正在加载图片...
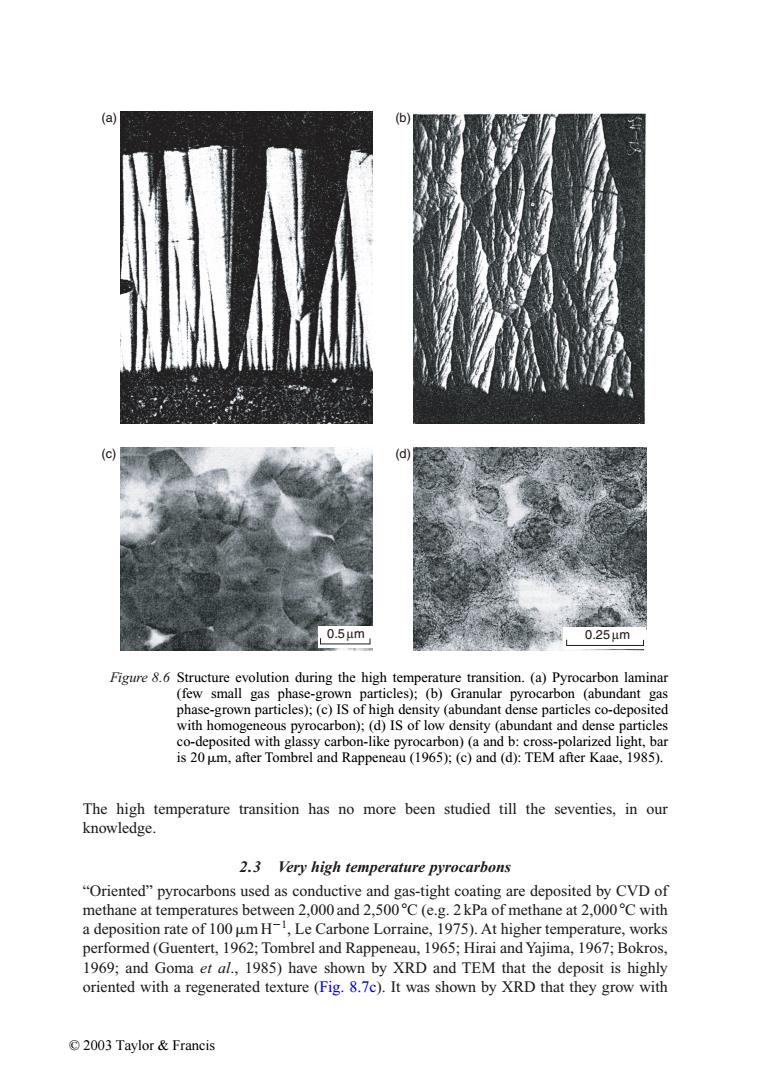
(a) (b) 0.5μm 0.25μm Figure 8.6 Structure evolution during the high temperature transition.(a)Pyrocarbon laminar (few small gas phase-grown particles);(b)Granular pyrocarbon (abundant gas phase-grown particles);(c)IS of high density(abundant dense particles co-deposited with homogeneous pyrocarbon);(d)IS of low density (abundant and dense particles co-deposited with glassy carbon-like pyrocarbon)(a and b:cross-polarized light,bar is 20 um,after Tombrel and Rappeneau(1965);(c)and(d):TEM after Kaae,1985). The high temperature transition has no more been studied till the seventies,in our knowledge. 2.3 Very high temperature pyrocarbons "Oriented"pyrocarbons used as conductive and gas-tight coating are deposited by CVD of methane at temperatures between 2,000 and 2,500C (e.g.2kPa of methane at 2,000C with a deposition rate of 100 um H-,Le Carbone Lorraine,1975).At higher temperature,works performed(Guentert,1962;Tombrel and Rappeneau,1965;Hirai and Yajima,1967;Bokros, 1969;and Goma et al.,1985)have shown by XRD and TEM that the deposit is highly oriented with a regenerated texture(Fig.8.7c).It was shown by XRD that they grow with ©2003 Taylor&FrancisThe high temperature transition has no more been studied till the seventies, in our knowledge. 2.3 Very high temperature pyrocarbons “Oriented” pyrocarbons used as conductive and gas-tight coating are deposited by CVD of methane at temperatures between 2,000 and 2,500 C (e.g. 2 kPa of methane at 2,000 C with a deposition rate of 100mH1 , Le Carbone Lorraine, 1975). At higher temperature, works performed (Guentert, 1962; Tombrel and Rappeneau, 1965; Hirai andYajima, 1967; Bokros, 1969; and Goma et al., 1985) have shown by XRD and TEM that the deposit is highly oriented with a regenerated texture (Fig. 8.7c). It was shown by XRD that they grow with Figure 8.6 Structure evolution during the high temperature transition. (a) Pyrocarbon laminar (few small gas phase-grown particles); (b) Granular pyrocarbon (abundant gas phase-grown particles); (c) IS of high density (abundant dense particles co-deposited with homogeneous pyrocarbon); (d) IS of low density (abundant and dense particles co-deposited with glassy carbon-like pyrocarbon) (a and b: cross-polarized light, bar is 20m, after Tombrel and Rappeneau (1965); (c) and (d): TEM after Kaae, 1985). 0.5 µm 0.25 µm (a) (b) (c) (d) © 2003 Taylor & Francis