正在加载图片...
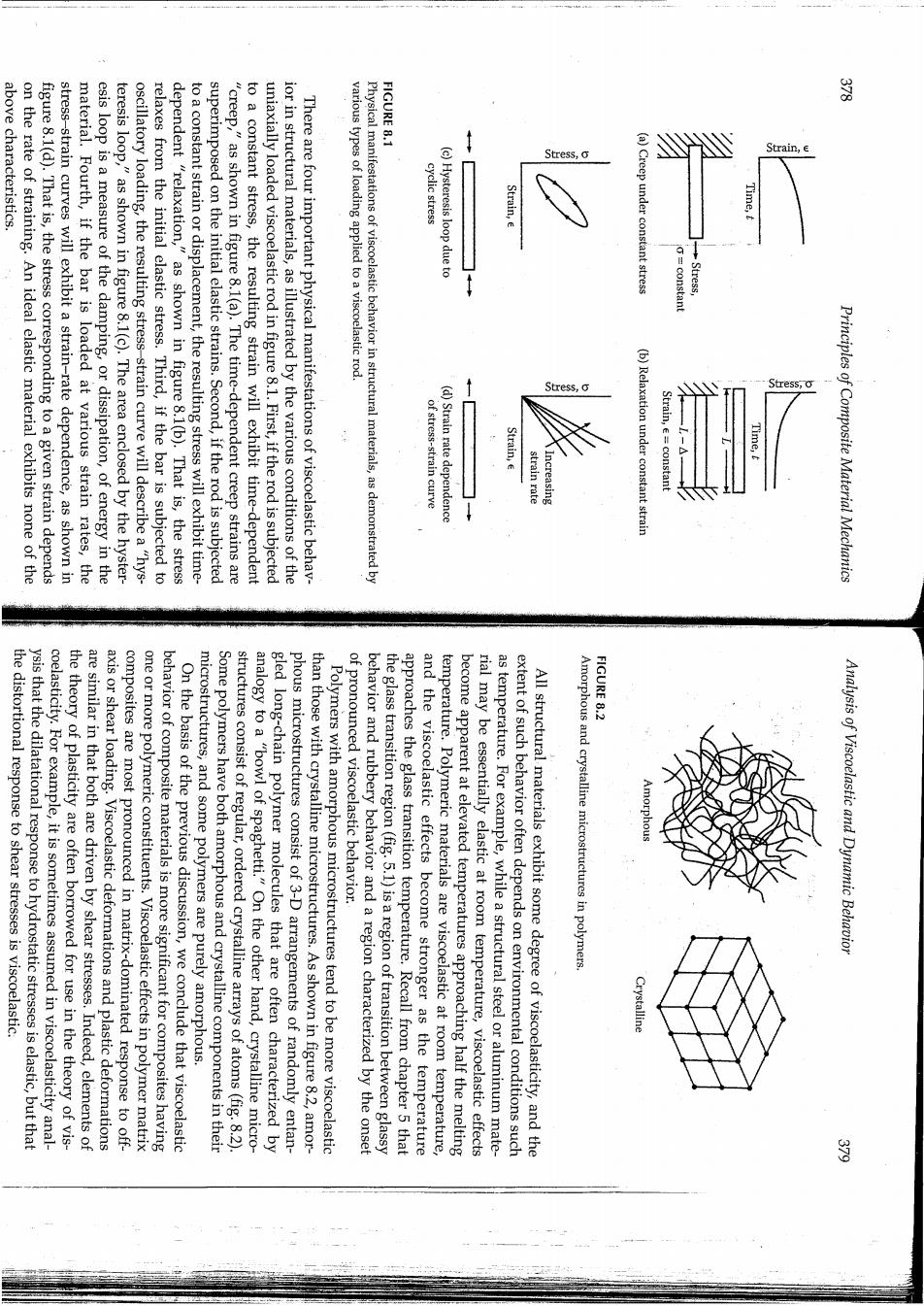
above characteristics ·1 FI Stress,o Strain,e on the rate of straining.An ideal elastic material exhibits none of the figure 8.1(d).That is,the stress corresponding to a given strain depends stress-strain curves will exhibit a strain-rate dependence,as shown in material.Fourth,if the bar is loaded at various strain rates,the esis loop is a measure of the damping,or dissipation,of energy in the teresis loop,"as shown in figure 8.1(c).The area enclosed by the hyster- oscillatory loading,the resulting stress-strain curve will describe a "hys- relaxes from the initial elastic stress.Third,if the bar is subjected to dependent "relaxation, to a constant strain or displacement,the resulting stress will exhibit time- superimposed on the initial elastic strains.Second,if the rod is subjected "creep,"as shown in figure 8.1(a).The time-dependent creep strains are to a constant stress,the resulting strain will exhibit time-dependent uniaxially loaded viscoelastic rod in figure 8.1.First,if the rod is subjected ior in structural materials,as illustrated by the various conditions of the There are four important physical manifestations of viscoelastic behav- various types of loading applied to a viscoelastic rod. Physical manifestations of viscoelastic behavior in structural materials,as demonstrated by cyclic stress (c)Hysteresis loop due to Strain,e (a)Creep under constant stress Time,t constan "as shown in figure 8.1(b).That is,the stress Stress ot stress-strain curve (d)Strain rate dependence Strain,E strain rate Increasing (b)Relaxation under constant strain St女ess Strain,e=constant Time, Principles of Composite Material Mechanics FIGURE 8.2 the distortional response to shear stresses is viscoelastic. ysis that the dilatational response to hydrostatic stresses is elastic,but that coelasticity.For example,it is sometimes assumed in viscoelasticity anal- the theory of plasticity are often borrowed for use in the theory of vis- are similar in that both are driven by shear stresses.Indeed,elements of axis or shear loading.Viscoelastic deformations and plastic deformations composites are most pronounced in matrix-dominated response to off- one or more polymeric constituents.Viscoelastic effects in polymer matrix behavior of composite materials is more significant for composites having On the basis of the previous discussion,we conclude that viscoelastic microstructures,and some polymers are purely amorphous. Some polymers have both amorphous and crystalline components in their structures consist of regular,ordered crystalline arrays of atoms(fig.8.2) gled long-chain polymer molecules that are often characterized by analogy to a"bowl of spaghetti."On the other hand,crystalline micro- phous microstructures consist of 3-D arrangements of randomly entan- than those with crystalline microstructures.As shown in figure 8.2,amor- Polymers with amorphous microstructures tend to be more viscoelastic behavior and rubbery behavior and a region characterized by the onset of pronounced viscoelastic behavior. the glass transition region(fig.5.1)is a region of transition between glassy approaches the glass transition temperature.Recall from chapter 5 that and the viscoelastic effects become stronger as the temperature temperature.Polymeric materials are viscoelastic at room temperature, become apparent at elevated temperatures approaching half the melting rial may be essentially elastic at room temperature,viscoelastic effects as temperature.For example,while a structural steel or aluminum mate- extent of such behavior often depends on environmental conditions such All structural materials exhibit some degree of viscoelasticity,and the Amorphous and crystalline microstructures Analysis of Viscoelastic and Dynamic Behavior in polymers Crystalline