正在加载图片...
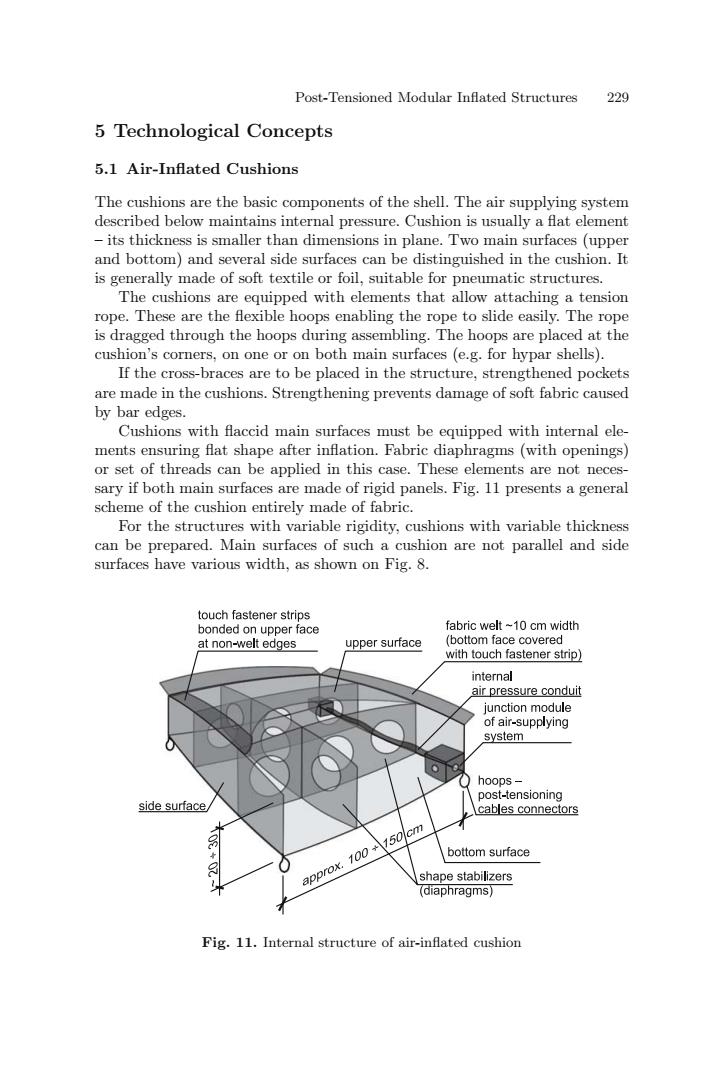
Post-Tensioned Modular Inflated Structures 229 5 Technological Concepts 5.1 Air-Inflated Cushions The cushions are the basic components of the shell.The air supplying system described below maintains internal pressure.Cushion is usually a flat element -its thickness is smaller than dimensions in plane.Two main surfaces (upper and bottom)and several side surfaces can be distinguished in the cushion.It is generally made of soft textile or foil,suitable for pneumatic structures The cushions are equipped with elements that allow attaching a tension rope.These are the flexible hoops enabling the rope to slide easily.The rope is dragged through the hoops during assembling.The hoops are placed at the cushion's corners,on one or on both main surfaces (e.g.for hypar shells). If the cross-braces are to be placed in the structure,strengthened pockets are made in the cushions.Strengthening prevents damage of soft fabric caused by bar edges. Cushions with flaccid main surfaces must be equipped with internal ele- ments ensuring flat shape after inflation.Fabric diaphragms(with openings) or set of threads can be applied in this case.These elements are not neces- sary if both main surfaces are made of rigid panels.Fig.11 presents a general scheme of the cushion entirely made of fabric. For the structures with variable rigidity,cushions with variable thickness can be prepared.Main surfaces of such a cushion are not parallel and side surfaces have various width,as shown on Fig.8. touch fastener strips bonded on upper face fabric welt-10 cm width at non-welt edges upper surface (bottom face covered with touch fastener strip) internal air pressure conduit junction module of air-supplying system hoops- post-tensioning side surface cables connectors approx.100+150cm bottom surface shape stabilizers (diaphragms) Fig.11.Internal structure of air-inflated cushionPost-Tensioned Modular Inflated Structures 229 5 Technological Concepts 5.1 Air-Inflated Cushions The cushions are the basic components of the shell. The air supplying system described below maintains internal pressure. Cushion is usually a flat element – its thickness is smaller than dimensions in plane. Two main surfaces (upper and bottom) and several side surfaces can be distinguished in the cushion. It is generally made of soft textile or foil, suitable for pneumatic structures. The cushions are equipped with elements that allow attaching a tension rope. These are the flexible hoops enabling the rope to slide easily. The rope is dragged through the hoops during assembling. The hoops are placed at the cushion’s corners, on one or on both main surfaces (e.g. for hypar shells). If the cross-braces are to be placed in the structure, strengthened pockets are made in the cushions. Strengthening prevents damage of soft fabric caused by bar edges. Cushions with flaccid main surfaces must be equipped with internal elements ensuring flat shape after inflation. Fabric diaphragms (with openings) or set of threads can be applied in this case. These elements are not necessary if both main surfaces are made of rigid panels. Fig. 11 presents a general scheme of the cushion entirely made of fabric. For the structures with variable rigidity, cushions with variable thickness can be prepared. Main surfaces of such a cushion are not parallel and side surfaces have various width, as shown on Fig. 8. Fig. 11. Internal structure of air-inflated cushion