正在加载图片...
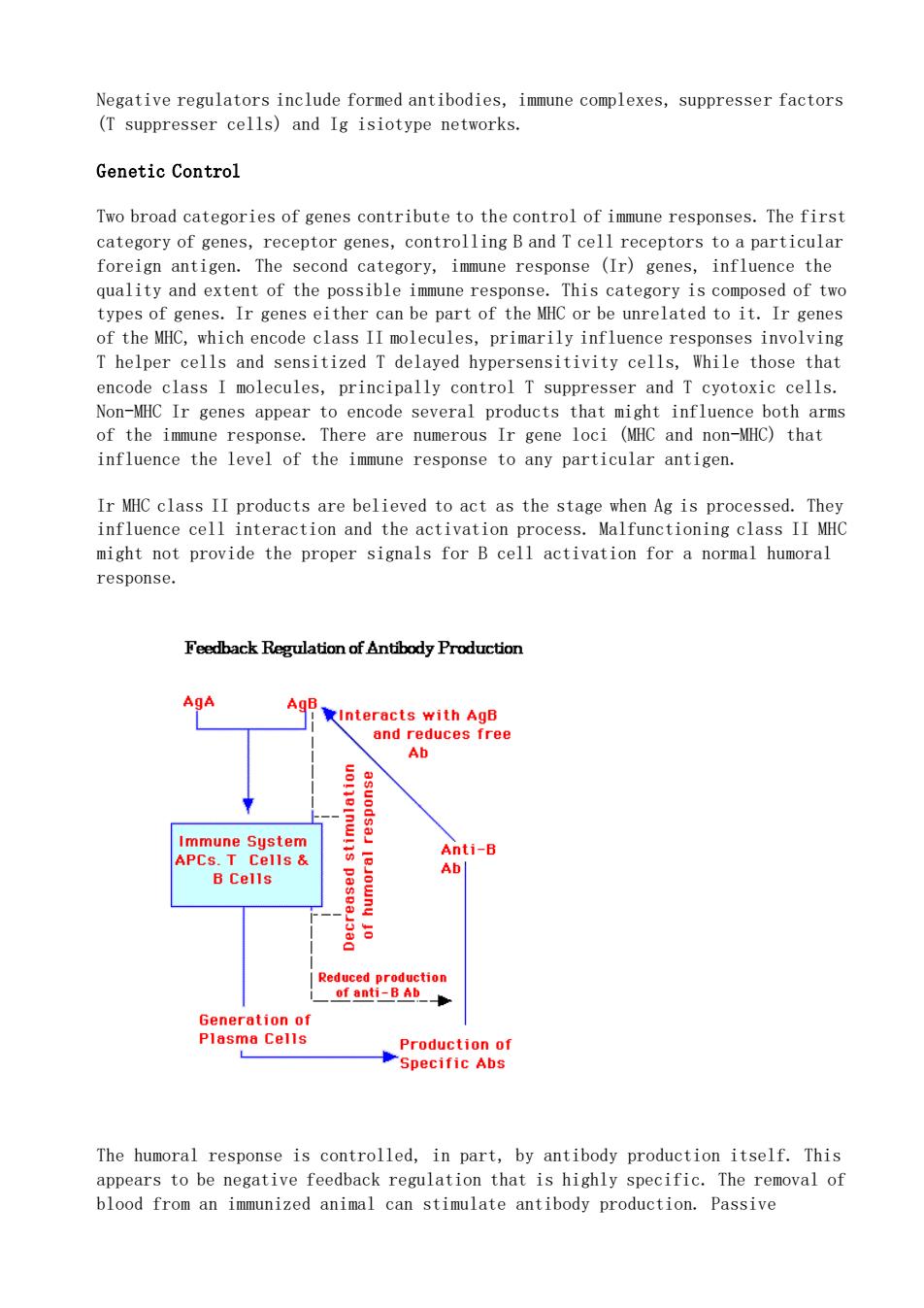
Negative regulators include formed antibodies,immune complexes,suppresser factors (T suppresser cells)and Ig isiotype networks. Genetic Control Two broad categories of genes contribute to the control of immune responses.The first category of genes,receptor genes,controlling B and T cell receptors to a particular foreign antigen.The second category,immune response (Ir)genes,influence the quality and extent of the possible immune response.This category is composed of two types of genes.Ir genes either can be part of the MHC or be unrelated to it.Ir genes of the MHC,which e ncode class II molecules,primarily influen olp oand iol bypersonsitivity encode class I molecules,principally control T suppresser and T cyotoxic cells. Non-MHC Ir genes appear to encode several products that might influence both arms of the immune response.There are numerous Ir gene loci (MHC and non-MHC)that influence the level of the immune response to any particular antigen Ir MHC class II products are believed to act as the stage when Ag is processed.They influence cell interaction and the activation process.Malfunctioning class II MH might not provide the proper signals for B cell activation for a normal humoral response. Feedback Regulation of Antibody Production AgA Ab Anti-B B Cells Production of Specific Abs The humoral response is controlled,in part,by antibody production itself.ThisNegative regulators include formed antibodies, immune complexes, suppresser factors (T suppresser cells) and Ig isiotype networks. Genetic Control Two broad categories of genes contribute to the control of immune responses. The first category of genes, receptor genes, controlling B and T cell receptors to a particular foreign antigen. The second category, immune response (Ir) genes, influence the quality and extent of the possible immune response. This category is composed of two types of genes. Ir genes either can be part of the MHC or be unrelated to it. Ir genes of the MHC, which encode class II molecules, primarily influence responses involving T helper cells and sensitized T delayed hypersensitivity cells, While those that encode class I molecules, principally control T suppresser and T cyotoxic cells. Non-MHC Ir genes appear to encode several products that might influence both arms of the immune response. There are numerous Ir gene loci (MHC and non-MHC) that influence the level of the immune response to any particular antigen. Ir MHC class II products are believed to act as the stage when Ag is processed. They influence cell interaction and the activation process. Malfunctioning class II MHC might not provide the proper signals for B cell activation for a normal humoral response. The humoral response is controlled, in part, by antibody production itself. This appears to be negative feedback regulation that is highly specific. The removal of blood from an immunized animal can stimulate antibody production. Passive