正在加载图片...
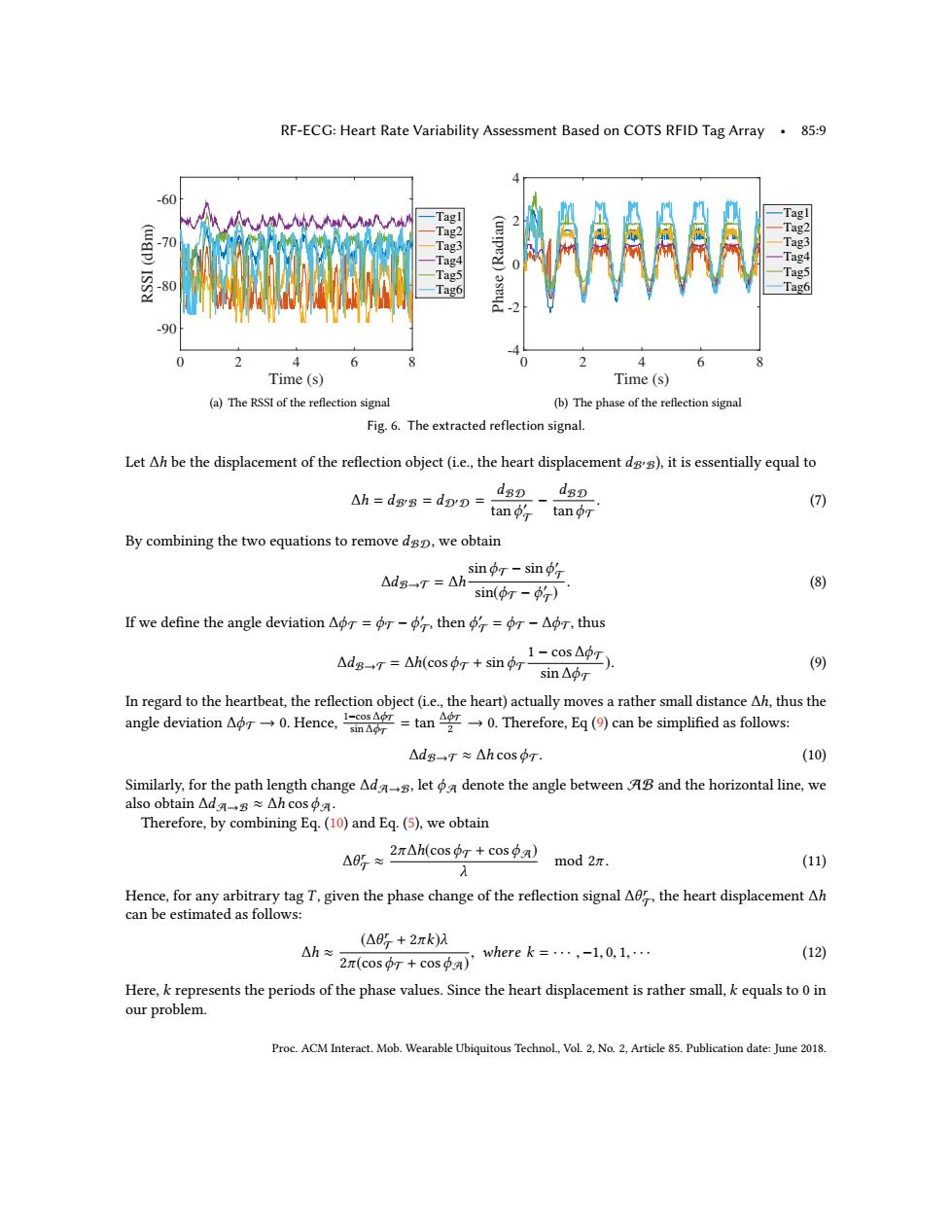
RF-ECG:Heart Rate Variability Assessment Based on COTS RFID Tag Array.85:9 -60 -Tagl Tagl -Tag2 Tag2 Tag3 Tag3 Tag4 0 Tag4 Tag5 Tag5 80 -Tag6 Tag6 -90 2 6 0 2 6 8 Time (s) Time (s) (a)The RSSI of the reflection signal (b)The phase of the reflection signal Fig.6.The extracted reflection signal. Let Ah be the displacement of the reflection object(i.e.,the heart displacement dgs),it is essentially equal to △h=dgg=dpD= dgD」 dsD tan (7) tano By combining the two equations to remove dsD,we obtain sino-sin △dg-T=△ (8) sin(or-) If we define the angle deviation Aor=or-o,then o=or-Aor,thus △dg-T=△h(cos+sin 1-cos△9虹). (9) sin△pr In regard to the heartbeat,the reflection object(ie.,the heart)actually moves a rather small distance Ah,thus the angle deviation.Hence=tan.Therefore,Eq()can be simplified as follows: △dg→T≈△h cos r. (10) Similarly,for the path length change Ads,let denote the angle between AB and the horizontal line,we also obtain△d→s≈△hcosoa, Therefore,by combining Eq.(10)and Eq.(5),we obtain △8g≈2 Ah(cos97+cos》 mod 2. (11) Hence,for any arbitrary tag T.given the phase change of the reflection signal A0,the heart displacement Ah can be estimated as follows: (△8+2πk)M △h≈ 2π(cosr+cosoa) ,where k=·,-1,0,1, (12) Here,k represents the periods of the phase values.Since the heart displacement is rather small,k equals to 0 in our problem. Proc.ACM Interact.Mob.Wearable Ubiquitous Technol,Vol.2,No.2,Article 85.Publication date:June 2018.RF-ECG: Heart Rate Variability Assessment Based on COTS RFID Tag Array • 85:9 Time (s) 0 2 4 6 8 RSSI (dBm) -90 -80 -70 -60 Tag1 Tag2 Tag3 Tag4 Tag5 Tag6 (a) The RSSI of the reflection signal Time (s) 0 2 4 6 8 Phase (Radian) -4 -2 0 2 4 Tag1 Tag2 Tag3 Tag4 Tag5 Tag6 (b) The phase of the reflection signal Fig. 6. The extracted reflection signal. Let ∆h be the displacement of the reflection object (i.e., the heart displacement dB′B), it is essentially equal to ∆h = dB′B = dD′D = dBD tanϕ ′ T − dBD tanϕT . (7) By combining the two equations to remove dBD, we obtain ∆dB→T = ∆h sinϕT − sinϕ ′ T sin(ϕT − ϕ ′ T ) . (8) If we define the angle deviation ∆ϕT = ϕT − ϕ ′ T , then ϕ ′ T = ϕT − ∆ϕT, thus ∆dB→T = ∆h(cosϕT + sinϕT 1 − cos ∆ϕT sin ∆ϕT ). (9) In regard to the heartbeat, the reflection object (i.e., the heart) actually moves a rather small distance ∆h, thus the angle deviation ∆ϕT → 0. Hence, 1−cos ∆ϕT sin ∆ϕT = tan ∆ϕT 2 → 0. Therefore, Eq (9) can be simplified as follows: ∆dB→T ≈ ∆h cosϕT. (10) Similarly, for the path length change ∆dA→B, let ϕA denote the angle between AB and the horizontal line, we also obtain ∆dA→B ≈ ∆h cosϕA . Therefore, by combining Eq. (10) and Eq. (5), we obtain ∆θ r T ≈ 2π∆h(cosϕT + cosϕA) λ mod 2π. (11) Hence, for any arbitrary tag T , given the phase change of the reflection signal ∆θ r T , the heart displacement ∆h can be estimated as follows: ∆h ≈ (∆θ r T + 2πk)λ 2π(cosϕT + cosϕA) , where k = · · · , −1, 0, 1, · · · (12) Here, k represents the periods of the phase values. Since the heart displacement is rather small, k equals to 0 in our problem. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol., Vol. 2, No. 2, Article 85. Publication date: June 2018