正在加载图片...
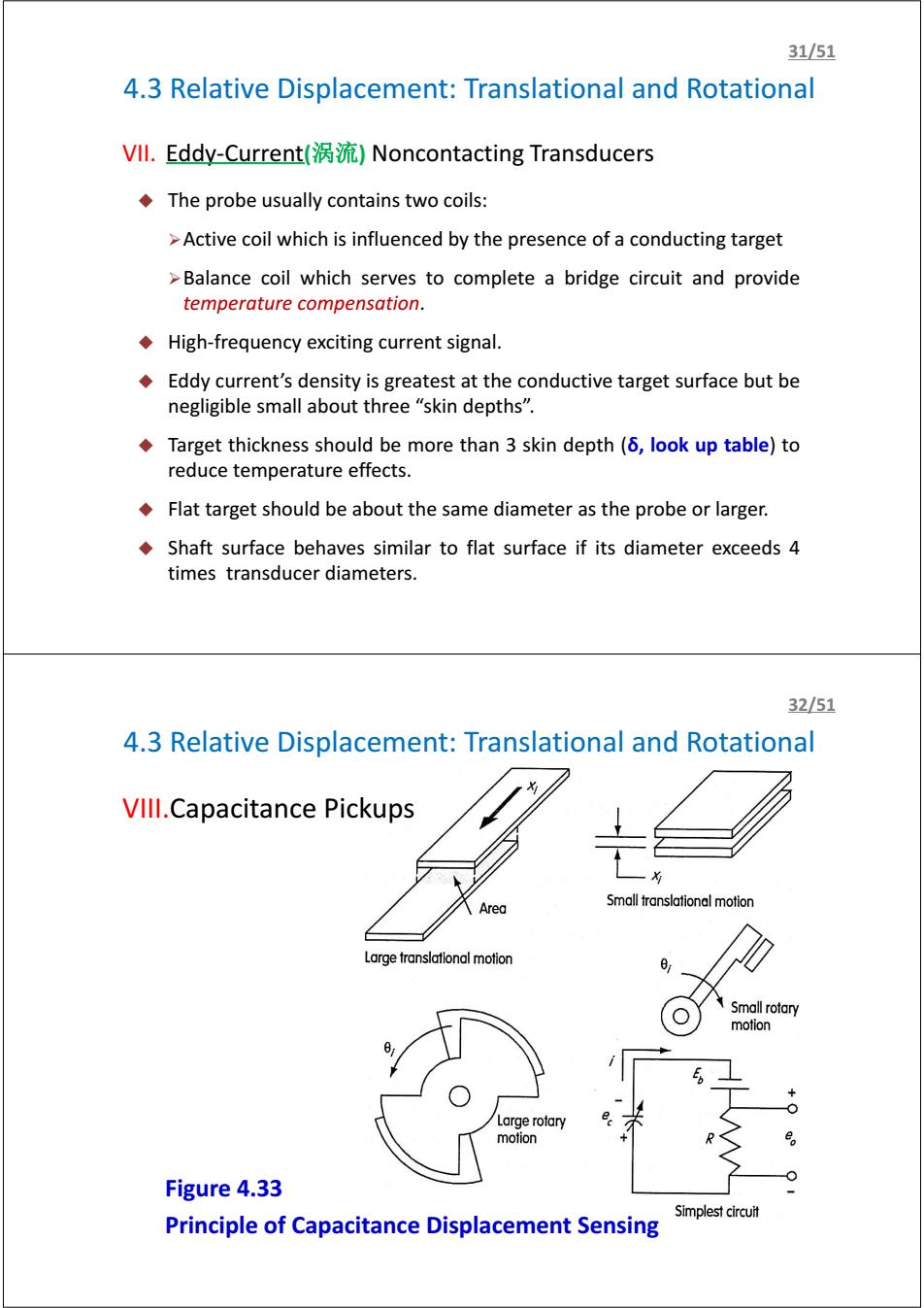
31/51 4.3 Relative Displacement:Translational and Rotational VIl.Eddy-Current()Noncontacting Transducers The probe usually contains two coils: >Active coil which is influenced by the presence of a conducting target >Balance coil which serves to complete a bridge circuit and provide temperature compensation. High-frequency exciting current signal. Eddy current's density is greatest at the conductive target surface but be negligible small about three "skin depths". Target thickness should be more than 3 skin depth(6,look up table)to reduce temperature effects. Flat target should be about the same diameter as the probe or larger. Shaft surface behaves similar to flat surface if its diameter exceeds 4 times transducer diameters. 32/51 4.3 Relative Displacement:Translational and Rotational VIll.Capacitance Pickups Area Small translational motion Large translational motion Small rotary motion Large rotary motion Figure 4.33 Simplest circuit Principle of Capacitance Displacement Sensing4.3 Relative Displacement: Translational and Rotational VII. Eddy-Current(涡流) Noncontacting Transducers The probe usually contains two coils: ¾Active coil which is influenced by the presence of a conducting target ¾Balance coil which serves to complete a bridge circuit and provide temperature compensation. High-frequency exciting current signal. Eddy current’s density is greatest at the conductive target surface but be negligible small about three “skin depths”. Target thickness should be more than 3 skin depth (δ, look up table) to reduce temperature effects. Flat target should be about the same diameter as the probe or larger. Shaft surface behaves similar to flat surface if its diameter exceeds 4 times transducer diameters. 31/51 4.3 Relative Displacement: Translational and Rotational VIII.Capacitance Pickups Figure 4.33 Principle of Capacitance Displacement Sensing 32/51