正在加载图片...
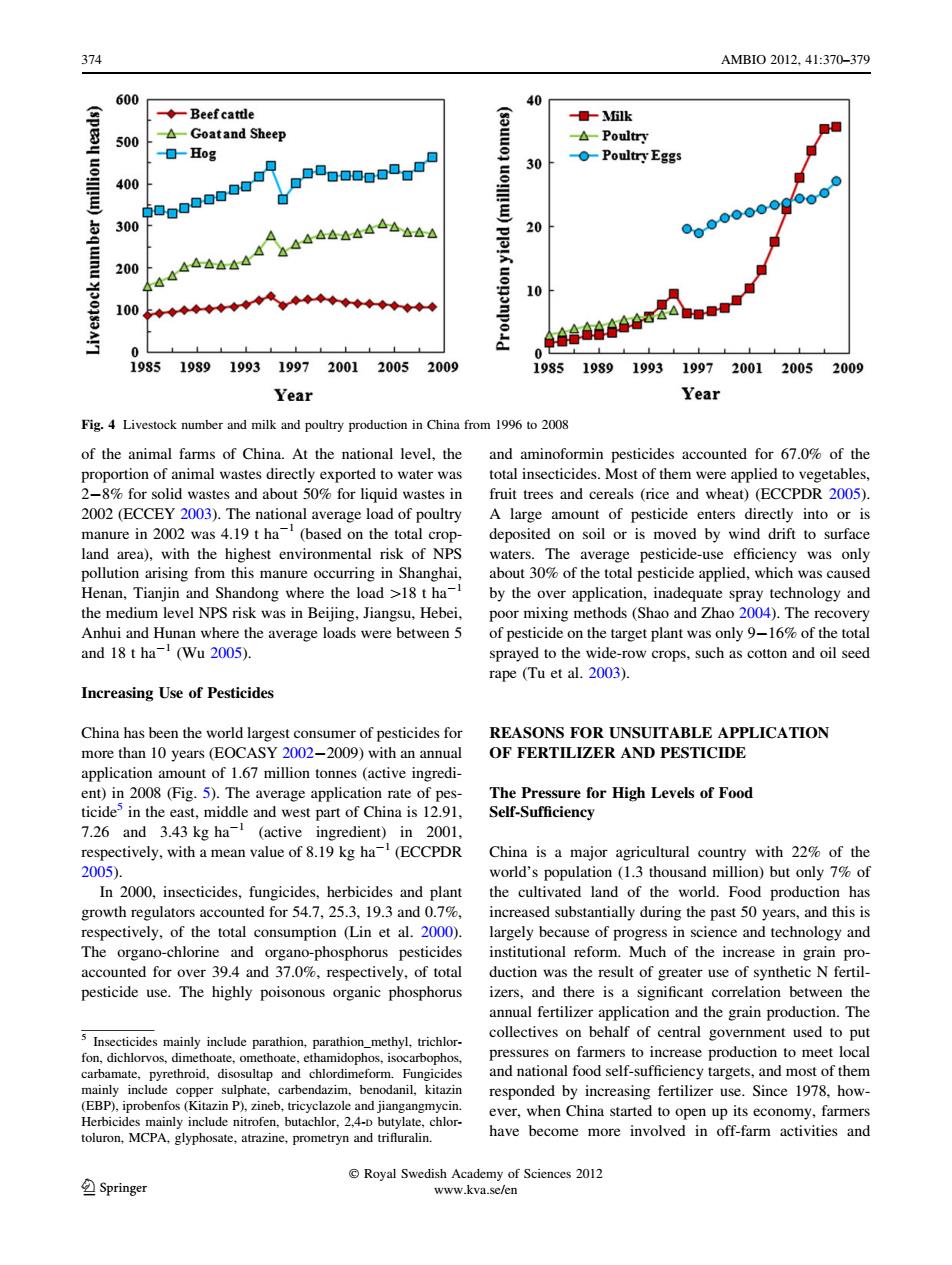
374 AMBI02012,41:370-379 600 o ◆-Beef cattle 口-k 500 △-Goatand Sheep -0-且og (s01 △-Poultry 30 -Poultry Eggs 400 00000000 uo!l! 300 44△△44△4 200 △△△△△△ 100 ◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆◆ 0 0 19851989 1993 1997200120052009 1985 1989 1993 1997200120052009 Year Year Fig.4 Livestock number and milk and poultry production in China from 1996 to 2008 of the animal farms of China.At the national level,the and aminoformin pesticides accounted for 67.0%of the proportion of animal wastes directly exported to water was total insecticides.Most of them were applied to vegetables, 2-8%for solid wastes and about 50%for liquid wastes in fruit trees and cereals(rice and wheat)(ECCPDR 2005). 2002 (ECCEY 2003).The national average load of poultry A large amount of pesticide enters directly into or is manure in 2002 was 4.19 t ha(based on the total crop- deposited on soil or is moved by wind drift to surface land area),with the highest environmental risk of NPS waters.The average pesticide-use efficiency was only pollution arising from this manure occurring in Shanghai, about 30%of the total pesticide applied,which was caused Henan,Tianjin and Shandong where the load >18 t ha- by the over application,inadequate spray technology and the medium level NPS risk was in Beijing,Jiangsu,Hebei, poor mixing methods(Shao and Zhao 2004).The recovery Anhui and Hunan where the average loads were between 5 of pesticide on the target plant was only 9-16%of the total and 18 t ha (Wu 2005). sprayed to the wide-row crops,such as cotton and oil seed rape (Tu et al.2003). Increasing Use of Pesticides China has been the world largest consumer of pesticides for REASONS FOR UNSUITABLE APPLICATION more than 10 years(EOCASY 2002-2009)with an annual OF FERTILIZER AND PESTICIDE application amount of 1.67 million tonnes (active ingredi- ent)in 2008(Fig.5).The average application rate of pes- The Pressure for High Levels of Food ticide in the east,middle and west part of China is 12.91, Self-Sufficiency 7.26 and 3.43 kg ha(active ingredient)in 2001, respectively,with a mean value of 8.19 kg ha(ECCPDR China is a major agricultural country with 22%of the 2005). world's population (1.3 thousand million)but only 7%of In 2000,insecticides,fungicides,herbicides and plant the cultivated land of the world.Food production has growth regulators accounted for 54.7.25.3.19.3 and 0.7%. increased substantially during the past 50 years,and this is respectively,of the total consumption (Lin et al.2000). largely because of progress in science and technology and The organo-chlorine and organo-phosphorus pesticides institutional reform.Much of the increase in grain pro- accounted for over 39.4 and 37.0%,respectively,of total duction was the result of greater use of synthetic N fertil- pesticide use.The highly poisonous organic phosphorus izers,and there is a significant correlation between the annual fertilizer application and the grain production.The s Insecticides mainly include parathion,parathion_methyl,trichlor- collectives on behalf of central government used to put fon,dichlorvos,dimethoate,omethoate,ethamidophos,isocarbophos, pressures on farmers to increase production to meet local carbamate,pyrethroid,disosultap and chlordimeform.Fungicides and national food self-sufficiency targets,and most of them mainly include copper sulphate,carbendazim,benodanil,kitazin responded by increasing fertilizer use.Since 1978,how- (EBP),iprobenfos(Kitazin P),zineb,tricyclazole and jiangangmycin. ever,when China started to open up its economy,farmers Herbicides mainly include nitrofen,butachlor,2,4-D butylate,chlor- toluron,MCPA,glyphosate,atrazine,prometryn and trifluralin. have become more involved in off-farm activities and Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences 2012 Springer www.kva.se/enof the animal farms of China. At the national level, the proportion of animal wastes directly exported to water was 2-8% for solid wastes and about 50% for liquid wastes in 2002 (ECCEY 2003). The national average load of poultry manure in 2002 was 4.19 t ha-1 (based on the total cropland area), with the highest environmental risk of NPS pollution arising from this manure occurring in Shanghai, Henan, Tianjin and Shandong where the load [18 t ha-1 the medium level NPS risk was in Beijing, Jiangsu, Hebei, Anhui and Hunan where the average loads were between 5 and 18 t ha-1 (Wu 2005). Increasing Use of Pesticides China has been the world largest consumer of pesticides for more than 10 years (EOCASY 2002-2009) with an annual application amount of 1.67 million tonnes (active ingredient) in 2008 (Fig. 5). The average application rate of pesticide5 in the east, middle and west part of China is 12.91, 7.26 and 3.43 kg ha-1 (active ingredient) in 2001, respectively, with a mean value of 8.19 kg ha-1 (ECCPDR 2005). In 2000, insecticides, fungicides, herbicides and plant growth regulators accounted for 54.7, 25.3, 19.3 and 0.7%, respectively, of the total consumption (Lin et al. 2000). The organo-chlorine and organo-phosphorus pesticides accounted for over 39.4 and 37.0%, respectively, of total pesticide use. The highly poisonous organic phosphorus and aminoformin pesticides accounted for 67.0% of the total insecticides. Most of them were applied to vegetables, fruit trees and cereals (rice and wheat) (ECCPDR 2005). A large amount of pesticide enters directly into or is deposited on soil or is moved by wind drift to surface waters. The average pesticide-use efficiency was only about 30% of the total pesticide applied, which was caused by the over application, inadequate spray technology and poor mixing methods (Shao and Zhao 2004). The recovery of pesticide on the target plant was only 9-16% of the total sprayed to the wide-row crops, such as cotton and oil seed rape (Tu et al. 2003). REASONS FOR UNSUITABLE APPLICATION OF FERTILIZER AND PESTICIDE The Pressure for High Levels of Food Self-Sufficiency China is a major agricultural country with 22% of the world’s population (1.3 thousand million) but only 7% of the cultivated land of the world. Food production has increased substantially during the past 50 years, and this is largely because of progress in science and technology and institutional reform. Much of the increase in grain production was the result of greater use of synthetic N fertilizers, and there is a significant correlation between the annual fertilizer application and the grain production. The collectives on behalf of central government used to put pressures on farmers to increase production to meet local and national food self-sufficiency targets, and most of them responded by increasing fertilizer use. Since 1978, however, when China started to open up its economy, farmers have become more involved in off-farm activities and Fig. 4 Livestock number and milk and poultry production in China from 1996 to 2008 5 Insecticides mainly include parathion, parathion_methyl, trichlorfon, dichlorvos, dimethoate, omethoate, ethamidophos, isocarbophos, carbamate, pyrethroid, disosultap and chlordimeform. Fungicides mainly include copper sulphate, carbendazim, benodanil, kitazin (EBP), iprobenfos (Kitazin P), zineb, tricyclazole and jiangangmycin. Herbicides mainly include nitrofen, butachlor, 2,4-D butylate, chlortoluron, MCPA, glyphosate, atrazine, prometryn and trifluralin. 374 AMBIO 2012, 41:370–379 123 Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences 2012 www.kva.se/en�