正在加载图片...
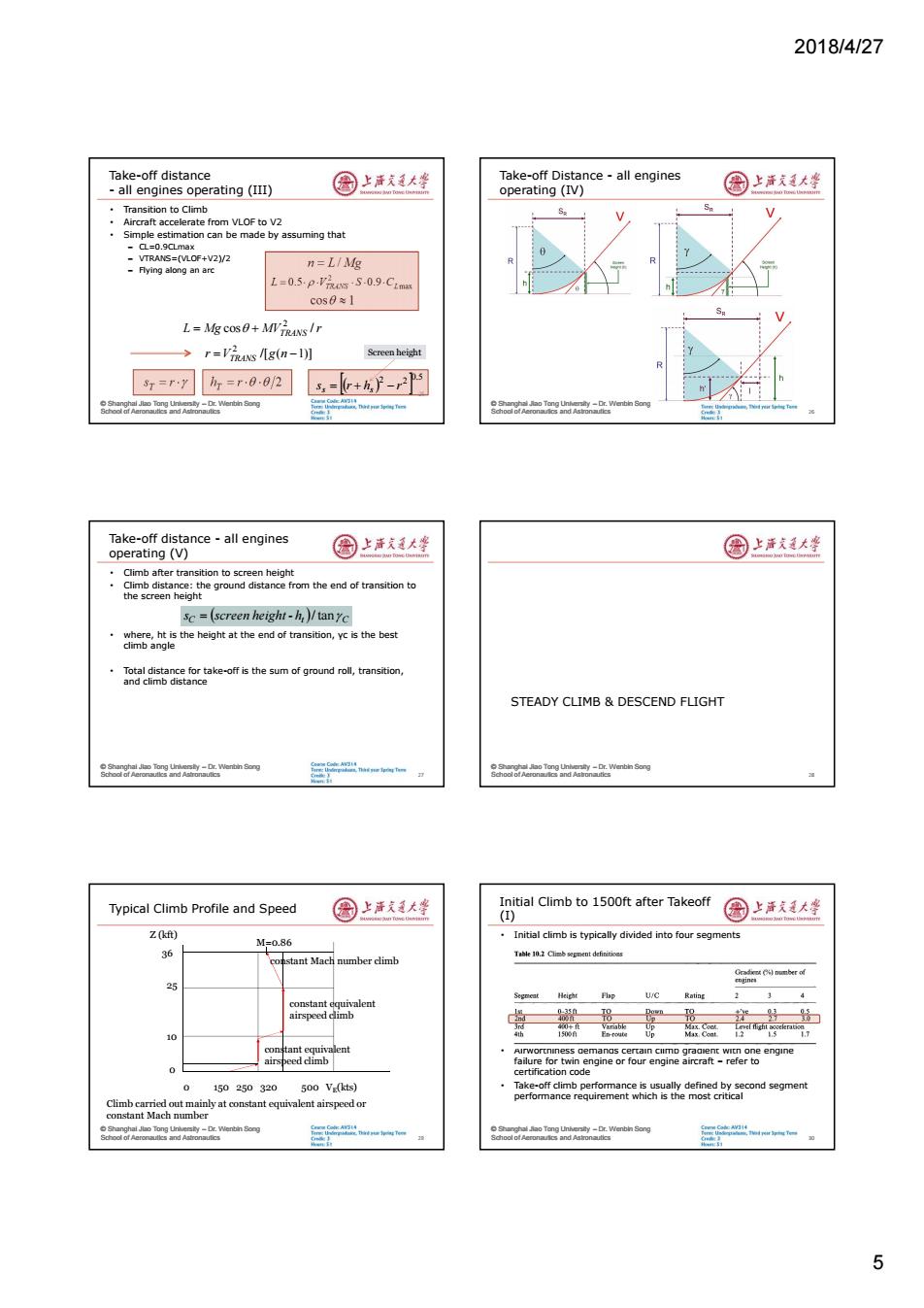
2018/4/27 Take-off distance 园上注庆大坐 Take-off Distance all engines all engines operating (III) operating (IV) 国上清大学 Transition to Climb Aircraft accelerate from VLOF to V2 Simple estimation can be made by assuming that -▣=0g□ma¥ -VTRANS=(VLOF+V2)/2 -Flying along an arc n=L/Mg 1=0.5-p-Vs5-0.9.Cima cos0≈1 L=Mg cos0+MVjmus/r r='g(-l月 Screen height ST=ry hr=r00/2 =G+-2 ong Take-off distance-all engines operating (V) 国上活大坐 国上活文大蜂 Climb after transition to screen height Climb distance:the ground distance from the end of transition to the screen height sc=(screen height-h)/tanyc where,ht is the height at the end of transition,yc is the best climb angle Total distance for take-off is the sum of ground roll,transition, and climb distance STEADY CLIMB DESCEND FLIGHT oon Wenbn ong Typical Climb Profile and Speed 图上洋大峰 Initial Climb to 1500ft after Takeoff (I) 国上洋大学 Z0) M=0.86 Initial climb is typically divided into four segments 36 constant Mach number climb Tahlemsement definitioes U/C Rating 4 constant equivalent airspeed climb En-route Up 0 0 150250320 500 Vg(kts) Take-off climb performance is usually defined by second segment performance requirement which is the most critical Climb carried out mainly at constant equivalent airspeed or constant Mach number y-Dr.Wenbin Song 52018/4/27 5 © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Take-off distance - all engines operating (III) • Transition to Climb • Aircraft accelerate from VLOF to V2 • Simple estimation can be made by assuming that – CL=0.9CLmax – VTRANS=(VLOF+V2)/2 – Flying along an arc 25 L Mg MV r TRANS cos / 2 n L / Mg max 2 L 0.5 VTRANS S 0.9 CL /[ ( 1)] 2 r VTRANS g n cos 1 s r T h r 2 T 0.5 2 2 s r h r s s Screen height © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Take-off Distance - all engines operating (IV) 26 © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Take-off distance - all engines operating (V) • Climb after transition to screen height • Climb distance: the ground distance from the end of transition to the screen height • where, ht is the height at the end of transition, γc is the best climb angle • Total distance for take-off is the sum of ground roll, transition, and climb distance 27 C t C s screen height - h / tan © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics STEADY CLIMB & DESCEND FLIGHT 28 © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Typical Climb Profile and Speed 29 Climb carried out mainly at constant equivalent airspeed or constant Mach number constant Mach number climb 0 150 250 320 500 VE (kts) Z (kft) 36 25 10 0 constant equivalent airspeed climb constant equivalent airspeed climb M=0.86 © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Initial Climb to 1500ft after Takeoff (I) • Initial climb is typically divided into four segments • Airworthiness demands certain climb gradient with one engine failure for twin engine or four engine aircraft – refer to certification code • Take-off climb performance is usually defined by second segment performance requirement which is the most critical 30