正在加载图片...
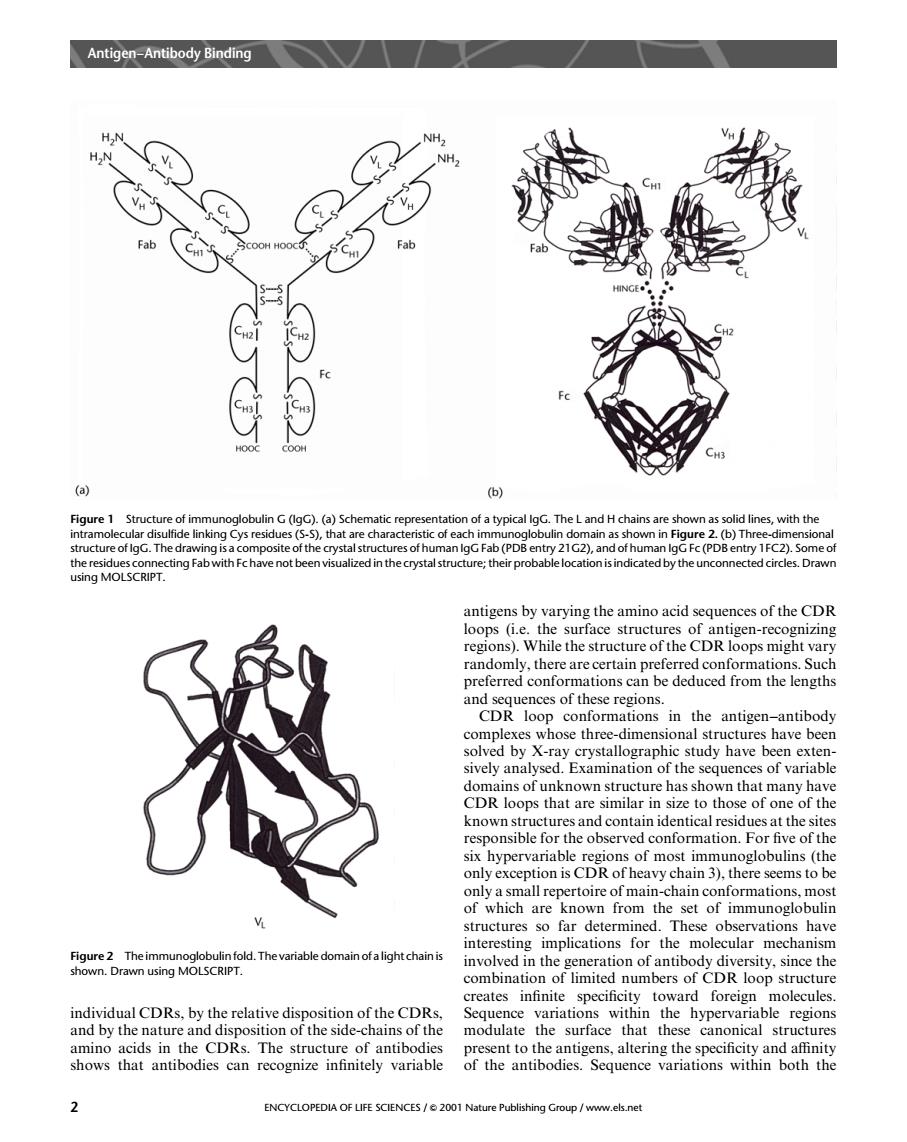
Antigen-Antibody Binding Fab a ) Figure 1 Structu uctu re of lgG.The n lgG Fa (PD sing MOLSCRIPT. regions).While the structure of the CDR loops might vary om he ces of these CDRtioni thentignantbdy study have been structure has shown that many hav CDR loops that are similar in size to those of one of the afonmationFthee ypeof moc ob (the erve only a small repertoire of main-chain conformations,most of which are known from the set of immunoglobulin tructures s iar乙emgtcpod.Tmnevarabtetomahotaightdhan on of antibody dive ity.since the comntoofiemersof Ructur toward ndhidmlcDRbyeterehiceiPinecfheCRe amino acids in the CDRs.The structure of antibodie sent to the antig ns,altering the specificity and affinity shows that antibodies can recognize infinitely variable of hetbdnceriations within both the ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES/2001 Na shingGroup/www.els.netindividual CDRs, by the relative disposition of the CDRs, and by the nature and disposition of the side-chains of the amino acids in the CDRs. The structure of antibodies shows that antibodies can recognize infinitely variable antigens by varying the amino acid sequences of the CDR loops (i.e. the surface structures of antigen-recognizing regions). While the structure of the CDR loops might vary randomly, there are certain preferred conformations. Such preferred conformations can be deduced from the lengths and sequences of these regions. CDR loop conformations in the antigen–antibody complexes whose three-dimensional structures have been solved by X-ray crystallographic study have been extensively analysed. Examination of the sequences of variable domains of unknown structure has shown that many have CDR loops that are similar in size to those of one of the known structures and contain identical residues at the sites responsible for the observed conformation. For five of the six hypervariable regions of most immunoglobulins (the only exception is CDR of heavy chain 3), there seems to be only a small repertoire of main-chain conformations, most of which are known from the set of immunoglobulin structures so far determined. These observations have interesting implications for the molecular mechanism involved in the generation of antibody diversity, since the combination of limited numbers of CDR loop structure creates infinite specificity toward foreign molecules. Sequence variations within the hypervariable regions modulate the surface that these canonical structures present to the antigens, altering the specificity and affinity of the antibodies. Sequence variations within both the Figure 1 Structure of immunoglobulin G (IgG). (a) Schematic representation of a typical IgG. The L and H chains are shown as solid lines, with the intramolecular disulfide linking Cys residues (S-S), that are characteristic of each immunoglobulin domain as shown in Figure 2. (b) Three-dimensional structure of IgG. The drawing is a composite of the crystal structures of human IgG Fab (PDB entry 21G2), and of human IgG Fc (PDB entry 1FC2). Some of the residues connecting Fab with Fc have not been visualized in the crystal structure; their probable location is indicated by the unconnected circles. Drawn using MOLSCRIPT. Figure 2 The immunoglobulin fold. The variable domain of a light chain is shown. Drawn using MOLSCRIPT. Antigen–Antibody Binding 2 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net