正在加载图片...
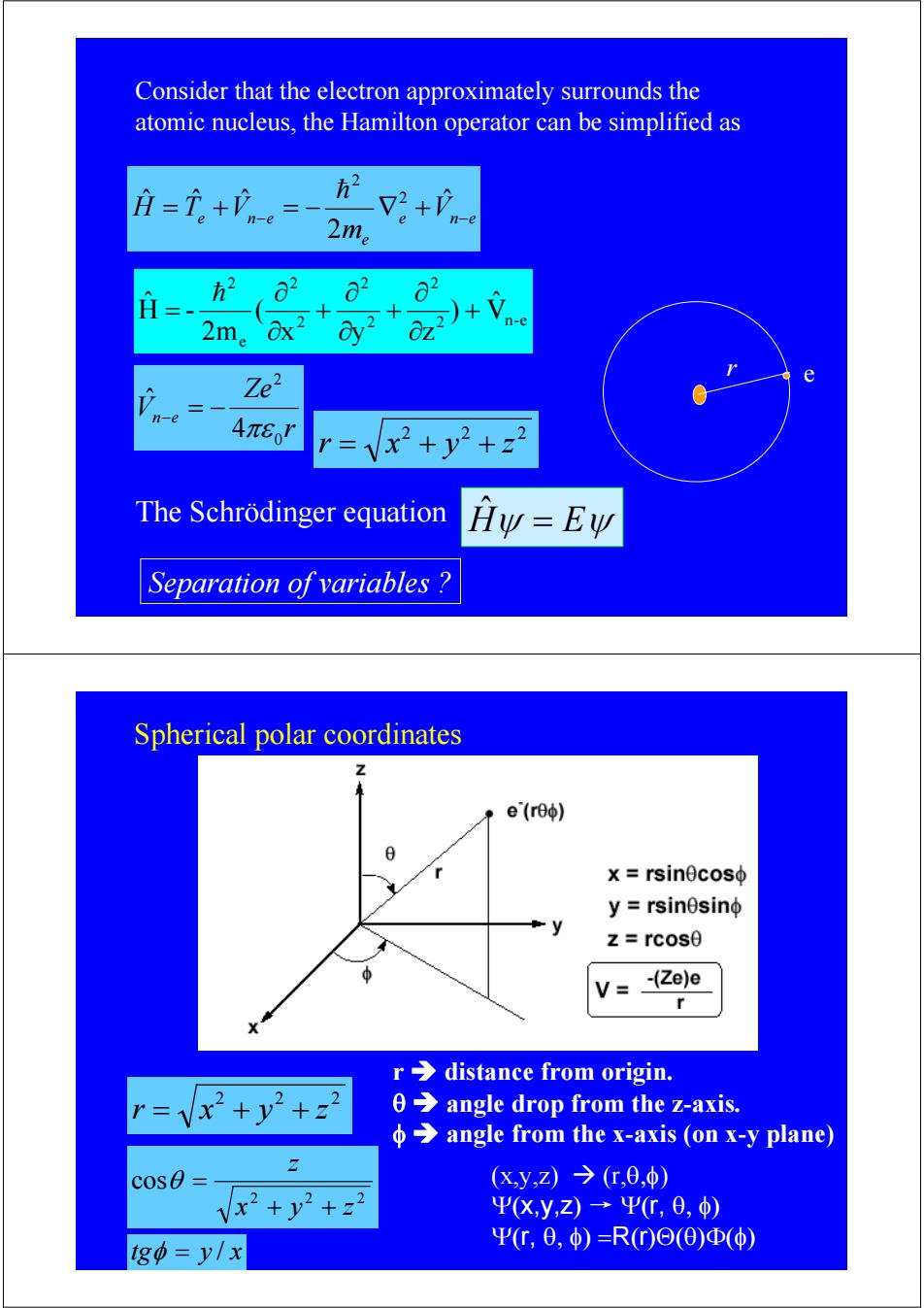
Consider that the electron approximately surrounds the atomic nucleus,the Hamilton operator can be simplified as =i。+n= 2+心 2m。 o2 62 2m。 2)+Vn-e OZ Ze2 e n-e 4πer r=Vx2+y2+z2 The Schrodinger equation Hy=Ew Separation of variables Spherical polar coordinates Z e(re) x rsinecoso y=rsinesinφ z=rcos0 V=_ (Ze)e r r>distance from origin. =Vx+y2+z2 0 angle drop from the z-axis. angle from the x-axis (on x-y plane) cos0= (x,y,Z)→(,0,φ) Vx2+y2+22 ΨX,y,z)→Ψr,6,) g中=y/x Ψr,0,φ)=R(r)Θ(Θ)Φ(φ)e n e e e n e V m H = T +V − = − ∇ + − ˆ 2 ˆ ˆ ˆ 2 2 h r Ze Vn e 0 2 4 ˆ πε − = − Consider that the electron approximately surrounds the atomic nucleus, the Hamilton operator can be simplified as r e 2 2 2 r = x + y + z 2 n-e 2 2 2 2 2 e 2 Vˆ ) x y z ( 2m H - ˆ + ∂ ∂ + ∂ ∂ + ∂ ∂ = h Separation of variables ? The Schrödinger equation Hˆψ = Eψ Spherical polar coordinates 2 2 2 r = x + y + z (x,y,z) Æ (r,θ,φ) Ψ(x,y,z) → Ψ(r, θ, φ) Ψ(r, θ, φ) =R(r)Θ(θ)Φ(φ) r Î distance from origin. θ Î angle drop from the z-axis. φ Î angle from the x-axis (on x-y plane) 2 2 2 cos x y z z + + θ = tgφ = y / x