正在加载图片...
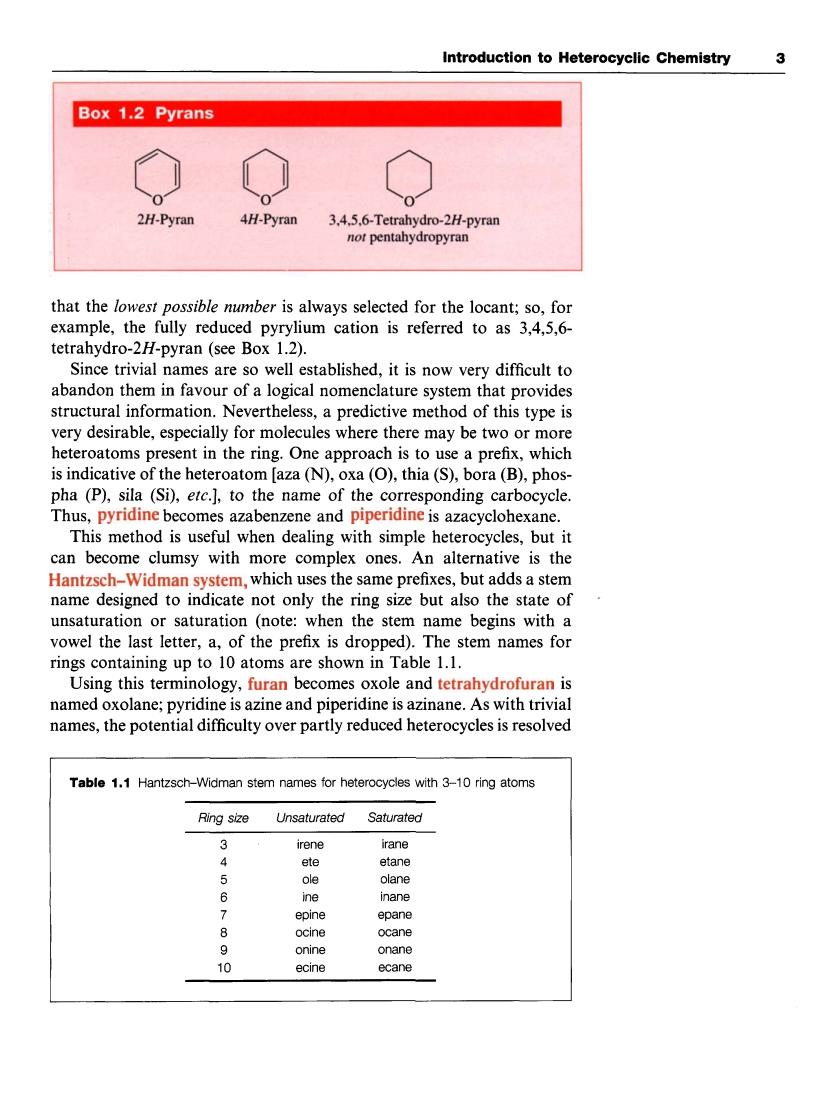
Introduction to Heterocyclic Chemistry 3 Box 1.2 Pyrans 2H-Pyran 4H-Pyran 3.4.5.6-Tetrahydro-2H/-pyran not pentahydropyran that the lowest possible mmber is always selected for the locant: example, fully reduced pyrylium cation is referred to as3.4.5.6- tetrahydro-2H-pyran (see Box 1.2). Since trivial names are so well established,it is now very difficult to abandon them in favour of a logical nomencature system that provides structural information.Nevertheless,a predictive method of this type is very desirable,especially for molecules where there may be two or more heteroatoms present in the ring.One approach is to use a prefix,which is indicative of the heteroatom [aza(N).oxa(O),thia(S),bora(B),phos- pha (P),sil (Si),ete.],to the name of the corresponding carbocycle Thus,pyridine becomes azabenzene and piperidine is azacyclohexane. This method is useful when dealing with simple heterocycles,but it can become clumsy with more complex ones.An alternative is the Hantzsch-Widman system,which uses the same prefixes,but adds a stem name designed to indicate not only the ring size but also the state of unsaturation or saturation (note:when the stem name begins with a vowel the last letter,a,of the prefix is dropped).The stem names for rings containing are shown in Table 1.1. Using this terminology,furan becomes oxole and tetrahydrofuran is named oxolane;pyridine is azine and piperidine is azinane.As with trivial names,the potential difficulty over partly reduced heterocycles is resolved Table1.1 Hantzsch-Widman stem names for heterocycles with 3-10 ring atoms Ring size Unsaturated Saturated 3 irene irane ete etane olane 6 ine epine 。 ecaneIntroduction to Heterocyclic Chemistry 3 that the lowest possible number is always selected for the locant; so, for example, the fully reduced pyrylium cation is referred to as 3,4,5,6- tetrahydro-2H-pyran (see Box 1.2). Since trivial names are so well established, it is now very difficult to abandon them in favour of a logical nomenclature system that provides structural information. Nevertheless, a predictive method of this type is very desirable, especially for molecules where there may be two or more heteroatoms present in the ring. One approach is to use a prefix, which is indicative of the heteroatom [aza (N), oxa (0), thia (S), bora (B), phospha (P), sila (Si), etc.], to the name of the corresponding carbocycle. Thus, pyridine becomes azabenzene and piperidine is azacyclohexane. This method is useful when dealing with simple heterocycles, but it can become clumsy with more complex ones. An alternative is the Hantzsch-Widman system, which uses the same prefixes, but adds a stem name designed to indicate not only the ring size but also the state of unsaturation or saturation (note: when the stem name begins with a vowel the last letter, a, of the prefix is dropped). The stem names for rings containing up to 10 atoms are shown in Table 1.1. Using this terminology, furan becomes oxole and tetrahydrofuran is named oxolane; pyridine is azine and piperidine is azinane. As with trivial names, the potential difficulty over partly reduced heterocycles is resolved - Table 1.1 Hantzsch-Widman stem names for heterocycles with 3-10 ring atoms Ring size Unsaturated Saturated 3 irene irane 4 ete etane 5 ole olane 6 ine inane 7 epine epane 8 ocine ocane 9 onine onane 10 ecine ecane