正在加载图片...
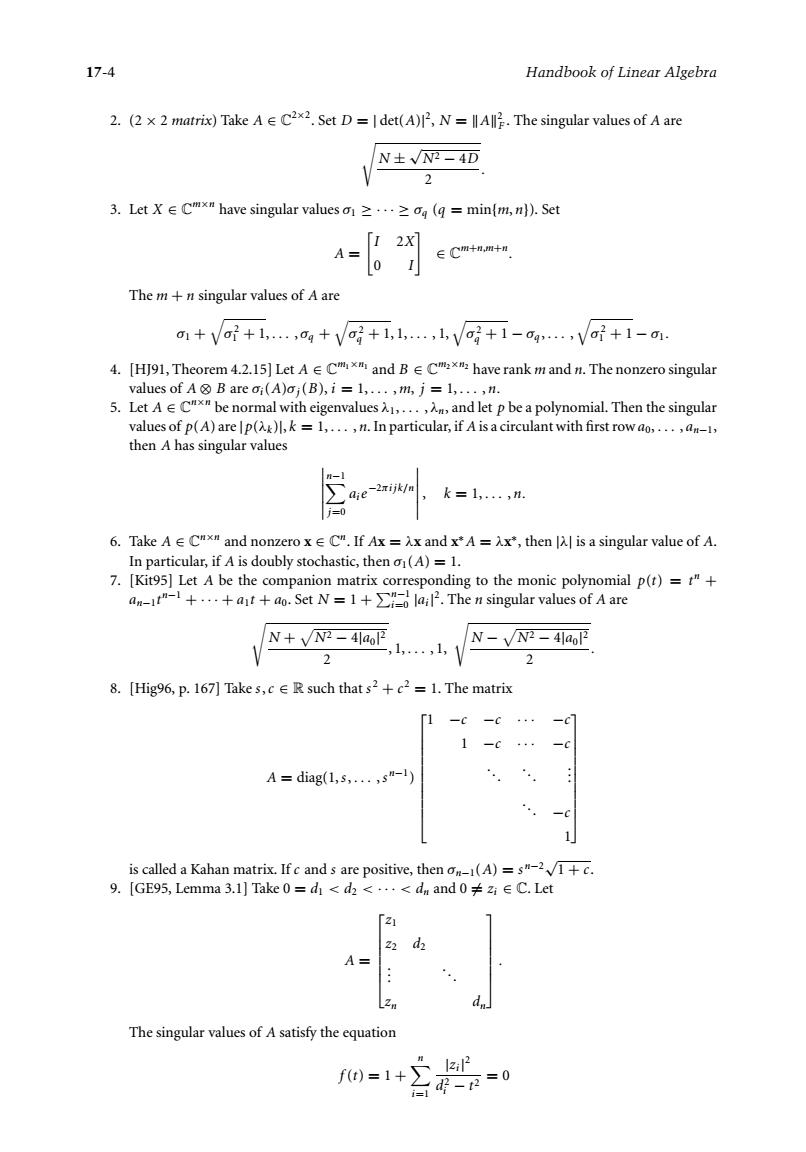
17-4 Handbook of Linear Algebra 2.(2x2 matrix)Take.Set D=Idet(A),N=singular values of A are N士N-4D 3.LetX∈Cmx"have singular values≥…≥ag(q=min(m,nj.Set A= 「12x ∈Cm+,m+n The m+n singular values of A are 1+V+1,…,g+V+1,l山V+1-4√+1-am 4.[HJ91,Theorem 4.2.15]Let ACm and BCx have rank mand n.The nonzero singular values of A B are ai(A)oj(B),i=1,...,mj=1,...,n. 5.LctA∈C" be normal with eigenvalues.. ,and let p be a polynomial.Then the singular values of p(A)are Ip(,=1,...,n.In particular,if A is a circulant with first row o,... then A has singular values k=1,,m 6.TakeA∈Cx la 7.[Kit9 ia些foub邮ohastic,e)=A二Ahca川ingar ae monic polyno mial p())=t+ N+y=4a,lVN--4a 2 2 8.[Hig96,p.167]Takes,cR such that s2+2=1.The matrix 「1-c-c···-c1 A=diag(1,s,.,s-l) is called a Kahan matrix.If c and s are positive,then(A)=s"21+c. 9.[GE95,Lemma3.l】Take0=d<d2<…<d.and0≠a∈C.Let d A= The singular values of A satisfy the equation f0=1+17-4 Handbook of Linear Algebra 2. (2 × 2 matrix) Take A ∈ C2×2 . Set D = | det(A)| 2, N = A2 F . The singular values of A are N ± √N2 − 4D 2 . 3. Let X ∈ Cm×n have singular values σ1 ≥···≥ σq (q = min{m, n}). Set A = I 2X 0 I ∈ Cm+n,m+n. The m + n singular values of A are σ1 + σ2 1 + 1, ... , σq + σ2 q + 1, 1, ... , 1, σ2 q + 1 − σq , ... , σ2 1 + 1 − σ1. 4. [HJ91, Theorem 4.2.15] Let A ∈ Cm1×n1 and B ∈ Cm2×n2 have rank m and n. The nonzero singular values of A ⊗ B are σi(A)σj(B), i = 1, ... , m, j = 1, ... , n. 5. Let A ∈ Cn×n be normal with eigenvalues λ1, ... , λn, and let p be a polynomial. Then the singular values of p(A) are |p(λk )|, k = 1, ... , n. In particular, if A is a circulant with first rowa0, ... , an−1, then A has singular values n−1 j=0 aie−2πijk/n , k = 1, ... , n. 6. Take A ∈ Cn×n and nonzero x ∈ Cn. If Ax = λx and x∗A = λx∗, then |λ| is a singular value of A. In particular, if A is doubly stochastic, then σ1(A) = 1. 7. [Kit95] Let A be the companion matrix corresponding to the monic polynomial p(t) = tn + an−1tn−1 +···+ a1t + a0. Set N = 1 + n−1 i=0 |ai| 2. The n singular values of A are N + N2 − 4|a0| 2 2 , 1, ... , 1, N − N2 − 4|a0| 2 2 . 8. [Hig96, p. 167] Take s,c ∈ R such that s 2 + c 2 = 1. The matrix A = diag(1,s, ... ,s n−1 ) ⎡ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ 1 −c −c ··· −c 1 −c ··· −c ... ... . . . ... −c 1 ⎤ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ is called a Kahan matrix. If c and s are positive, then σn−1(A) = s n−2 √1 + c. 9. [GE95, Lemma 3.1] Take 0 = d1 < d2 < ··· < dn and 0 = zi ∈ C. Let A = ⎡ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎢ ⎣ z1 z2 d2 . . . ... zn dn ⎤ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎥ ⎦ . The singular values of A satisfy the equation f (t) = 1 +n i=1 |zi| 2 d2 i − t2 = 0���