正在加载图片...
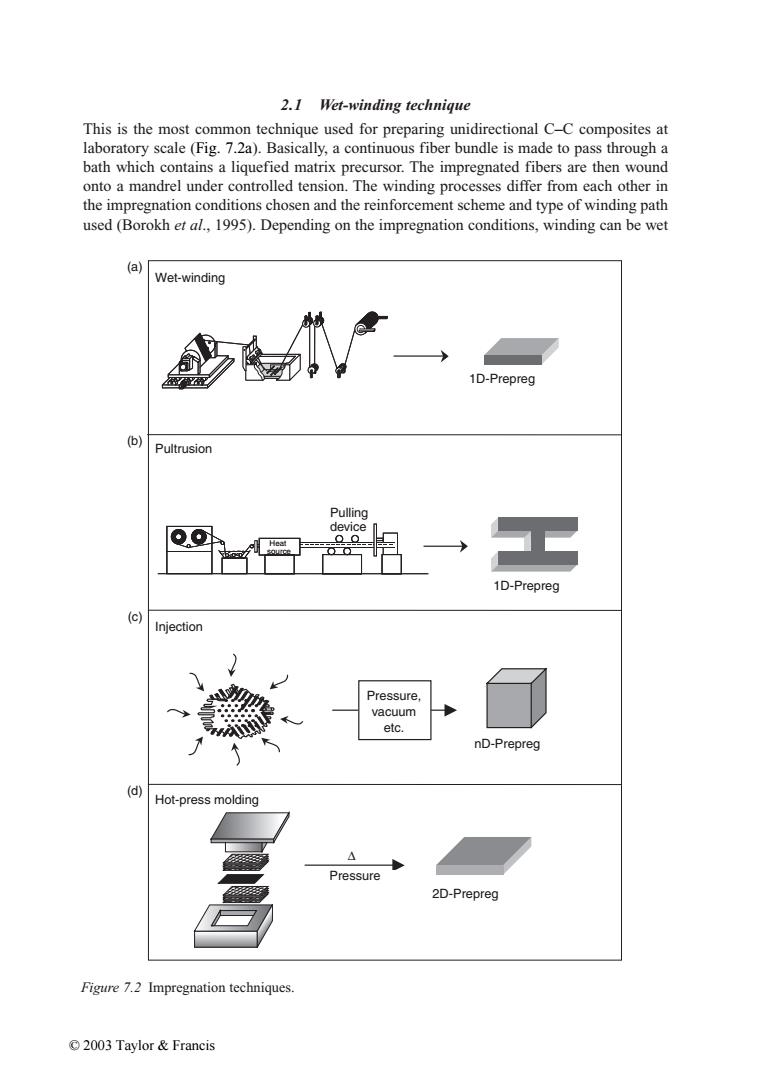
2.1 Wet-winding technique This is the most common technique used for preparing unidirectional C-C composites at laboratory scale(Fig.7.2a).Basically,a continuous fiber bundle is made to pass through a bath which contains a liquefied matrix precursor.The impregnated fibers are then wound onto a mandrel under controlled tension.The winding processes differ from each other in the impregnation conditions chosen and the reinforcement scheme and type of winding path used (Borokh et al.,1995).Depending on the impregnation conditions,winding can be wet (a) Wet-winding 1D-Prepreg (b) Pultrusion Pulling device Heat 1D-Prepreg (c) Injection Pressure, vacuum etc. nD-Prepreg (d) Hot-press molding △ Pressure 2D-Prepreg Figure 7.2 Impregnation techniques. ©2003 Taylor&Francis2.1 Wet-winding technique This is the most common technique used for preparing unidirectional C–C composites at laboratory scale (Fig. 7.2a). Basically, a continuous fiber bundle is made to pass through a bath which contains a liquefied matrix precursor. The impregnated fibers are then wound onto a mandrel under controlled tension. The winding processes differ from each other in the impregnation conditions chosen and the reinforcement scheme and type of winding path used (Borokh et al., 1995). Depending on the impregnation conditions, winding can be wet Figure 7.2 Impregnation techniques. Wet-winding ∆ Pressure Pressure, vacuum etc. Injection nD-Prepreg 1D-Prepreg Pultrusion Heat source Pulling device 1D-Prepreg 2D-Prepreg Hot-press molding (a) (b) (c) (d) © 2003 Taylor & Francis