congress are constitutional and declare them void when it finds that they are not. THE BILL OF RIGHTS Within Congress,there is a further check on legislative power:for legislation to be passed,a majority in each house of Congress is required.Thus the Senate Although the delegates to the Philadelphia convention discussed the possibility and the House of Representatives have a veto over each other's actions. of placing a list of individual rights(such as freedom of speech and the right to a fair trial)in the Constitution,they ultimately decided that such a list was Shared Executive Powers unnecessary because of the doctrine of expressed powers:government could not lawfully assume powers,such as the abridgment of human rights,that were not Executive power is vested in the president,but the Framers meant this power to authorized by the Constitution.Moreover,the delegates concluded that a bill of be constrained by legislative and judicial checks.The president's power to make rights was undesirable because government might feel free to disregard any right that was inadvertently left off the list or that emerged at some future time