正在加载图片...
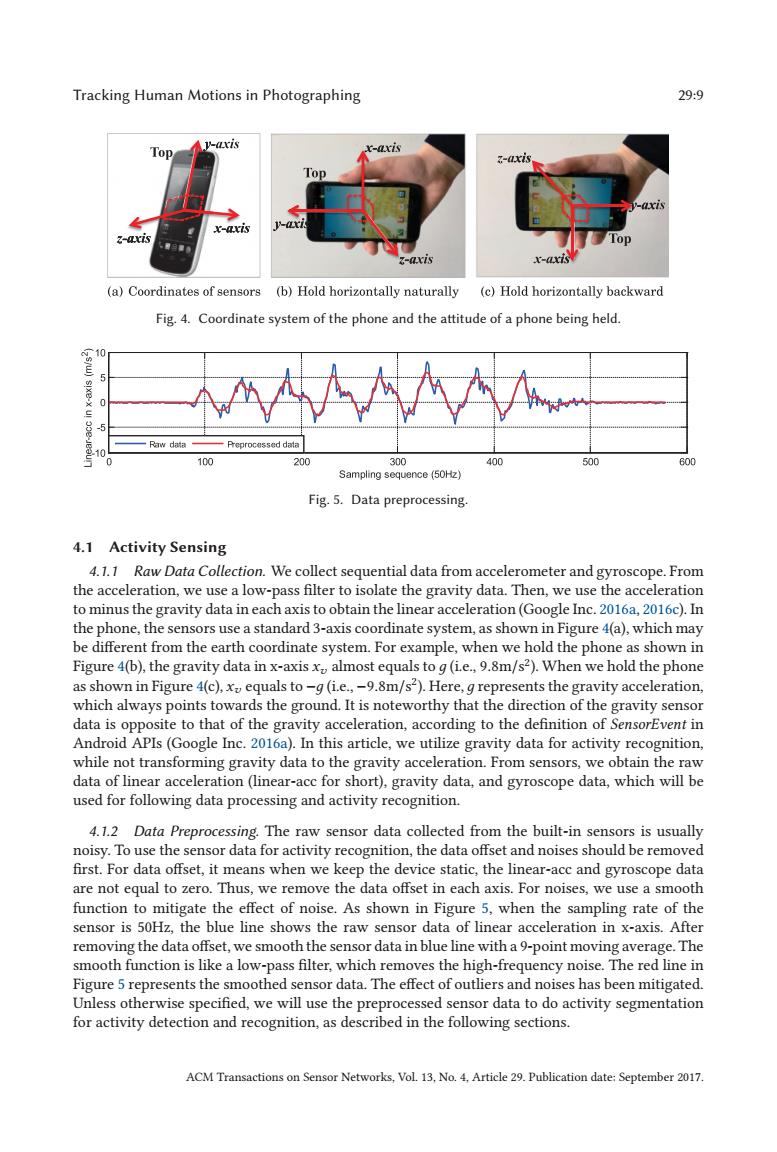
Tracking Human Motions in Photographing 299 y-axis x-axis 3-axis Top -axis x-axis y-ax Top z-axis x-axis (a)Coordinates of sensors (b)Hold horizontally naturally (c)Hold horizontally backward Fig.4.Coordinate system of the phone and the attitude of a phone being held. 10 Raw dae eprocs5 ed data 10 100 200 300 400 500 600 Sampling sequence (50Hz) Fig.5.Data preprocessing. 4.1 Activity Sensing 4.1.1 Raw Data Collection.We collect sequential data from accelerometer and gyroscope.From the acceleration,we use a low-pass filter to isolate the gravity data.Then,we use the acceleration to minus the gravity data in each axis to obtain the linear acceleration(Google Inc.2016a,2016c).In the phone,the sensors use a standard 3-axis coordinate system,as shown in Figure 4(a),which may be different from the earth coordinate system.For example,when we hold the phone as shown in Figure 4(b),the gravity data in x-axis x almost equals to g(ie.,9.8m/s2).When we hold the phone as shown in Figure 4(c),x equals to-g(i.e.,-9.8m/s2).Here,g represents the gravity acceleration, which always points towards the ground.It is noteworthy that the direction of the gravity sensor data is opposite to that of the gravity acceleration,according to the definition of SensorEvent in Android APIs(Google Inc.2016a).In this article,we utilize gravity data for activity recognition, while not transforming gravity data to the gravity acceleration.From sensors,we obtain the raw data of linear acceleration(linear-acc for short),gravity data,and gyroscope data,which will be used for following data processing and activity recognition. 4.1.2 Data Preprocessing.The raw sensor data collected from the built-in sensors is usually noisy.To use the sensor data for activity recognition,the data offset and noises should be removed first.For data offset,it means when we keep the device static,the linear-acc and gyroscope data are not equal to zero.Thus,we remove the data offset in each axis.For noises,we use a smooth function to mitigate the effect of noise.As shown in Figure 5,when the sampling rate of the sensor is 50Hz,the blue line shows the raw sensor data of linear acceleration in x-axis.After removing the data offset,we smooth the sensor data in blue line with a 9-point moving average.The smooth function is like a low-pass filter,which removes the high-frequency noise.The red line in Figure 5 represents the smoothed sensor data.The effect of outliers and noises has been mitigated. Unless otherwise specified,we will use the preprocessed sensor data to do activity segmentation for activity detection and recognition,as described in the following sections. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks,Vol.13,No.4,Article 29.Publication date:September 2017.Tracking Human Motions in Photographing 29:9 Fig. 4. Coordinate system of the phone and the attitude of a phone being held. Fig. 5. Data preprocessing. 4.1 Activity Sensing 4.1.1 Raw Data Collection. We collect sequential data from accelerometer and gyroscope. From the acceleration, we use a low-pass filter to isolate the gravity data. Then, we use the acceleration to minus the gravity data in each axis to obtain the linear acceleration (Google Inc. 2016a, 2016c). In the phone, the sensors use a standard 3-axis coordinate system, as shown in Figure 4(a), which may be different from the earth coordinate system. For example, when we hold the phone as shown in Figure 4(b), the gravity data in x-axis xv almost equals to д (i.e., 9.8m/s2). When we hold the phone as shown in Figure 4(c), xv equals to −д (i.e., −9.8m/s2). Here, д represents the gravity acceleration, which always points towards the ground. It is noteworthy that the direction of the gravity sensor data is opposite to that of the gravity acceleration, according to the definition of SensorEvent in Android APIs (Google Inc. 2016a). In this article, we utilize gravity data for activity recognition, while not transforming gravity data to the gravity acceleration. From sensors, we obtain the raw data of linear acceleration (linear-acc for short), gravity data, and gyroscope data, which will be used for following data processing and activity recognition. 4.1.2 Data Preprocessing. The raw sensor data collected from the built-in sensors is usually noisy. To use the sensor data for activity recognition, the data offset and noises should be removed first. For data offset, it means when we keep the device static, the linear-acc and gyroscope data are not equal to zero. Thus, we remove the data offset in each axis. For noises, we use a smooth function to mitigate the effect of noise. As shown in Figure 5, when the sampling rate of the sensor is 50Hz, the blue line shows the raw sensor data of linear acceleration in x-axis. After removing the data offset, we smooth the sensor data in blue line with a 9-point moving average. The smooth function is like a low-pass filter, which removes the high-frequency noise. The red line in Figure 5 represents the smoothed sensor data. The effect of outliers and noises has been mitigated. Unless otherwise specified, we will use the preprocessed sensor data to do activity segmentation for activity detection and recognition, as described in the following sections. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, Vol. 13, No. 4, Article 29. Publication date: September 2017