正在加载图片...
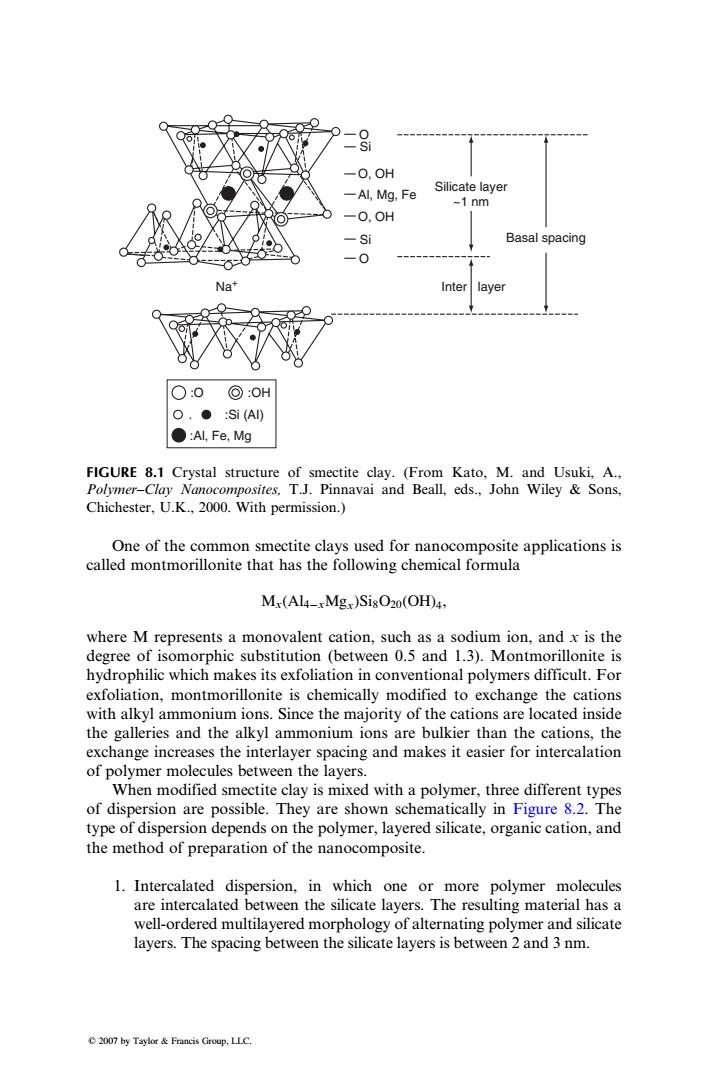
8 -O.OH -Al,Mg.Fe Silicate layer ~1 nm -0,0H Si Basal spacing -0 Na" Inter layer ○:0:OH O.●:Si(A) ●:Al,Fe,Mg FIGURE 8.1 Crystal structure of smectite clay.(From Kato,M.and Usuki,A., Polymer-Clay Nanocomposites.T.J.Pinnavai and Beall,eds.,John Wiley Sons, Chichester,U.K.,2000.With permission.) One of the common smectite clays used for nanocomposite applications is called montmorillonite that has the following chemical formula Mx(Al4-xMgx)SisO20(OH)4, where M represents a monovalent cation,such as a sodium ion,and x is the degree of isomorphic substitution (between 0.5 and 1.3).Montmorillonite is hydrophilic which makes its exfoliation in conventional polymers difficult.For exfoliation,montmorillonite is chemically modified to exchange the cations with alkyl ammonium ions.Since the majority of the cations are located inside the galleries and the alkyl ammonium ions are bulkier than the cations,the exchange increases the interlayer spacing and makes it easier for intercalation of polymer molecules between the layers. When modified smectite clay is mixed with a polymer,three different types of dispersion are possible.They are shown schematically in Figure 8.2.The type of dispersion depends on the polymer,layered silicate,organic cation,and the method of preparation of the nanocomposite. 1.Intercalated dispersion,in which one or more polymer molecules are intercalated between the silicate layers.The resulting material has a well-ordered multilayered morphology of alternating polymer and silicate layers.The spacing between the silicate layers is between 2 and 3 nm. 2007 by Taylor Francis Group,LLC.One of the common smectite clays used for nanocomposite applications is called montmorillonite that has the following chemical formula Mx(Al4xMgx)Si8O20(OH)4, where M represents a monovalent cation, such as a sodium ion, and x is the degree of isomorphic substitution (between 0.5 and 1.3). Montmorillonite is hydrophilic which makes its exfoliation in conventional polymers difficult. For exfoliation, montmorillonite is chemically modified to exchange the cations with alkyl ammonium ions. Since the majority of the cations are located inside the galleries and the alkyl ammonium ions are bulkier than the cations, the exchange increases the interlayer spacing and makes it easier for intercalation of polymer molecules between the layers. When modified smectite clay is mixed with a polymer, three different types of dispersion are possible. They are shown schematically in Figure 8.2. The type of dispersion depends on the polymer, layered silicate, organic cation, and the method of preparation of the nanocomposite. 1. Intercalated dispersion, in which one or more polymer molecules are intercalated between the silicate layers. The resulting material has a well-ordered multilayered morphology of alternating polymer and silicate layers. The spacing between the silicate layers is between 2 and 3 nm. O Basal spacing Inter layer Silicate layer ~1 nm Si Si O, OH O, OH Al, Mg, Fe O Na+ :O :OH . :Si (AI) :Al, Fe, Mg FIGURE 8.1 Crystal structure of smectite clay. (From Kato, M. and Usuki, A., Polymer–Clay Nanocomposites, T.J. Pinnavai and Beall, eds., John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, U.K., 2000. With permission.) 2007 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.�