正在加载图片...
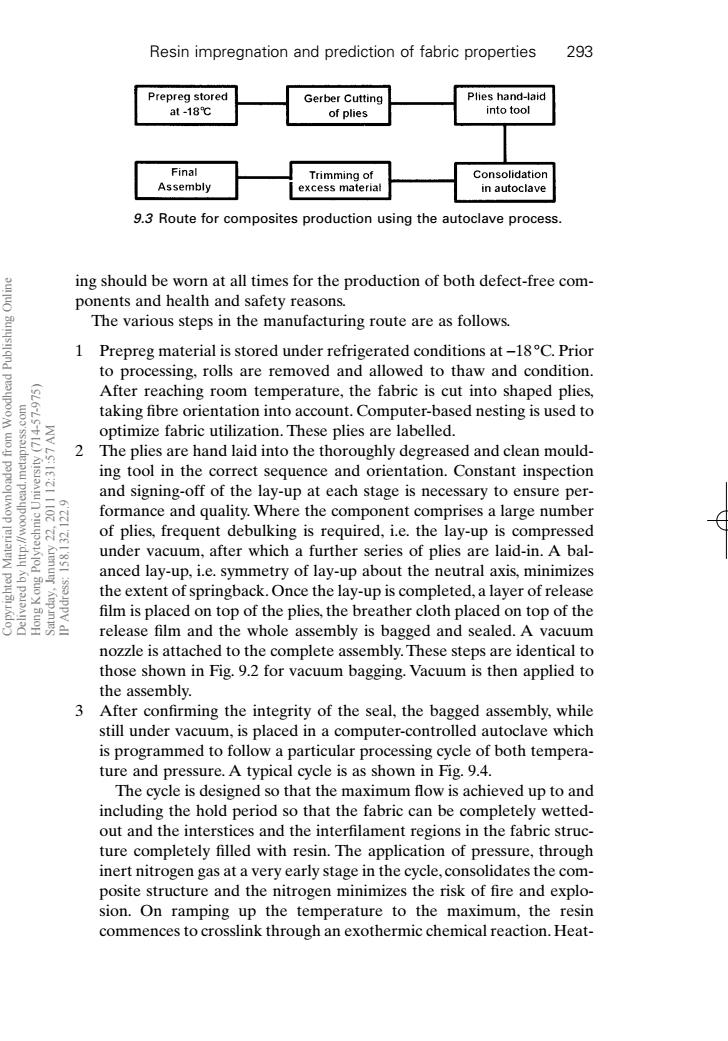
Resin impregnation and prediction of fabric properties 293 Prepreg stored Gerber Cutting Plies hand-laid at-18℃ of plies into tool Final Trimming of Consolidation Assembly excess material in autoclave 9.3 Route for composites production using the autoclave process. ing should be worn at all times for the production of both defect-free com- ponents and health and safety reasons. The various steps in the manufacturing route are as follows. 1 Prepreg material is stored under refrigerated conditions at-18C.Prior to processing,rolls are removed and allowed to thaw and condition. 9 After reaching room temperature,the fabric is cut into shaped plies, poo taking fibre orientation into account.Computer-based nesting is used to optimize fabric utilization.These plies are labelled. 2 The plies are hand laid into the thoroughly degreased and clean mould- ing tool in the correct sequence and orientation.Constant inspection and signing-off of the lay-up at each stage is necessary to ensure per- formance and quality.Where the component comprises a large number A of plies,frequent debulking is required,i.e.the lay-up is compressed under vacuum,after which a further series of plies are laid-in.A bal- 9 anced lay-up,i.e.symmetry of lay-up about the neutral axis,minimizes the extent of springback.Once the lay-up is completed,a layer of release film is placed on top of the plies,the breather cloth placed on top of the release film and the whole assembly is bagged and sealed.A vacuum nozzle is attached to the complete assembly.These steps are identical to those shown in Fig.9.2 for vacuum bagging.Vacuum is then applied to the assembly. 3 After confirming the integrity of the seal,the bagged assembly,while still under vacuum,is placed in a computer-controlled autoclave which is programmed to follow a particular processing cycle of both tempera- ture and pressure.A typical cycle is as shown in Fig.9.4. The cycle is designed so that the maximum flow is achieved up to and including the hold period so that the fabric can be completely wetted- out and the interstices and the interfilament regions in the fabric struc- ture completely filled with resin.The application of pressure,through inert nitrogen gas at a very early stage in the cycle,consolidates the com- posite structure and the nitrogen minimizes the risk of fire and explo- sion.On ramping up the temperature to the maximum,the resin commences to crosslink through an exothermic chemical reaction.Heat-ing should be worn at all times for the production of both defect-free components and health and safety reasons. The various steps in the manufacturing route are as follows. 1 Prepreg material is stored under refrigerated conditions at -18 °C. Prior to processing, rolls are removed and allowed to thaw and condition. After reaching room temperature, the fabric is cut into shaped plies, taking fibre orientation into account. Computer-based nesting is used to optimize fabric utilization. These plies are labelled. 2 The plies are hand laid into the thoroughly degreased and clean moulding tool in the correct sequence and orientation. Constant inspection and signing-off of the lay-up at each stage is necessary to ensure performance and quality. Where the component comprises a large number of plies, frequent debulking is required, i.e. the lay-up is compressed under vacuum, after which a further series of plies are laid-in. A balanced lay-up, i.e. symmetry of lay-up about the neutral axis, minimizes the extent of springback. Once the lay-up is completed, a layer of release film is placed on top of the plies, the breather cloth placed on top of the release film and the whole assembly is bagged and sealed. A vacuum nozzle is attached to the complete assembly. These steps are identical to those shown in Fig. 9.2 for vacuum bagging. Vacuum is then applied to the assembly. 3 After confirming the integrity of the seal, the bagged assembly, while still under vacuum, is placed in a computer-controlled autoclave which is programmed to follow a particular processing cycle of both temperature and pressure. A typical cycle is as shown in Fig. 9.4. The cycle is designed so that the maximum flow is achieved up to and including the hold period so that the fabric can be completely wettedout and the interstices and the interfilament regions in the fabric structure completely filled with resin. The application of pressure, through inert nitrogen gas at a very early stage in the cycle, consolidates the composite structure and the nitrogen minimizes the risk of fire and explosion. On ramping up the temperature to the maximum, the resin commences to crosslink through an exothermic chemical reaction. HeatResin impregnation and prediction of fabric properties 293 9.3 Route for composites production using the autoclave process. RIC9 7/10/99 8:32 PM Page 293 Copyrighted Material downloaded from Woodhead Publishing Online Delivered by http://woodhead.metapress.com Hong Kong Polytechnic University (714-57-975) Saturday, January 22, 2011 12:31:57 AM IP Address: 158.132.122.9