正在加载图片...
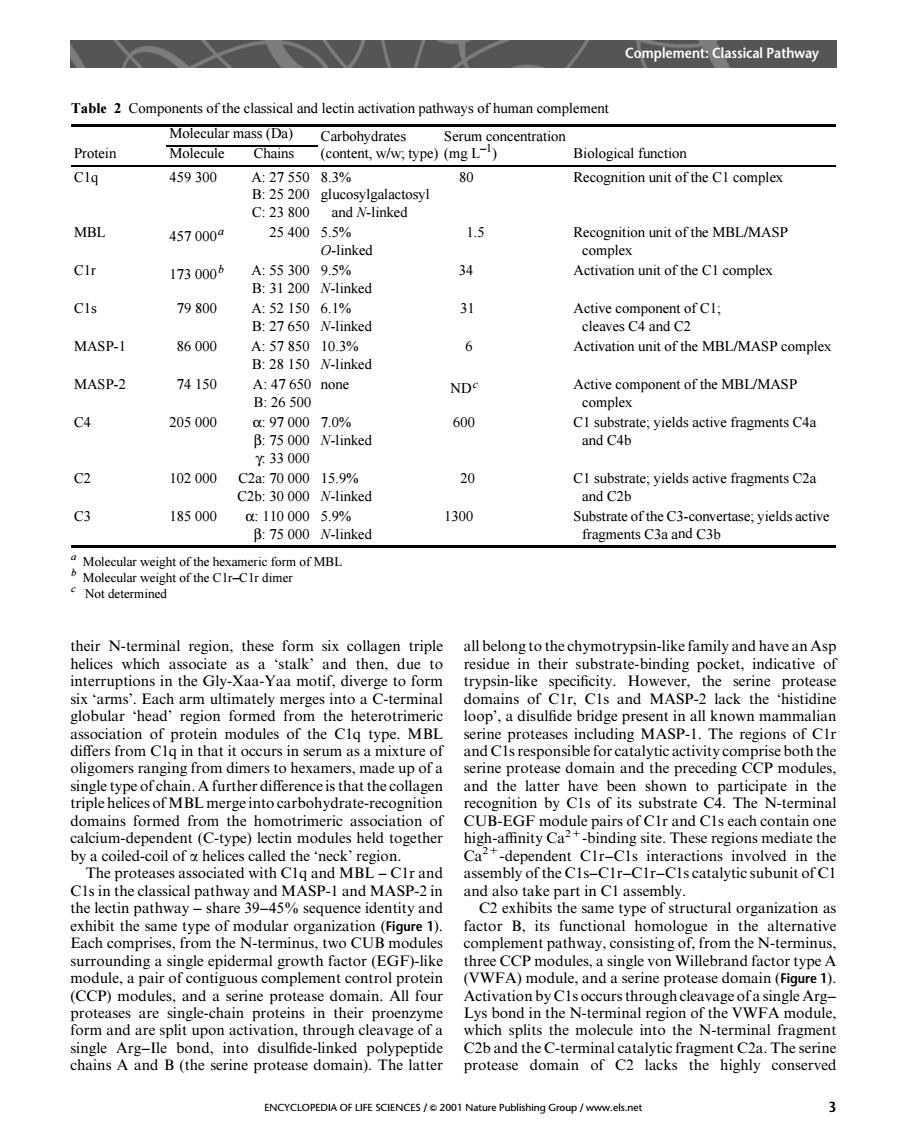
Complement:Classical Pathway Table 2 Components of the classical and lectin activation pathways of human complement Carbohydrates Protein Chains (content,w/w:type)(mg L) Biological function Cla 459300 A:275508.3% 80 Recognition unit of the Cl complex B:25 200 glucosylgalactosyl C:23800 and N-linked MBL 4570000 2540055 1.5 Recognition unit of the MBL/MASP CIr 1730005 34 Activation unit of the CI complex 79800 31 MASP-I 86000 Activation unit of the MBL/MASP complex B28150 6 MASP-2 74150 47650 none B26500 ND Active component of the MBL/MASP C4 205000 a970007.00% CI substrate.yields active fragments C4a B:75 000 N-linked and C4h t33000 102000 C2a:7000015.9% 20 CI substrate;yields active fragments C2a C2b:30 000 N-linked and C2b C3 185000 1100005.9% 1300 Substrate of the C3-convertase:yields active B:75 000 N-linked fragments C3a and C3b a six collas triple all belong to the chy as a 'stalk'and then.due to esidue interruptions in the Gly-Xaa-Yaa motif,diverge to form trypsin-like specificity.Howeve the serine protease imately merges r,Cls and MA lack the 'histidine pop',a d own m MAD differs from Cla in that it occurs in serum as a mixture of oligomers ranging from dimers to hexamers,made up of a serine protease domain and the preceding CCP modules, gle type ofcha A further difference is that theco and th latter have waeepiepatemh d fr drate-recogn CUB-E calcium-dependent (C-type)lectin modules held together high-affinity Cabinding site.These regions mediate the by a coiled-coil of helices called the'neck'region. Ca dependent CIr-Cls interactions involved in the and mbly of the Cls CIr-CIr Cls catalytic subunit of C a3945 part in Cl assem exhibit the same type of modular organizati on (Figure 1) factor B.its functional homologue in the alterative Each comprises.from the N-terminus.two CUB modules comple nent pathway,consisting of,from the N-terminus les, single von Willebrand factor type a pair me protease (F Lys bond in the N-terminal region of the VWFA module ation.through cleavage of a which splits the molecule into the N-terminal fragment chains Nand'(the semne proteae a.The serine conserve ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES/2001 Nature Publishing Group/www.els.net their N-terminal region, these form six collagen triple helices which associate as a ‘stalk’ and then, due to interruptions in the Gly-Xaa-Yaa motif, diverge to form six ‘arms’. Each arm ultimately merges into a C-terminal globular ‘head’ region formed from the heterotrimeric association of protein modules of the C1q type. MBL differs from C1q in that it occurs in serum as a mixture of oligomers ranging from dimers to hexamers, made up of a single type of chain. A further difference is that the collagen triple helices of MBL merge into carbohydrate-recognition domains formed from the homotrimeric association of calcium-dependent (C-type) lectin modules held together by a coiled-coil of a helices called the ‘neck’ region. The proteases associated with C1q and MBL – C1r and C1s in the classical pathway and MASP-1 and MASP-2 in the lectin pathway – share 39–45% sequence identity and exhibit the same type of modular organization (Figure 1). Each comprises, from the N-terminus, two CUB modules surrounding a single epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like module, a pair of contiguous complement control protein (CCP) modules, and a serine protease domain. All four proteases are single-chain proteins in their proenzyme form and are split upon activation, through cleavage of a single Arg–Ile bond, into disulfide-linked polypeptide chains A and B (the serine protease domain). The latter all belong to the chymotrypsin-like family and have an Asp residue in their substrate-binding pocket, indicative of trypsin-like specificity. However, the serine protease domains of C1r, C1s and MASP-2 lack the ‘histidine loop’, a disulfide bridge present in all known mammalian serine proteases including MASP-1. The regions of C1r and C1s responsible for catalytic activity comprise both the serine protease domain and the preceding CCP modules, and the latter have been shown to participate in the recognition by C1s of its substrate C4. The N-terminal CUB-EGF module pairs of C1r and C1s each contain one high-affinity Ca2+-binding site. These regions mediate the Ca2+-dependent C1r–C1s interactions involved in the assembly of the C1s–C1r–C1r–C1s catalytic subunit of C1 and also take part in C1 assembly. C2 exhibits the same type of structural organization as factor B, its functional homologue in the alternative complement pathway, consisting of, from the N-terminus, three CCP modules, a single von Willebrand factor type A (VWFA) module, and a serine protease domain (Figure 1). Activation by C1s occurs through cleavage of a single Arg– Lys bond in the N-terminal region of the VWFA module, which splits the molecule into the N-terminal fragment C2b and the C-terminal catalytic fragment C2a. The serine protease domain of C2 lacks the highly conserved Table 2 Components of the classical and lectin activation pathways of human complement a Molecular weight of the hexameric form of MBL b Molecular weight of the C1r–C1r dimer c Not determined Protein Molecular mass (Da) Carbohydrates (content, w/w; type) Serum concentration (mg L–1 Molecule Chains ) Biological function C1q 459 300 A: 27 550 B: 25 200 C: 23 800 8.3% glucosylgalactosyl and N-linked 80 Recognition unit of the C1 complex MBL 457 000a 25 400 5.5% O-linked 1.5 Recognition unit of the MBL/MASP complex C1r 173 000b A: 55 300 B: 31 200 9.5% N-linked 34 Activation unit of the C1 complex C1s 79 800 A: 52 150 B: 27 650 6.1% N-linked 31 Active component of C1; cleaves C4 and C2 MASP-1 86 000 A: 57 850 B: 28 150 10.3% N-linked 6 Activation unit of the MBL/MASP complex MASP-2 74 150 A: 47 650 B: 26 500 none NDc Active component of the MBL/MASP complex C4 205 000 α: 97 000 β: 75 000 γ: 33 000 7.0% N-linked 600 C1 substrate; yields active fragments C4a and C4b C2 102 000 C2a: 70 000 C2b: 30 000 15.9% N-linked 20 C1 substrate; yields active fragments C2a and C2b C3 185 000 α: 110 000 β: 75 000 5.9% N-linked 1300 Substrate of the C3-convertase; yields active fragments C3a and C3b Complement: Classical Pathway ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net 3