正在加载图片...
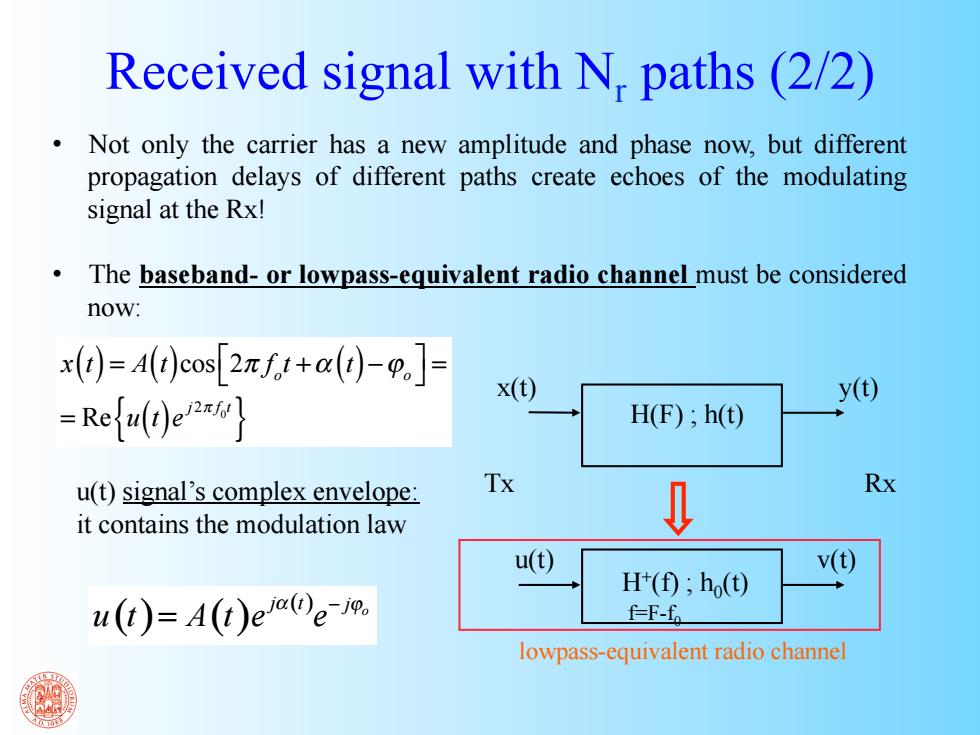
Received signal with N,paths(2/2) Not only the carrier has a new amplitude and phase now,but different propagation delays of different paths create echoes of the modulating signal at the Rx! The baseband-or lowpass-equivalent radio channel must be considered now: x(1)=A(t)cos[2zf.t+a()-0.J- x(t) -Refu(t)ex y(t) H(F);h(t) u(t)signal's complex envelope: Tx Rx it contains the modulation law u() v() H(0;h() u(t)=A(t)ee- f-F-fo lowpass-equivalent radio channel x(t) y(t) H(F) ; h(t) u(t) v(t) H+(f) ; h0(t) f=F-f0 u(t) signal’s complex envelope: it contains the modulation law x(t) = A(t)cos 2π fo t +α (t) −ϕo ⎡ ⎣ ⎤ ⎦ = = Re u(t)e j2π f 0t { } ( ) ( ) ( ) o j t j u t A t e e α − ϕ = Received signal with Nr paths (2/2) • Not only the carrier has a new amplitude and phase now, but different propagation delays of different paths create echoes of the modulating signal at the Rx! • The baseband- or lowpass-equivalent radio channel must be considered now: Tx Rx lowpass-equivalent radio channel