正在加载图片...
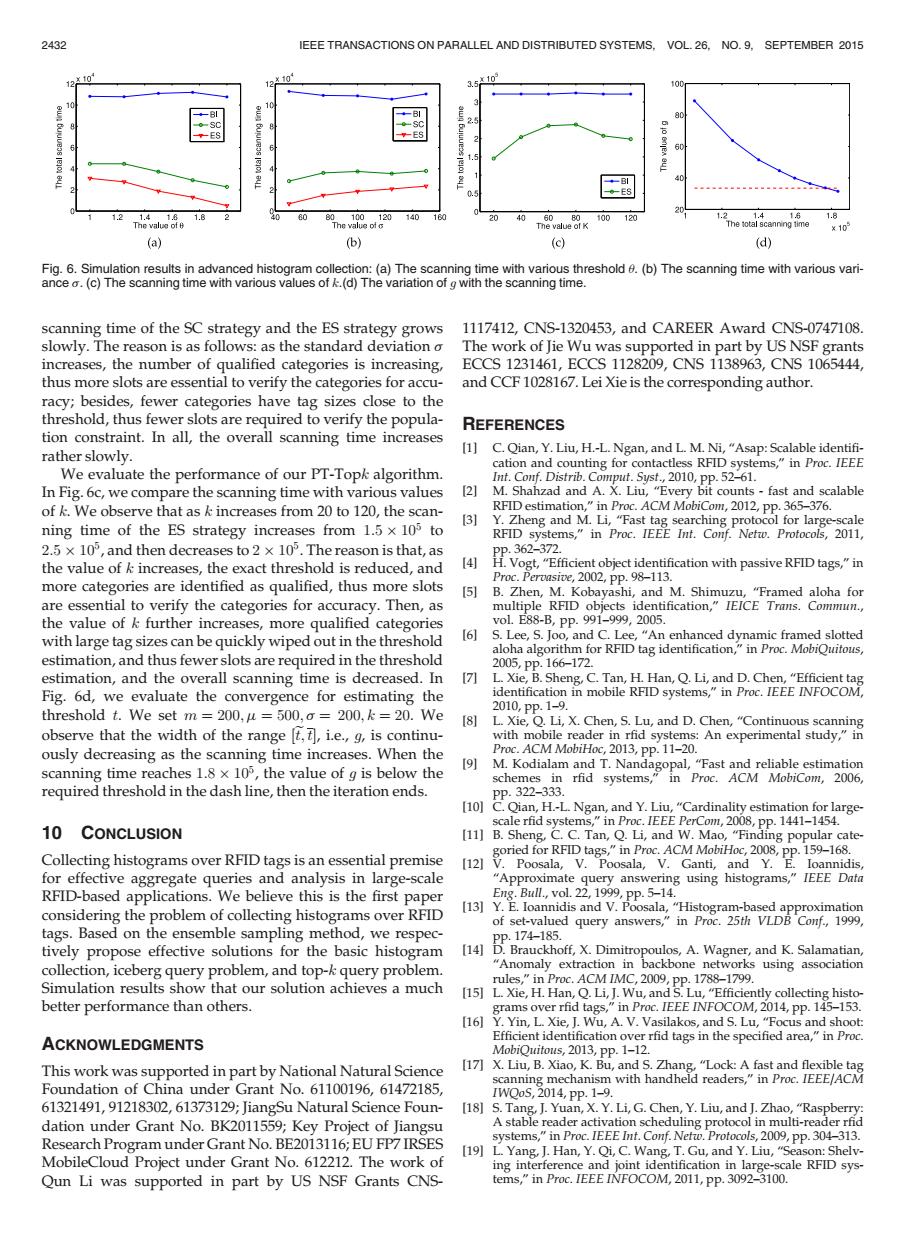
2432 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS,VOL.26.NO.9.SEPTEMBER 2015 SC -ES 60 -BI 40 -ES 12 80 100.120 140 40 The value of c The valueK 60 100 120 1.2 1.8 x103 (a) (b) ( (d) Fig.6.Simulation results in advanced histogram collection:(a)The scanning time with various threshold 6.(b)The scanning time with various vari- ance o.(c)The scanning time with various values of k.(d)The variation of g with the scanning time. scanning time of the SC strategy and the ES strategy grows 1117412,CNS-1320453,and CAREER Award CNS-0747108. slowly.The reason is as follows:as the standard deviation o The work of Jie Wu was supported in part by US NSF grants increases,the number of qualified categories is increasing, ECCS1231461,ECCS1128209,CNS1138963,CNS1065444, thus more slots are essential to verify the categories for accu- and CCF 1028167.Lei Xie is the corresponding author. racy;besides,fewer categories have tag sizes close to the threshold,thus fewer slots are required to verify the popula- REFERENCES tion constraint.In all,the overall scanning time increases [1]C.Qian,Y.Liu,H.-L.Ngan,and L.M.Ni,"Asap:Scalable identifi- rather slowly. cation and counting for contactless RFID systems,"in Proc.IEEE We evaluate the performance of our PT-Topk algorithm Int.Conf.Distrib.Comput.Syst.,2010,pp.52-61. In Fig.6c,we compare the scanning time with various values 2] M.Shahzad and A.X.Liu,"Every bit counts-fast and scalable of k.We observe that as k increases from 20 to 120,the scan- RFID estimation,"in Proc.ACM MobiCom,2012,Pp.365-376. 31 Y.Zheng and M.Li,"Fast tag searching protocol for large-scale ning time of the ES strategy increases from 1.5 x 105 to RFID systems,"in Proc.IEEE Int.Conf.Netw.Protocols,2011, 2.5 x 10,and then decreases to 2 x 10%.The reason is that,as Pp.362-372. the value of k increases,the exact threshold is reduced,and [4] H.Vogt,"Efficient object identification with passive RFID tags,"in more categories are identified as qualified,thus more slots Proc.Pervasive,2002,pp.98-113. [5] B.Zhen,M.Kobayashi,and M.Shimuzu,"Framed aloha for are essential to verify the categories for accuracy.Then,as multiple RFID objects identification,"IEICE Trans.Commun., the value of k further increases,more qualified categories vol.E88-B,pp.991-999,2005. with large tag sizes can be quickly wiped out in the threshold L6] S.Lee,S.Joo,and C.Lee,"An enhanced dynamic framed slotted aloha algorithm for RFID tag identification,in Proc.MobiQuitous, estimation,and thus fewer slots are required in the threshold 2005,pp.166-172. estimation,and the overall scanning time is decreased.In 71 L.Xie,B.Sheng,C.Tan,H.Han,Q.Li,and D.Chen,"Efficient tag Fig.6d,we evaluate the convergence for estimating the identification in mobile RFID systems,"in Proc.IEEE INFOCOM, threshold t.We set m 200,u=500,o =200,k 20.We 2010,pp.1-9. [8I L.Xie,Q.Li,X.Chen,S.Lu,and D.Chen,"Continuous scanning observe that the width of the range [t,t,i.e.,g,is continu- with mobile reader in rfid systems:An experimental study,"in ously decreasing as the scanning time increases.When the Proc.ACM MobiHoc,2013,pp.11-20. [9 scanning time reaches 1.8 x 105,the value of g is below the M.Kodialam and T.Nandagopal,"Fast and reliable estimation schemes in rfid systems,"in Proc.ACM MobiCom,2006, required threshold in the dash line,then the iteration ends. PP.322-333. [10]C.Qian,H.-L.Ngan,and Y.Liu,"Cardinality estimation for large scale rfid systems,"in Proc.IEEE PerCom,2008,pp.1441-1454. 10 CONCLUSION [11]B.Sheng,C.C.Tan,Q.Li,and W.Mao,"Finding popular cate- Collecting histograms over RFID tags is an essential premise goried for RFID tags,"in Proc.ACM MobiHoc,2008,pp.159-168. [12]V.Poosala,V.Poosala,V.Ganti,and Y.E.loannidis for effective aggregate queries and analysis in large-scale "Approximate query answering using histograms,"IEEE Data RFID-based applications.We believe this is the first paper Eg.Bul,vol.22,1999,Pp.5-14. considering the problem of collecting histograms over RFID [13]Y.E.Ioannidis and V.Poosala,"Histogram-based approximation of set-valued query answers,"in Proc.25th VLDB Conf.,1999 tags.Based on the ensemble sampling method,we respec- PP.174-185 tively propose effective solutions for the basic histogram [14]D.Brauckhoff,X.Dimitropoulos,A.Wagner,and K.Salamatian collection,iceberg query problem,and top-k query problem. "Anomaly extraction in backbone networks using association Simulation results show that our solution achieves a much rules,"in Proc.ACM IMC,2009,pp.1788-1799. [15] L.Xie,H.Han,Q.Li,J.Wu,and S.Lu,"Efficiently collecting histo- better performance than others. grams over rfid tags,"in Proc.IEEE INFOCOM,2014,pp.145-153. [161 Y.Yin,L.Xie,J.Wu,A.V.Vasilakos,and S.Lu,"Focus and shoot: ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Efficient identification over rfid tags in the specified area,"in Proc. MobiQuitous,2013,pp.1-12. This work was supported in part by National Natural Science [17]X.Liu,B.Xiao,K.Bu,and S.Zhang,"Lock:A fast and flexible tag scanning mechanism with handheld readers,"in Proc.IEEE/ACM Foundation of China under Grant No.61100196,61472185, IWQoS,2014,Pp.1-9. 61321491,91218302,61373129;JiangSu Natural Science Foun- [18]S.Tang,J.Yuan,X.Y.Li,G.Chen,Y.Liu,and J.Zhao,"Raspberry: dation under Grant No.BK2011559;Key Project of Jiangsu A stable reader activation scheduling protocol in multi-reader rfid Research Program under Grant No.BE2013116;EU FP7 IRSES systems,"in Proc.IEEE Int.Conf.Netw.Protocols,2009,pp.304-313. [19]L.Yang,J.Han,Y.Qi,C.Wang,T.Gu,and Y.Liu,"Season:Shelv- MobileCloud Project under Grant No.612212.The work of ing interference and joint identification in large-scale RFID sys- Qun Li was supported in part by US NSF Grants CNS- tems,"in Proc.IEEE INFOCOM,2011,pp.3092-3100.scanning time of the SC strategy and the ES strategy grows slowly. The reason is as follows: as the standard deviation s increases, the number of qualified categories is increasing, thus more slots are essential to verify the categories for accuracy; besides, fewer categories have tag sizes close to the threshold, thus fewer slots are required to verify the population constraint. In all, the overall scanning time increases rather slowly. We evaluate the performance of our PT-Topk algorithm. In Fig. 6c, we compare the scanning time with various values of k. We observe that as k increases from 20 to 120, the scanning time of the ES strategy increases from 1:5
105 to 2:5
105, and then decreases to 2
105. The reason is that, as the value of k increases, the exact threshold is reduced, and more categories are identified as qualified, thus more slots are essential to verify the categories for accuracy. Then, as the value of k further increases, more qualified categories with large tag sizes can be quickly wiped out in the threshold estimation, and thus fewer slots are required in the threshold estimation, and the overall scanning time is decreased. In Fig. 6d, we evaluate the convergence for estimating the threshold t. We set m ¼ 200;m ¼ 500; s ¼ 200; k ¼ 20. We observe that the width of the range ½et;t, i.e., g, is continuously decreasing as the scanning time increases. When the scanning time reaches 1:8
105, the value of g is below the required threshold in the dash line, then the iteration ends. 10 CONCLUSION Collecting histograms over RFID tags is an essential premise for effective aggregate queries and analysis in large-scale RFID-based applications. We believe this is the first paper considering the problem of collecting histograms over RFID tags. Based on the ensemble sampling method, we respectively propose effective solutions for the basic histogram collection, iceberg query problem, and top-k query problem. Simulation results show that our solution achieves a much better performance than others. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61100196, 61472185, 61321491, 91218302, 61373129; JiangSu Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. BK2011559; Key Project of Jiangsu Research Program under Grant No. BE2013116; EU FP7 IRSES MobileCloud Project under Grant No. 612212. The work of Qun Li was supported in part by US NSF Grants CNS- 1117412, CNS-1320453, and CAREER Award CNS-0747108. The work of Jie Wu was supported in part by US NSF grants ECCS 1231461, ECCS 1128209, CNS 1138963, CNS 1065444, and CCF 1028167. Lei Xie is the corresponding author. REFERENCES [1] C. Qian, Y. Liu, H.-L. Ngan, and L. M. Ni, “Asap: Scalable identifi- cation and counting for contactless RFID systems,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Distrib. Comput. Syst., 2010, pp. 52–61. [2] M. Shahzad and A. X. Liu, “Every bit counts - fast and scalable RFID estimation,” in Proc. ACM MobiCom, 2012, pp. 365–376. [3] Y. Zheng and M. Li, “Fast tag searching protocol for large-scale RFID systems,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Netw. Protocols, 2011, pp. 362–372. [4] H. Vogt, “Efficient object identification with passive RFID tags,” in Proc. Pervasive, 2002, pp. 98–113. [5] B. Zhen, M. Kobayashi, and M. Shimuzu, “Framed aloha for multiple RFID objects identification,” IEICE Trans. Commun., vol. E88-B, pp. 991–999, 2005. [6] S. Lee, S. Joo, and C. Lee, “An enhanced dynamic framed slotted aloha algorithm for RFID tag identification,” in Proc. MobiQuitous, 2005, pp. 166–172. [7] L. Xie, B. Sheng, C. Tan, H. Han, Q. Li, and D. Chen, “Efficient tag identification in mobile RFID systems,” in Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, 2010, pp. 1–9. [8] L. Xie, Q. Li, X. Chen, S. Lu, and D. Chen, “Continuous scanning with mobile reader in rfid systems: An experimental study,” in Proc. ACM MobiHoc, 2013, pp. 11–20. [9] M. Kodialam and T. Nandagopal, “Fast and reliable estimation schemes in rfid systems,” in Proc. ACM MobiCom, 2006, pp. 322–333. [10] C. Qian, H.-L. Ngan, and Y. Liu, “Cardinality estimation for largescale rfid systems,” in Proc. IEEE PerCom, 2008, pp. 1441–1454. [11] B. Sheng, C. C. Tan, Q. Li, and W. Mao, “Finding popular categoried for RFID tags,” in Proc. ACM MobiHoc, 2008, pp. 159–168. [12] V. Poosala, V. Poosala, V. Ganti, and Y. E. Ioannidis, “Approximate query answering using histograms,” IEEE Data Eng. Bull., vol. 22, 1999, pp. 5–14. [13] Y. E. Ioannidis and V. Poosala, “Histogram-based approximation of set-valued query answers,” in Proc. 25th VLDB Conf., 1999, pp. 174–185. [14] D. Brauckhoff, X. Dimitropoulos, A. Wagner, and K. Salamatian, “Anomaly extraction in backbone networks using association rules,” in Proc. ACM IMC, 2009, pp. 1788–1799. [15] L. Xie, H. Han, Q. Li, J. Wu, and S. Lu, “Efficiently collecting histograms over rfid tags,” in Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, 2014, pp. 145–153. [16] Y. Yin, L. Xie, J. Wu, A. V. Vasilakos, and S. Lu, “Focus and shoot: Efficient identification over rfid tags in the specified area,” in Proc. MobiQuitous, 2013, pp. 1–12. [17] X. Liu, B. Xiao, K. Bu, and S. Zhang, “Lock: A fast and flexible tag scanning mechanism with handheld readers,” in Proc. IEEE/ACM IWQoS, 2014, pp. 1–9. [18] S. Tang, J. Yuan, X. Y. Li, G. Chen, Y. Liu, and J. Zhao, “Raspberry: A stable reader activation scheduling protocol in multi-reader rfid systems,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Netw. Protocols, 2009, pp. 304–313. [19] L. Yang, J. Han, Y. Qi, C. Wang, T. Gu, and Y. Liu, “Season: Shelving interference and joint identification in large-scale RFID systems,” in Proc. IEEE INFOCOM, 2011, pp. 3092–3100. Fig. 6. Simulation results in advanced histogram collection: (a) The scanning time with various threshold u. (b) The scanning time with various variance s. (c) The scanning time with various values of k.(d) The variation of g with the scanning time. 2432 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON PARALLEL AND DISTRIBUTED SYSTEMS, VOL. 26, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2015