正在加载图片...
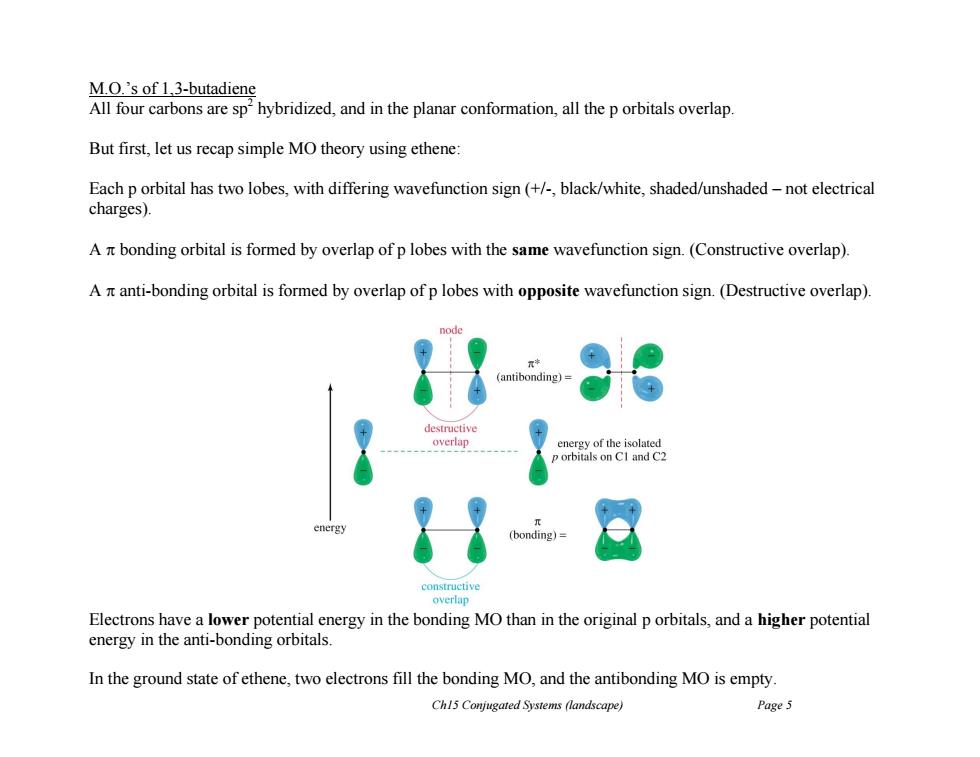
M.O.'s of 1,3-butadiene All four carbons are sphybridized,and in the planar conformation,all the p orbitals overlap. But first,let us recap simple MO theory using ethene: Each p orbital has two lobes,with differing wavefunction sign (+/-black/white,shaded/unshaded-not electrical charges). A nt bonding orbital is formed by overlap of p lobes with the same wavefunction sign.(Constructive overlap). A nt anti-bonding orbital is formed by overlap of p lobes with opposite wavefunction sign.(Destructive overlap). antibonding destructive overlap energy of the isolated p orbitals on CI and C2 energy (bonding)= constructive overlap Electrons have a lower potential energy in the bonding MO than in the original p orbitals,and a higher potential energy in the anti-bonding orbitals. In the ground state of ethene,two electrons fill the bonding MO,and the antibonding MO is empty Ch15 Conjugated Systems (landscape) Page 5 Ch15 Conjugated Systems (landscape) Page 5 M.O.’s of 1,3-butadiene All four carbons are sp 2 hybridized, and in the planar conformation, all the p orbitals overlap. But first, let us recap simple MO theory using ethene: Each p orbital has two lobes, with differing wavefunction sign (+/-, black/white, shaded/unshaded – not electrical charges). A bonding orbital is formed by overlap of p lobes with the same wavefunction sign. (Constructive overlap). A anti-bonding orbital is formed by overlap of p lobes with opposite wavefunction sign. (Destructive overlap). Electrons have a lower potential energy in the bonding MO than in the original p orbitals, and a higher potential energy in the anti-bonding orbitals. In the ground state of ethene, two electrons fill the bonding MO, and the antibonding MO is empty