正在加载图片...
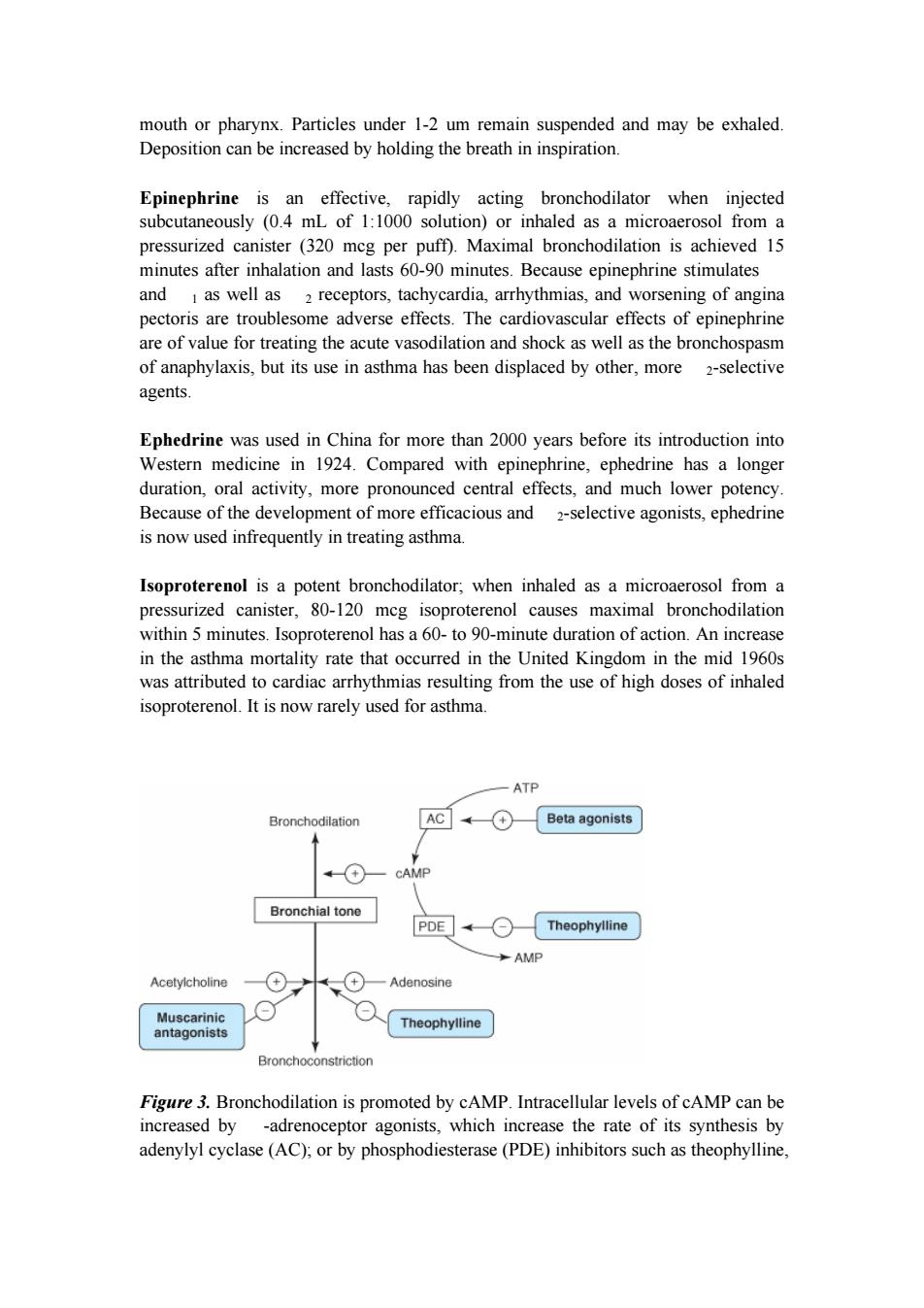
mouth or pharynx.Particles under 1-2 um remain suspended and may be exhaled. Deposition can be increased by holding the breath in inspiration. Epinephrine is an effective,rapidly acting bronchodilator when injected subcutaneously (0.4 mL of 1:1000 solution)or inhaled as a microaerosol from a pressurized canister (320 mcg per puff).Maximal bronchodilation is achieved 15 minutes after inhalation and lasts 60-90 minutes.Because epinephrine stimulates and I as well as 2 receptors,tachycardia,arrhythmias,and worsening of angina pectoris are troublesome adverse effects.The cardiovascular effects of epinephrine are of value for treating the acute vasodilation and shock as well as the bronchospasm of anaphylaxis,but its use in asthma has been displaced by other,more 2-selective agents. Ephedrine was used in China for more than 2000 years before its introduction into Western medicine in 1924.Compared with epinephrine,ephedrine has a longer duration,oral activity,more pronounced central effects,and much lower potency. Because of the development of more efficacious and 2-selective agonists,ephedrine is now used infrequently in treating asthma. Isoproterenol is a potent bronchodilator;when inhaled as a microaerosol from a pressurized canister,80-120 mcg isoproterenol causes maximal bronchodilation within 5 minutes.Isoproterenol has a 60-to 90-minute duration of action.An increase in the asthma mortality rate that occurred in the United Kingdom in the mid 1960s was attributed to cardiac arrhythmias resulting from the use of high doses of inhaled isoproterenol.It is now rarely used for asthma. ATP Bronchodilation AC (+ Beta agonists A + CAMP Bronchial tone PDE Theophylline AMP Acetylcholine Adenosine Muscarinic Theophylline antagonists Bronchoconstriction Figure 3.Bronchodilation is promoted by cAMP.Intracellular levels of cAMP can be increased by -adrenoceptor agonists,which increase the rate of its synthesis by adenylyl cyclase(AC);or by phosphodiesterase(PDE)inhibitors such as theophylline,mouth or pharynx. Particles under 1-2 um remain suspended and may be exhaled. Deposition can be increased by holding the breath in inspiration. Epinephrine is an effective, rapidly acting bronchodilator when injected subcutaneously (0.4 mL of 1:1000 solution) or inhaled as a microaerosol from a pressurized canister (320 mcg per puff). Maximal bronchodilation is achieved 15 minutes after inhalation and lasts 60-90 minutes. Because epinephrine stimulates and 1 as well as 2 receptors, tachycardia, arrhythmias, and worsening of angina pectoris are troublesome adverse effects. The cardiovascular effects of epinephrine are of value for treating the acute vasodilation and shock as well as the bronchospasm of anaphylaxis, but its use in asthma has been displaced by other, more 2-selective agents. Ephedrine was used in China for more than 2000 years before its introduction into Western medicine in 1924. Compared with epinephrine, ephedrine has a longer duration, oral activity, more pronounced central effects, and much lower potency. Because of the development of more efficacious and 2-selective agonists, ephedrine is now used infrequently in treating asthma. Isoproterenol is a potent bronchodilator; when inhaled as a microaerosol from a pressurized canister, 80-120 mcg isoproterenol causes maximal bronchodilation within 5 minutes. Isoproterenol has a 60- to 90-minute duration of action. An increase in the asthma mortality rate that occurred in the United Kingdom in the mid 1960s was attributed to cardiac arrhythmias resulting from the use of high doses of inhaled isoproterenol. It is now rarely used for asthma. Figure 3. Bronchodilation is promoted by cAMP. Intracellular levels of cAMP can be increased by -adrenoceptor agonists, which increase the rate of its synthesis by adenylyl cyclase (AC); or by phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors such as theophylline