正在加载图片...
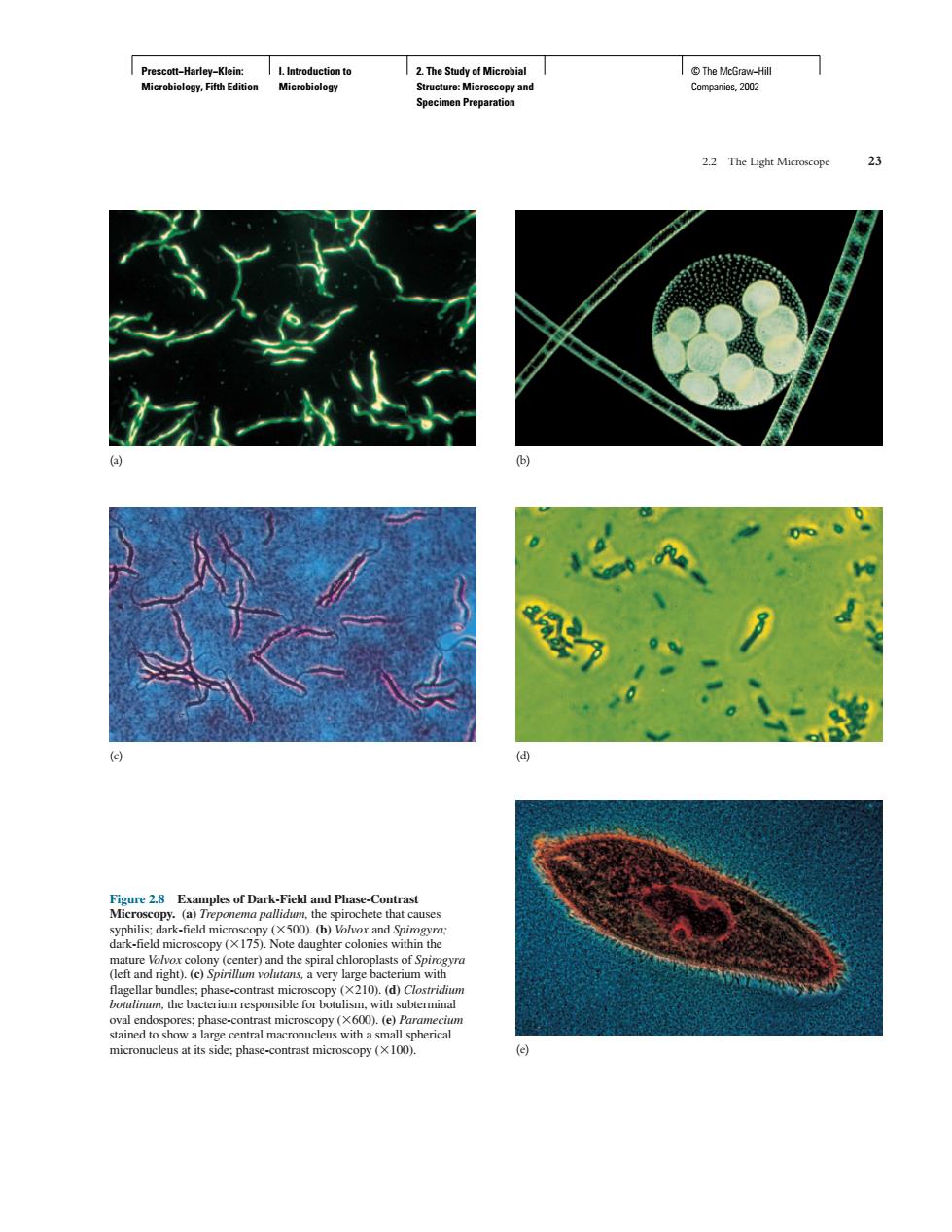
hao” Examples of Dark-Field and Phase-Contrast i)() t)e)Sn d the b inal d toPrescott−Harley−Klein: Microbiology, Fifth Edition I. Introduction to Microbiology 2. The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation © The McGraw−Hill Companies, 2002 2.2 The Light Microscope 23 (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Figure 2.8 Examples of Dark-Field and Phase-Contrast Microscopy. (a) Treponema pallidum, the spirochete that causes syphilis; dark-field microscopy (500). (b) Volvox and Spirogyra; dark-field microscopy (175). Note daughter colonies within the mature Volvox colony (center) and the spiral chloroplasts of Spirogyra (left and right). (c) Spirillum volutans, a very large bacterium with flagellar bundles; phase-contrast microscopy (210). (d) Clostridium botulinum, the bacterium responsible for botulism, with subterminal oval endospores; phase-contrast microscopy (600). (e) Paramecium stained to show a large central macronucleus with a small spherical micronucleus at its side; phase-contrast microscopy (100)