正在加载图片...
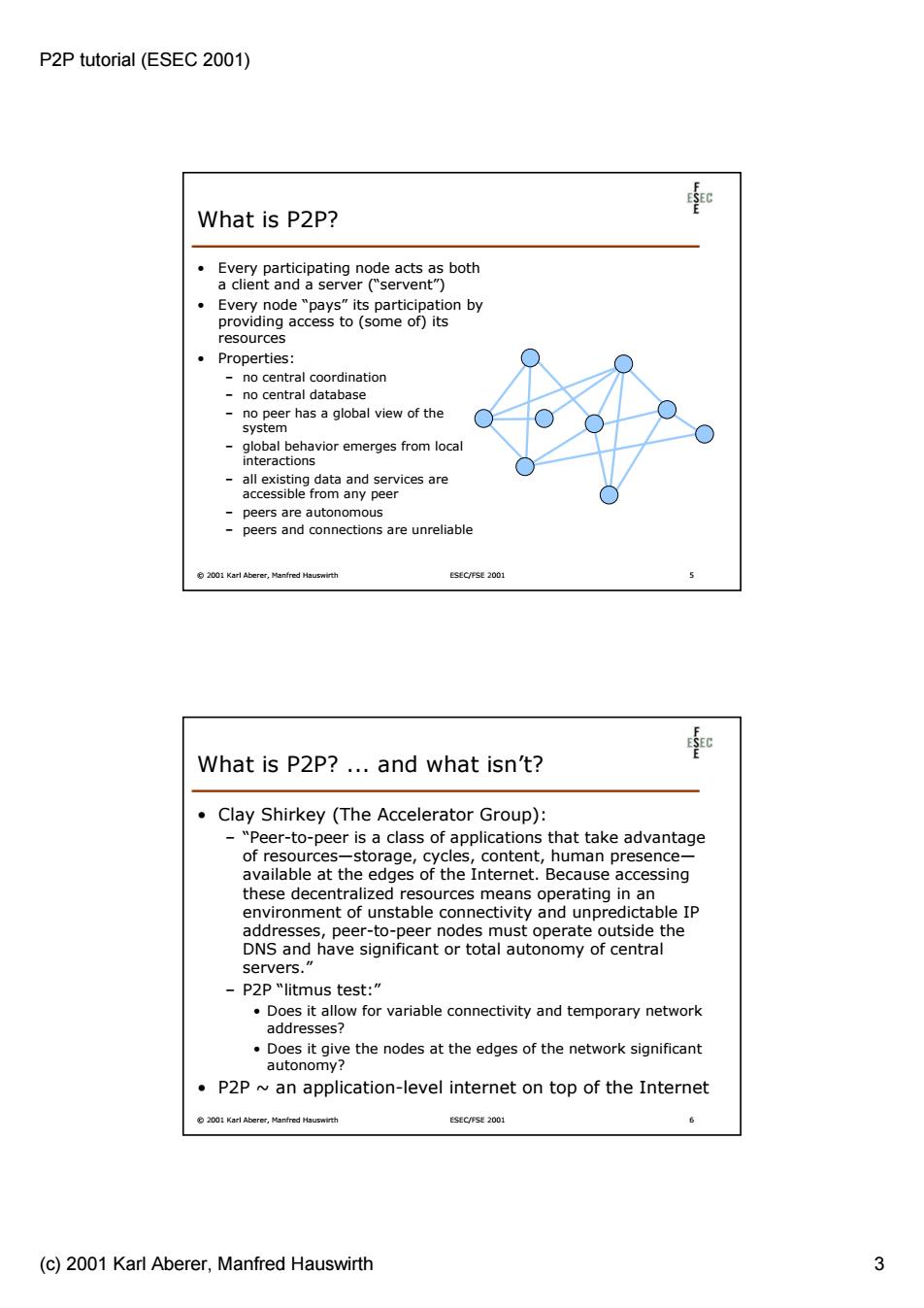
P2P tutorial (ESEC 2001) 和 What is P2P? Every participating node acts as both a client and a server (servent") Every node "pays"its participation by providing access to (some of)its resources Properties: no central coordination no central database no peer has a global view of the system global behavior emerges from local interactions all existing data and services are accessible from any peer peers are autonomous peers and connections are unreliable 82001 Karl Abe ESEC/FSE 2001 What is P2P?...and what isn't? Clay Shirkey (The Accelerator Group): -"Peer-to-peer is a class of applications that take advantage of resources-storage,cycles,content,human presence- available at the edges of the Internet.Because accessing these decentralized resources means operating in an environment of unstable connectivity and unpredictable IP addresses,peer-to-peer nodes must operate outside the DNS and have significant or total autonomy of central servers. P2P "litmus test: Does it allow for variable connectivity and temporary network addresses? Does it give the nodes at the edges of the network significant autonomy? P2P an application-level internet on top of the Internet 2001 Karl Aberer,Manfred Hauswirth ESEC/FSE 2001 (c)2001 Karl Aberer,Manfred Hauswirth 3P2P tutorial (ESEC 2001) (c) 2001 Karl Aberer, Manfred Hauswirth 3 © 2001 Karl Aberer, Manfred Hauswirth ESEC/FSE 2001 5 What is P2P? • Every participating node acts as both a client and a server (“servent”) • Every node “pays” its participation by providing access to (some of) its resources • Properties: – no central coordination – no central database – no peer has a global view of the system – global behavior emerges from local interactions – all existing data and services are accessible from any peer – peers are autonomous – peers and connections are unreliable © 2001 Karl Aberer, Manfred Hauswirth ESEC/FSE 2001 6 What is P2P? ... and what isn’t? • Clay Shirkey (The Accelerator Group): – “Peer-to-peer is a class of applications that take advantage of resources—storage, cycles, content, human presence— available at the edges of the Internet. Because accessing these decentralized resources means operating in an environment of unstable connectivity and unpredictable IP addresses, peer-to-peer nodes must operate outside the DNS and have significant or total autonomy of central servers.” – P2P “litmus test:” • Does it allow for variable connectivity and temporary network addresses? • Does it give the nodes at the edges of the network significant autonomy? • P2P ~ an application-level internet on top of the Internet