正在加载图片...
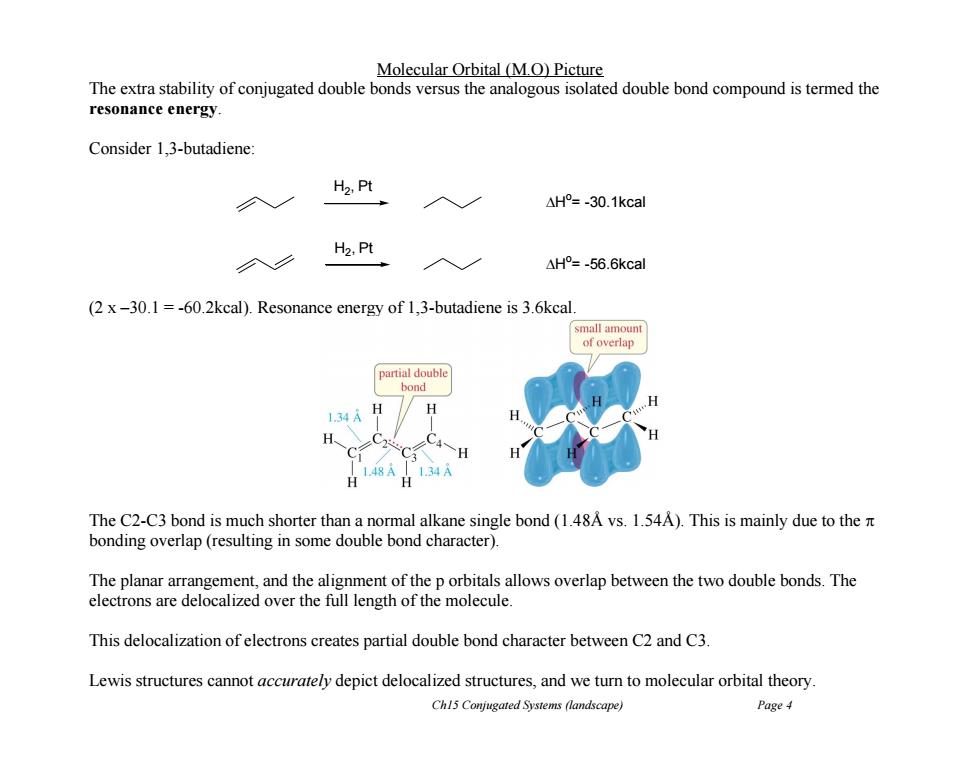
Molecular Orbital (M.O)Picture The extra stability of conjugated double bonds versus the analogous isolated double bond compound is termed the resonance energy Consider 1,3-butadiene: H2,Pt △H°=-30.1kcal H2,Pt △H°=-56.6kcal (2 x-30.1=-60.2kcal).Resonance energy of 1,3-butadiene is 3.6kcal. small amount of overlap partial double bond H 1.34A H 1.48A 1.34A H The C2-C3 bond is much shorter than a normal alkane single bond(1.48A vs.1.54A).This is mainly due to the n bonding overlap(resulting in some double bond character). The planar arrangement,and the alignment of the p orbitals allows overlap between the two double bonds.The electrons are delocalized over the full length of the molecule. This delocalization of electrons creates partial double bond character between C2 and C3. Lewis structures cannot accurately depict delocalized structures,and we turn to molecular orbital theory Chl5 Conjugated Systems (landscape) Page 4Ch15 Conjugated Systems (landscape) Page 4 Molecular Orbital (M.O) Picture The extra stability of conjugated double bonds versus the analogous isolated double bond compound is termed the resonance energy. Consider 1,3-butadiene: (2 x –30.1 = -60.2kcal). Resonance energy of 1,3-butadiene is 3.6kcal. The C2-C3 bond is much shorter than a normal alkane single bond (1.48Å vs. 1.54Å). This is mainly due to the bonding overlap (resulting in some double bond character). The planar arrangement, and the alignment of the p orbitals allows overlap between the two double bonds. The electrons are delocalized over the full length of the molecule. This delocalization of electrons creates partial double bond character between C2 and C3. Lewis structures cannot accurately depict delocalized structures, and we turn to molecular orbital theory. H2 , Pt H o = -30.1kcal H2 , Pt H o = -56.6kcal