正在加载图片...
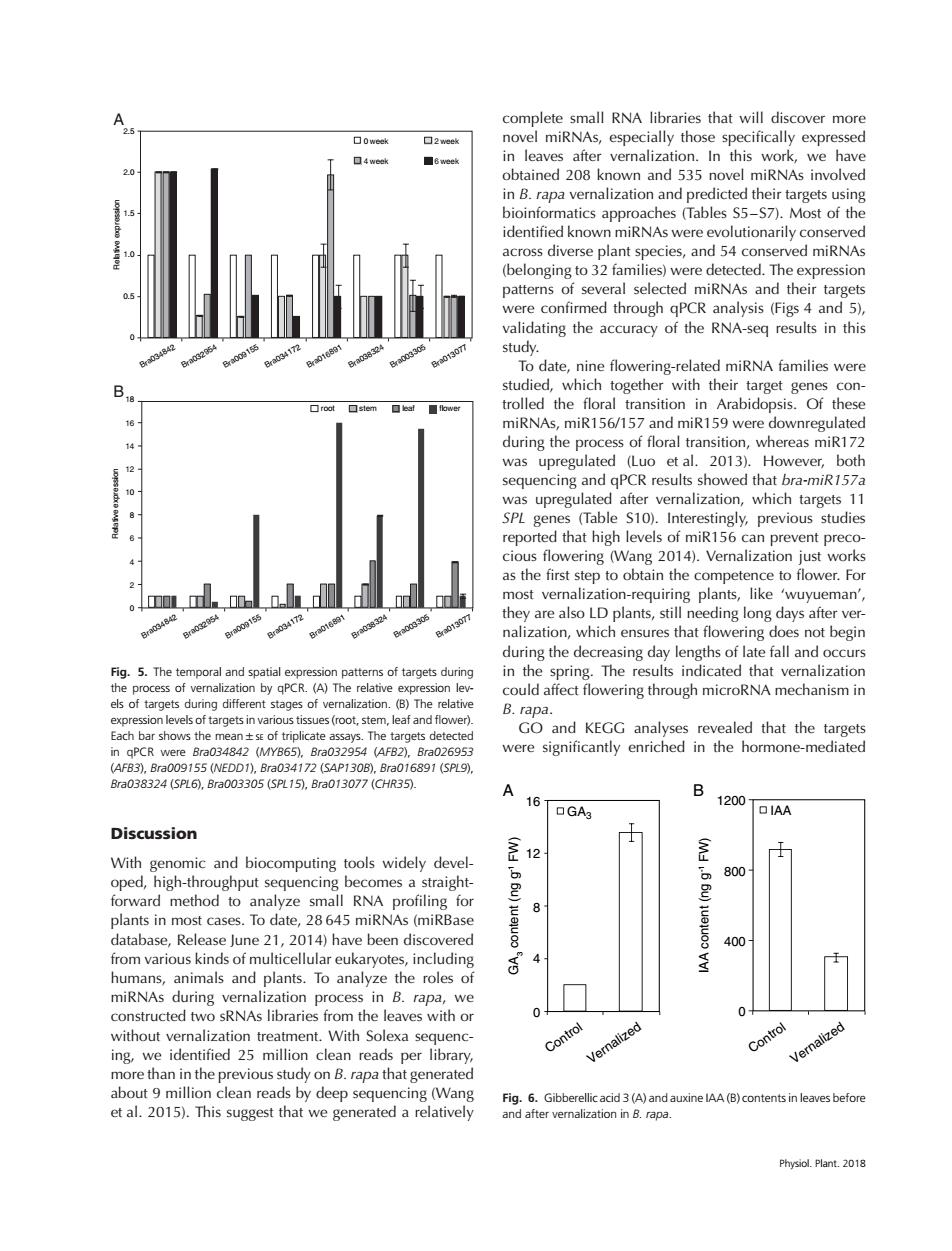
complete small RNA libraries that will discover more 25 口0week ▣2week novel miRNAs,especially those specifically expressed 口4week ■6week in leaves after vernalization.In this work,we have obtained 208 known and 535 novel miRNAs involved in B.rapa vernalization and predicted their targets using bioinformatics approaches (Tables S5-S7).Most of the identified known miRNAs were evolutionarily conserved across diverse plant species,and 54 conserved miRNAs (belonging to 32 families)were detected.The expression patterns of several selected miRNAs and their targets were confirmed through qPCR analysis(Figs 4 and 5), validating the accuracy of the RNA-seg results in this 172 study. To date,nine flowering-related miRNA families were studied,which together with their target genes con- trolled the floral transition in Arabidopsis.Of these miRNAs,miR156/157 and miR159 were downregulated 14 during the process of floral transition,whereas miR172 was upregulated (Luo et al.2013).However,both sequencing and gPCR results showed that bra-miR157a was upregulated after vernalization,which targets 11 8 SPL genes (Table S10).Interestingly,previous studies reported that high levels of miR156 can prevent preco- cious flowering (Wang 2014).Vernalization just works as the first step to obtain the competence to flower.For most vernalization-requiring plants,like 'wuyueman', ra003305 91307 they are also LD plants,still needing long days after ver- nalization,which ensures that flowering does not begin during the decreasing day lengths of late fall and occurs Fig.5.The temporal and spatial expression patterns of targets during in the spring.The results indicated that vernalization the process of vernalization by qPCR.(A)The relative expression lev- could affect flowering through microRNA mechanism in els of targets during different stages of vernalization.(B)The relative B.rapa. expression levels of targets in various tissues(root,stem,leaf and flower). Each bar shows the mean +sE of triplicate assays.The targets detected GO and KEGG analyses revealed that the targets in qPCR were Bra034842 (MYB65),Bra032954 (AFB2),Bra026953 were significantly enriched in the hormone-mediated (AFB3),Bra009155(NEDD1),Bra034172(5AP130B).Bra016891(5PL9). Bra038324(5PL6),Bra003305(SPL15),Bra013077(CHR35. A B 16T 1200 GA3 OIAA Discussion With genomic and biocomputing tools widely devel- 800 oped,high-throughput sequencing becomes a straight- forward method to analyze small RNA profiling for 8 plants in most cases.To date,28645 miRNAs(miRBase database,Release June 21,2014)have been discovered 400 from various kinds of multicellular eukaryotes,including 4 humans,animals and plants.To analyze the roles of miRNAs during vernalization process in B.rapa,we constructed two sRNAs libraries from the leaves with or 0 0 without vernalization treatment.With Solexa sequenc- Control ing,we identified 25 million clean reads per library, Vernalized Control Vernalized more than in the previous study on B.rapa that generated about 9 million clean reads by deep sequencing (Wang Fig.6.Gibberellic acid 3(A)and auxine IAA(B)contents in leaves before et al.2015).This suggest that we generated a relatively and after vernalization in B.rapa. Physiol.Plant.20180 week 2 week 4 week 2.5 A B 2.0 1.5 6 week 1.0 0.5 0 Relative expression Bra034842 Bra032954 Bra009155 Bra034172 Bra016891 Bra038324 Bra003305 Bra013077 10 8 6 4 2 0 Relative expression Bra034842 Bra032954 Bra009155 Bra034172 Bra016891 Bra038324 Bra003305 Bra013077 root stem leaf 18 16 14 12 flower Fig. 5. The temporal and spatial expression patterns of targets during the process of vernalization by qPCR. (A) The relative expression levels of targets during different stages of vernalization. (B) The relative expression levels of targets in various tissues (root, stem, leaf and flower). Each bar shows the mean±SE of triplicate assays. The targets detected in qPCR were Bra034842 (MYB65), Bra032954 (AFB2), Bra026953 (AFB3), Bra009155 (NEDD1), Bra034172 (SAP130B), Bra016891 (SPL9), Bra038324 (SPL6), Bra003305 (SPL15), Bra013077 (CHR35). Discussion With genomic and biocomputing tools widely developed, high-throughput sequencing becomes a straightforward method to analyze small RNA profiling for plants in most cases. To date, 28 645 miRNAs (miRBase database, Release June 21, 2014) have been discovered from various kinds of multicellular eukaryotes, including humans, animals and plants. To analyze the roles of miRNAs during vernalization process in B. rapa, we constructed two sRNAs libraries from the leaves with or without vernalization treatment. With Solexa sequencing, we identified 25 million clean reads per library, more than in the previous study on B. rapa that generated about 9 million clean reads by deep sequencing (Wang et al. 2015). This suggest that we generated a relatively complete small RNA libraries that will discover more novel miRNAs, especially those specifically expressed in leaves after vernalization. In this work, we have obtained 208 known and 535 novel miRNAs involved in B. rapa vernalization and predicted their targets using bioinformatics approaches (Tables S5–S7). Most of the identified known miRNAs were evolutionarily conserved across diverse plant species, and 54 conserved miRNAs (belonging to 32 families) were detected. The expression patterns of several selected miRNAs and their targets were confirmed through qPCR analysis (Figs 4 and 5), validating the accuracy of the RNA-seq results in this study. To date, nine flowering-related miRNA families were studied, which together with their target genes controlled the floral transition in Arabidopsis. Of these miRNAs, miR156/157 and miR159 were downregulated during the process of floral transition, whereas miR172 was upregulated (Luo et al. 2013). However, both sequencing and qPCR results showed that bra-miR157a was upregulated after vernalization, which targets 11 SPL genes (Table S10). Interestingly, previous studies reported that high levels of miR156 can prevent precocious flowering (Wang 2014). Vernalization just works as the first step to obtain the competence to flower. For most vernalization-requiring plants, like ‘wuyueman’, they are also LD plants, still needing long days after vernalization, which ensures that flowering does not begin during the decreasing day lengths of late fall and occurs in the spring. The results indicated that vernalization could affect flowering through microRNA mechanism in B. rapa. GO and KEGG analyses revealed that the targets were significantly enriched in the hormone-mediated 16 12 8 4 0 GA3 GA3 content (ng g-1 FW) 1200 800 400 0 IAA A IAA content (ng g-1 FW) B Control Vernalized Control Vernalized Fig. 6. Gibberellic acid 3 (A) and auxine IAA (B) contents in leaves before and after vernalization in B. rapa. Physiol. Plant. 2018