正在加载图片...
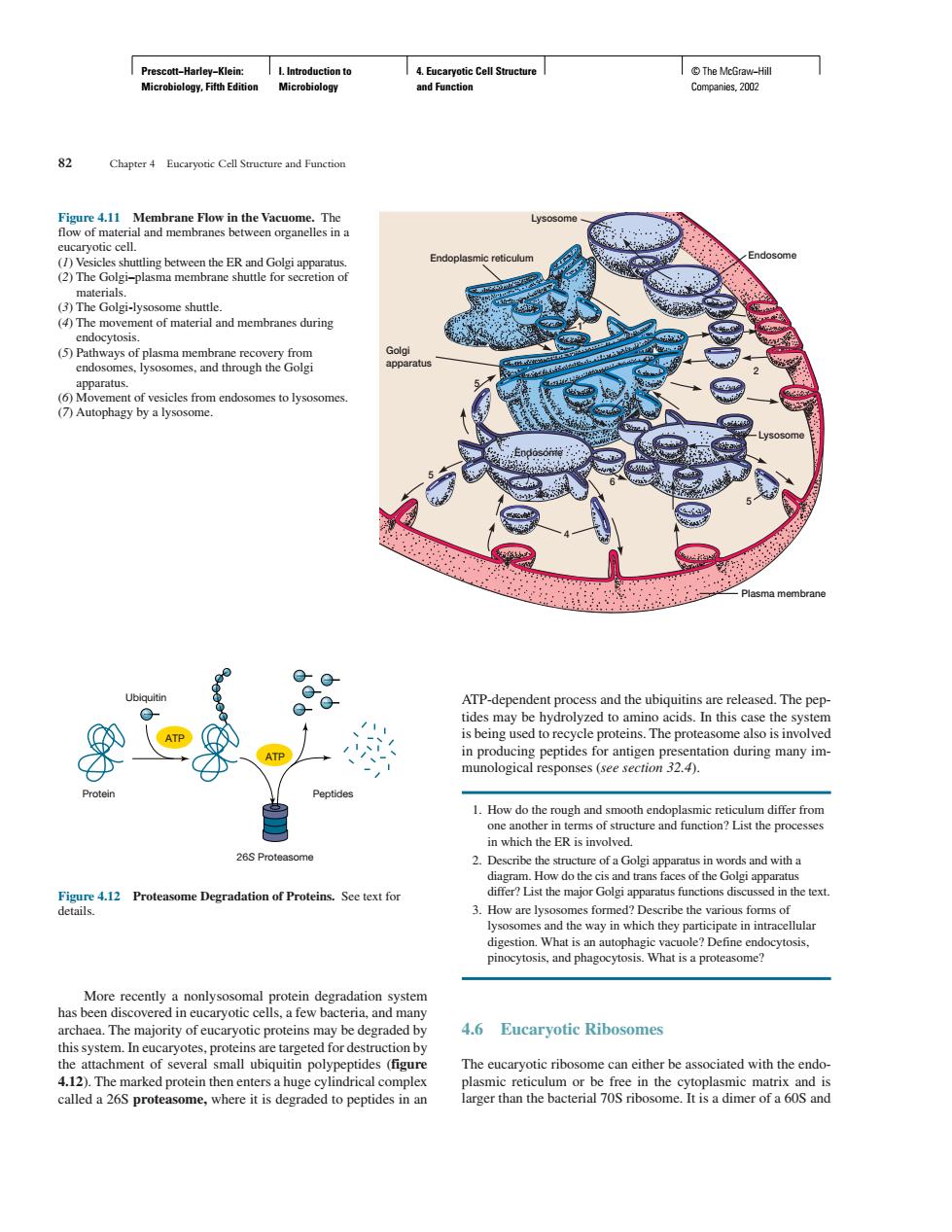
2 Chapter 4 Eucaryonic Cell Structure and Functioe Q ATP-dependent process and the ubiquitins are released.The pep 1.How do th 26S Pr de and with C5andtnansf es of the Go 3.How are lysoso es fomed?De scribe the various forms of digestion.What is pinocytosi飞,and phagocytos More al 4.6 Eucaryotic RibosomesPrescott−Harley−Klein: Microbiology, Fifth Edition I. Introduction to Microbiology 4. Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function © The McGraw−Hill Companies, 2002 More recently a nonlysosomal protein degradation system has been discovered in eucaryotic cells, a few bacteria, and many archaea. The majority of eucaryotic proteins may be degraded by this system. In eucaryotes, proteins are targeted for destruction by the attachment of several small ubiquitin polypeptides (figure 4.12). The marked protein then enters a huge cylindrical complex called a 26S proteasome, where it is degraded to peptides in an ATP-dependent process and the ubiquitins are released. The peptides may be hydrolyzed to amino acids. In this case the system is being used to recycle proteins. The proteasome also is involved in producing peptides for antigen presentation during many immunological responses (see section 32.4). 1. How do the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum differ from one another in terms of structure and function? List the processes in which the ER is involved. 2. Describe the structure of a Golgi apparatus in words and with a diagram. How do the cis and trans faces of the Golgi apparatus differ? List the major Golgi apparatus functions discussed in the text. 3. How are lysosomes formed? Describe the various forms of lysosomes and the way in which they participate in intracellular digestion. What is an autophagic vacuole? Define endocytosis, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis. What is a proteasome? 4.6 Eucaryotic Ribosomes The eucaryotic ribosome can either be associated with the endoplasmic reticulum or be free in the cytoplasmic matrix and is larger than the bacterial 70S ribosome. It is a dimer of a 60S and 82 Chapter 4 Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function Endoplasmic reticulum Lysosome Endosome Lysosome 5 7 2 3 6 4 Endosome 5 5 1 Plasma membrane Golgi apparatus Figure 4.11 Membrane Flow in the Vacuome. The flow of material and membranes between organelles in a eucaryotic cell. (1) Vesicles shuttling between the ER and Golgi apparatus. (2) The Golgi–plasma membrane shuttle for secretion of materials. (3) The Golgi-lysosome shuttle. (4) The movement of material and membranes during endocytosis. (5) Pathways of plasma membrane recovery from endosomes, lysosomes, and through the Golgi apparatus. (6) Movement of vesicles from endosomes to lysosomes. (7) Autophagy by a lysosome. Protein Ubiquitin Peptides ATP 26S Proteasome ATP Figure 4.12 Proteasome Degradation of Proteins. See text for details