正在加载图片...
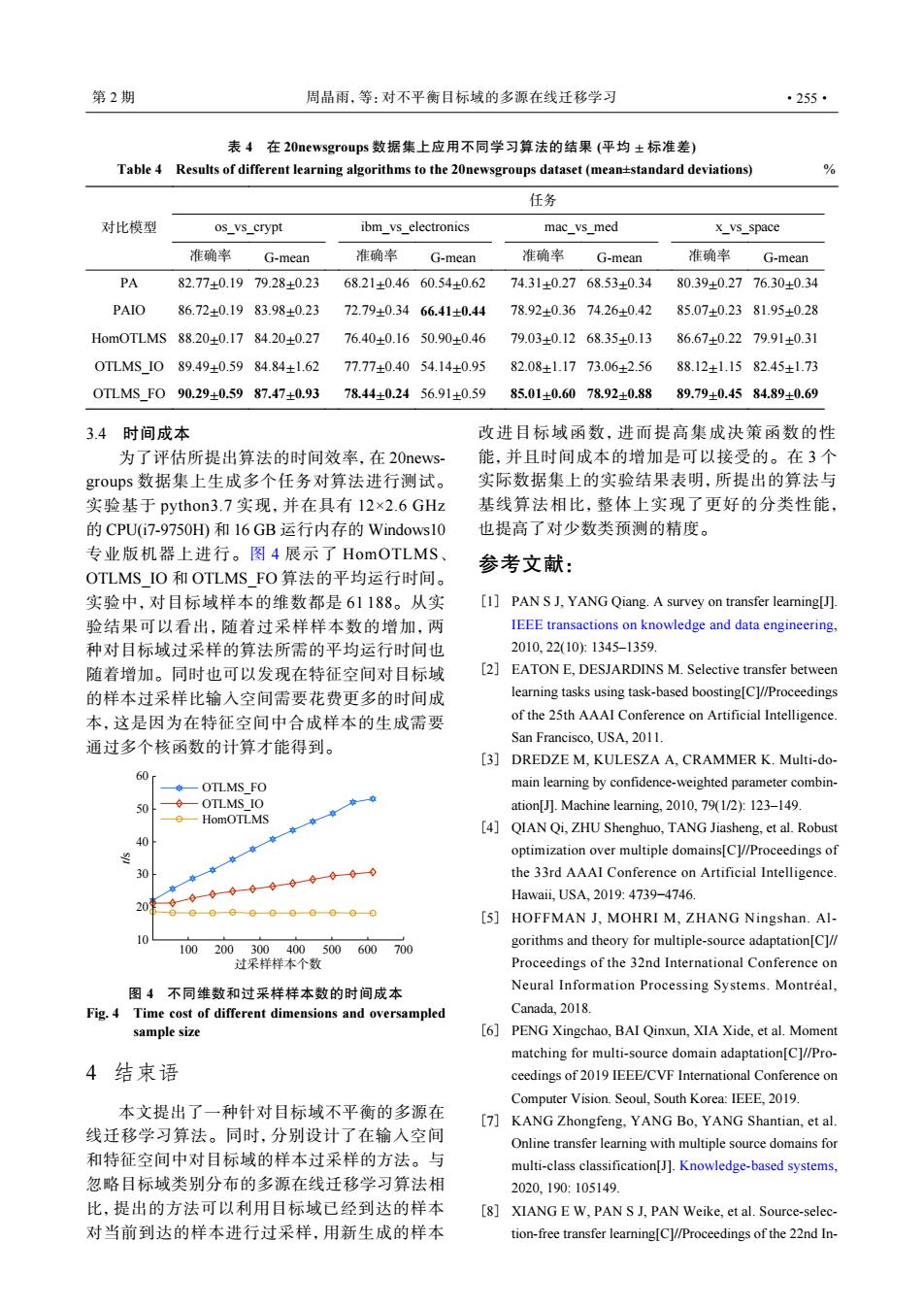
第2期 周晶雨,等:对不平衡目标域的多源在线迁移学习 ·255· 表4在20 newsgroups数据集上应用不同学习算法的结果(平均±标准差) Table 4 Results of different learning algorithms to the 20newsgroups dataset(mean+standard deviations) 号 任务 对比模型 os_vs_crypt ibm_vs_electronics mac_vs_med x_vs_space 准确率 G-mean 准确率 G-mean 准确率 G-mean 准确率 G-mean PA 82.77±0.1979.28±0.23 68.21±0.4660.54±0.62 74.31±0.2768.53±0.34 80.39±0.2776.30±0.34 PAIO 86.72±0.1983.98±0.23 72.79±0.3466.41±0.44 78.92±0.3674.26±0.42 85.07±0.2381.95±0.28 Hom0TLMS88.20+0.1784.20+0.2776.40+0.1650.90+0.46 79.03+0.1268.35±0.13 86.67±0.2279.91±0.31 0 TLMS I089.49±0.5984.84±1.6277.77±0.4054.14±0.95 82.08±1.1773.06±2.56 88.12±1.1582.45±1.73 0 TLMS F090.29±0.5987.47±0.93 78.44±0.2456.91±0.59 85.01±0.6078.92±0.88 89.79±0.4584.89±0.69 3.4时间成本 改进目标域函数,进而提高集成决策函数的性 为了评估所提出算法的时间效率,在20news- 能,并且时间成本的增加是可以接受的。在3个 groups数据集上生成多个任务对算法进行测试。 实际数据集上的实验结果表明,所提出的算法与 实验基于python:3.7实现,并在具有12×2.6GHz 基线算法相比,整体上实现了更好的分类性能, 的CPU(i7-9750H田和16GB运行内存的Windows10 也提高了对少数类预测的精度。 专业版机器上进行。图4展示了HomOTLMS、 参考文献: OTLMS IO和OTLMS FO算法的平均运行时间。 实验中,对目标域样本的维数都是61188。从实 [1]PAN S J,YANG Qiang.A survey on transfer learning[J]. 验结果可以看出,随着过采样样本数的增加,两 IEEE transactions on knowledge and data engineering, 种对目标域过采样的算法所需的平均运行时间也 2010,22(10):1345-1359 随着增加。同时也可以发现在特征空间对目标域 [2]EATON E.DESJARDINS M.Selective transfer between 的样本过采样比输入空间需要花费更多的时间成 learning tasks using task-based boosting[C]//Proceedings 本,这是因为在特征空间中合成样本的生成需要 of the 25th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco,USA.2011. 通过多个核函数的计算才能得到。 [3]DREDZE M,KULESZA A,CRAMMER K.Multi-do- 60 -OTLMS FO main learning by confidence-weighted parameter combin- -OTLMS IO ation[J].Machine learning,2010,79(1/2):123-149. -HomOTLMS [4]QIAN Qi,ZHU Shenghuo,TANG Jiasheng,et al.Robust 40 optimization over multiple domains[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Hawaii,USA,2019:4739-4746. 20 [5]HOFFMAN J,MOHRI M,ZHANG Ningshan.Al- 10 100200300400500600700 gorithms and theory for multiple-source adaptation[C]// 过采样样本个数 Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on 图4不同维数和过采样样本数的时间成本 Neural Information Processing Systems.Montreal, Fig.4 Time cost of different dimensions and oversampled Canada,2018 sample size [6]PENG Xingchao,BAI Qinxun,XIA Xide,et al.Moment matching for multi-source domain adaptation[C]//Pro- 4结束语 ceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Seoul,South Korea:IEEE,2019 本文提出了一种针对目标域不平衡的多源在 [7]KANG Zhongfeng,YANG Bo,YANG Shantian,et al. 线迁移学习算法。同时,分别设计了在输入空间 Online transfer learning with multiple source domains for 和特征空间中对目标域的样本过采样的方法。与 multi-class classification[J].Knowledge-based systems, 忽略目标域类别分布的多源在线迁移学习算法相 2020,190:105149. 比,提出的方法可以利用目标域已经到达的样本 [8]XIANG E W.PAN S J.PAN Weike,et al.Source-selec- 对当前到达的样本进行过采样,用新生成的样本 tion-free transfer learning[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd In-表 4 在 20newsgroups 数据集上应用不同学习算法的结果 (平均 ± 标准差) Table 4 Results of different learning algorithms to the 20newsgroups dataset (mean±standard deviations) % 对比模型 任务 os_vs_crypt ibm_vs_electronics mac_vs_med x_vs_space 准确率 G-mean 准确率 G-mean 准确率 G-mean 准确率 G-mean PA 82.77 ± 0.19 79.28 ± 0.23 68.21 ± 0.46 60.54 ± 0.62 74.31 ± 0.27 68.53 ± 0.34 80.39 ± 0.27 76.30 ± 0.34 PAIO 86.72 ± 0.19 83.98 ± 0.23 72.79 ± 0.34 66.41 ± 0.44 78.92 ± 0.36 74.26 ± 0.42 85.07 ± 0.23 81.95 ± 0.28 HomOTLMS 88.20 ± 0.17 84.20 ± 0.27 76.40 ± 0.16 50.90 ± 0.46 79.03 ± 0.12 68.35 ± 0.13 86.67 ± 0.22 79.91 ± 0.31 OTLMS_IO 89.49 ± 0.59 84.84 ± 1.62 77.77 ± 0.40 54.14 ± 0.95 82.08 ± 1.17 73.06 ± 2.56 88.12 ± 1.15 82.45 ± 1.73 OTLMS_FO 90.29 ± 0.59 87.47 ± 0.93 78.44 ± 0.24 56.91 ± 0.59 85.01 ± 0.60 78.92 ± 0.88 89.79 ± 0.45 84.89 ± 0.69 3.4 时间成本 为了评估所提出算法的时间效率,在 20newsgroups 数据集上生成多个任务对算法进行测试。 实验基于 python3.7 实现,并在具有 12×2.6 GHz 的 CPU(i7-9750H) 和 16 GB 运行内存的 Windows10 专业版机器上进行。图 4 展示了 HomOTLMS、 OTLMS_IO 和 OTLMS_FO 算法的平均运行时间。 实验中,对目标域样本的维数都是 61 188。从实 验结果可以看出,随着过采样样本数的增加,两 种对目标域过采样的算法所需的平均运行时间也 随着增加。同时也可以发现在特征空间对目标域 的样本过采样比输入空间需要花费更多的时间成 本,这是因为在特征空间中合成样本的生成需要 通过多个核函数的计算才能得到。 60 50 40 30 20 10 t/s 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 过采样样本个数 OTLMS_FO OTLMS_IO HomOTLMS 图 4 不同维数和过采样样本数的时间成本 Fig. 4 Time cost of different dimensions and oversampled sample size 4 结束语 本文提出了一种针对目标域不平衡的多源在 线迁移学习算法。同时,分别设计了在输入空间 和特征空间中对目标域的样本过采样的方法。与 忽略目标域类别分布的多源在线迁移学习算法相 比,提出的方法可以利用目标域已经到达的样本 对当前到达的样本进行过采样,用新生成的样本 改进目标域函数,进而提高集成决策函数的性 能,并且时间成本的增加是可以接受的。在 3 个 实际数据集上的实验结果表明,所提出的算法与 基线算法相比,整体上实现了更好的分类性能, 也提高了对少数类预测的精度。 参考文献: PAN S J, YANG Qiang. A survey on transfer learning[J]. IEEE transactions on knowledge and data engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345–1359. [1] EATON E, DESJARDINS M. Selective transfer between learning tasks using task-based boosting[C]//Proceedings of the 25th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, USA, 2011. [2] DREDZE M, KULESZA A, CRAMMER K. Multi-domain learning by confidence-weighted parameter combination[J]. Machine learning, 2010, 79(1/2): 123–149. [3] QIAN Qi, ZHU Shenghuo, TANG Jiasheng, et al. Robust optimization over multiple domains[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Hawaii, USA, 2019: 4739−4746. [4] HOFFMAN J, MOHRI M, ZHANG Ningshan. Algorithms and theory for multiple-source adaptation[C]// Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada, 2018. [5] PENG Xingchao, BAI Qinxun, XIA Xide, et al. Moment matching for multi-source domain adaptation[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. [6] KANG Zhongfeng, YANG Bo, YANG Shantian, et al. Online transfer learning with multiple source domains for multi-class classification[J]. Knowledge-based systems, 2020, 190: 105149. [7] XIANG E W, PAN S J, PAN Weike, et al. Source-selection-free transfer learning[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd In- [8] 第 2 期 周晶雨,等:对不平衡目标域的多源在线迁移学习 ·255·