
上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 5.Analysis 强 SHANG 1日日G ERSITY
5. Analysis

上游充通大¥ Outline SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Analysis:Bridging What to How 国 Models for Analysis Activities during object modeling Object Identifications Identify Associations ·Identify Aggregates ·Identify Attributes Reviewing the Analysis Model Managing Analysis Case Study Software Engineering
Software Engineering Outline Analysis: Bridging What to How Models for Analysis Activities during object modeling • Object Identifications • Identify Associations • Identify Aggregates • Identify Attributes • Reviewing the Analysis Model Managing Analysis Case Study
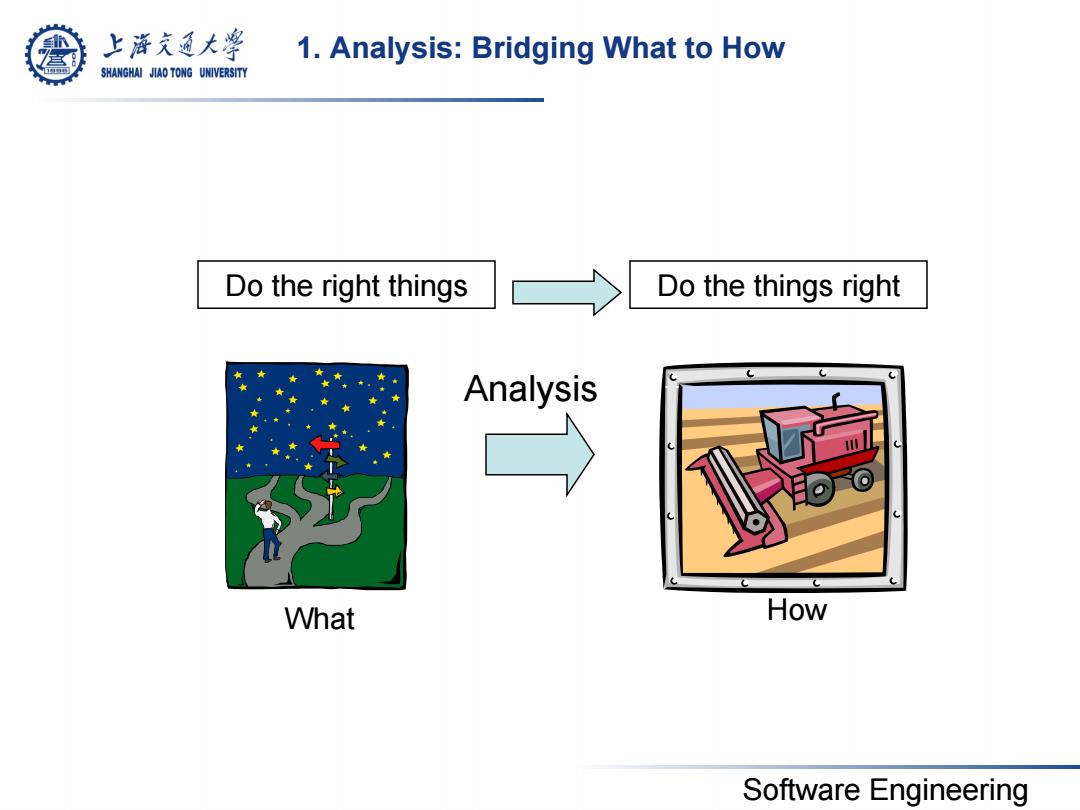
上降充通大学 1.Analysis:Bridging What to How SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Do the right things Do the things right Analysis What How Software Engineering
Software Engineering 1. Analysis: Bridging What to How Do the right things Do the things right What How Analysis

上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 2.Models for Analysis Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2. Models for Analysis
上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 2.1 Reality and Model Reality R: Real Things,People,Processes happening during some time,Relationship between things Model M:Abstractions from (really existing or only thought of things,people processes and relationships between these abstractions. Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.1 Reality and Model Reality R: Real Things, People, Processes happening during some time, Relationship between things Model M: Abstractions from (really existing or only thought of ) things, people , processes and relationships between these abstractions

上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 2.2 Why models? ④Ve use models To abstract away from details in the reality,so we can draw complicated conclusions in the reality with simple steps in the model To get insights into the past or presence To make predictions about the future Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.2 Why models? We use models • To abstract away from details in the reality, so we can draw complicated conclusions in the reality with simple steps in the model • To get insights into the past or presence • To make predictions about the future
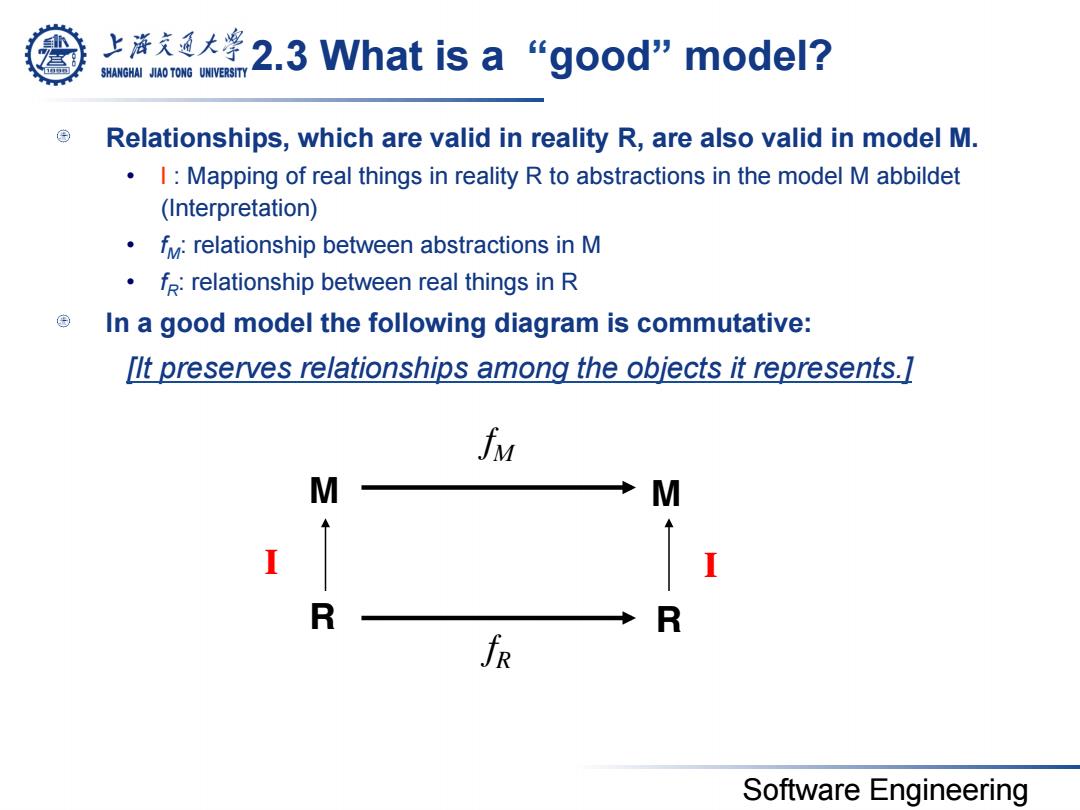
上大学2.3 What is a“good'model? SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Relationships,which are valid in reality R,are also valid in model M. I:Mapping of real things in reality R to abstractions in the model M abbildet (Interpretation) f:relationship between abstractions in M f:relationship between real things in R In a good model the following diagram is commutative: [lt preserves relationships among the objects it represents.] fu M M I R R fR Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.3 What is a “good” model? Relationships, which are valid in reality R, are also valid in model M. • I : Mapping of real things in reality R to abstractions in the model M abbildet (Interpretation) • fM: relationship between abstractions in M • fR: relationship between real things in R In a good model the following diagram is commutative: [It preserves relationships among the objects it represents.] fM fR M M R R I I
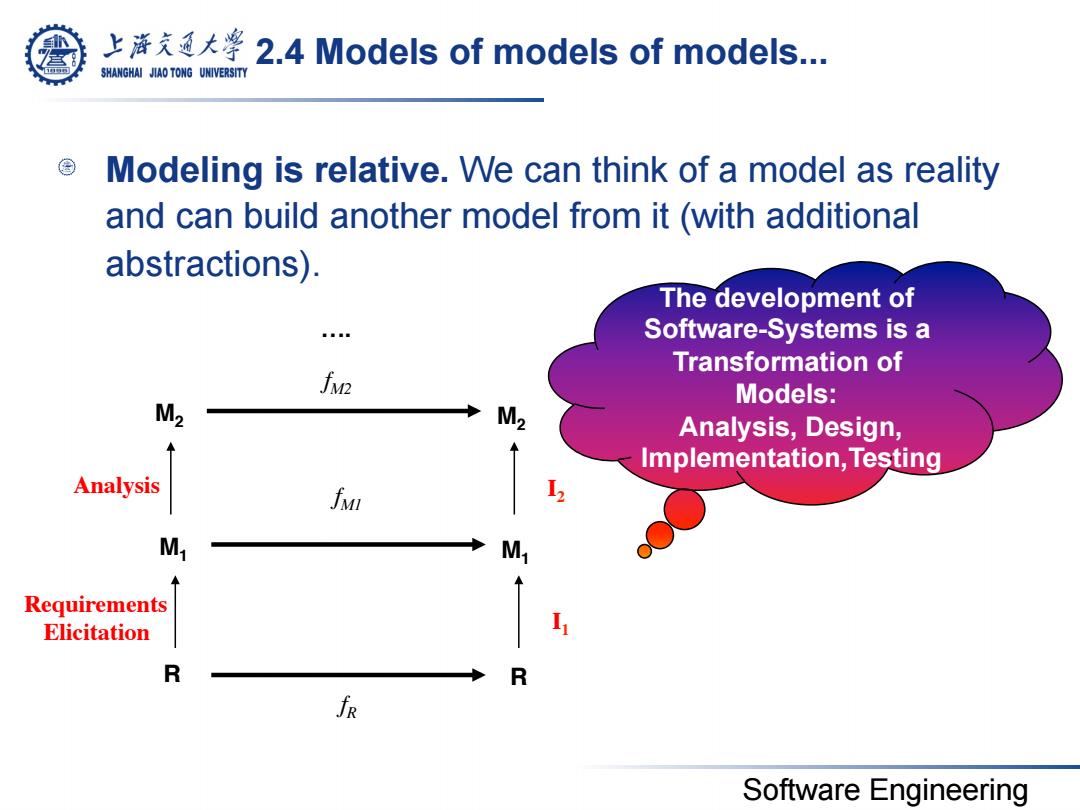
上充大¥2.4 Models of models of models. SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Modeling is relative.We can think of a model as reality and can build another model from it(with additional abstractions). The development of Software-Systems is a Transformation of fv2 Models: M2 M2 Analysis,Design, Implementation,Testing Analysis fv M M, Requirements Elicitation R R Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.4 Models of models of models... Modeling is relative. We can think of a model as reality and can build another model from it (with additional abstractions). fM1 fR M1 M1 R R Requirements Elicitation I1 M2 M2 Analysis I2 fM2 …. The development of Software-Systems is a Transformation of Models: Analysis, Design, Implementation,Testing
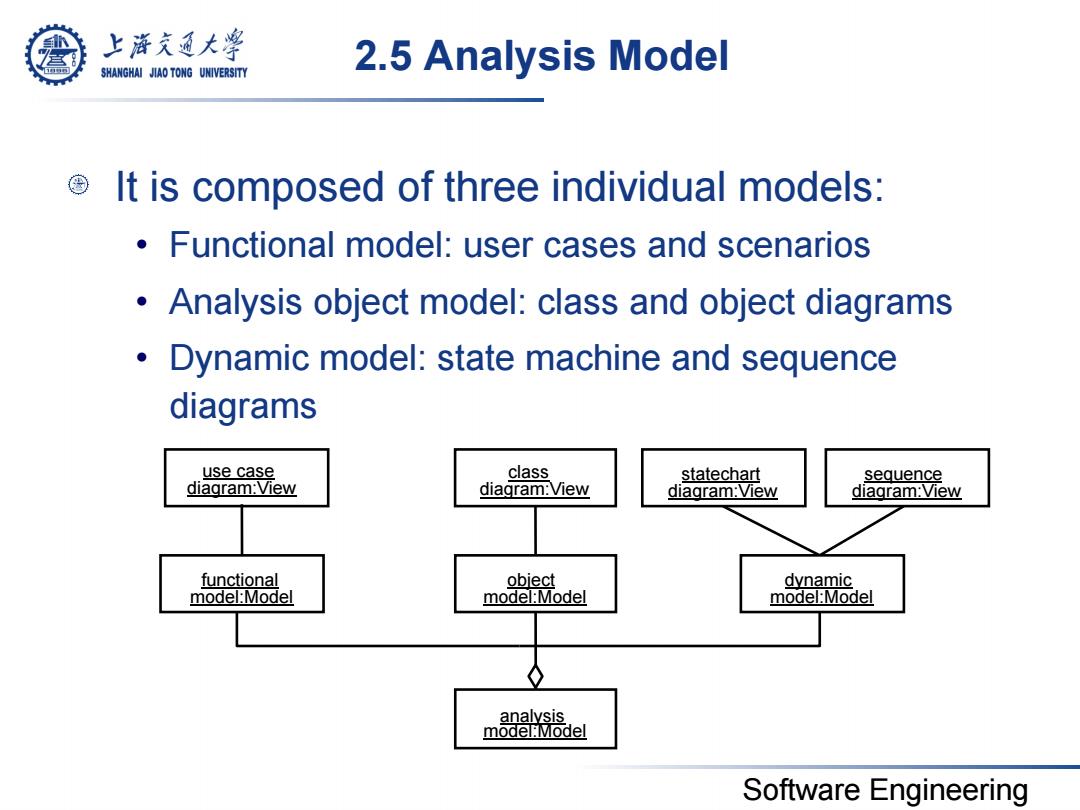
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 2.5 Analysis Model It is composed of three individual models: Functional model:user cases and scenarios Analysis object model:class and object diagrams Dynamic model:state machine and sequence diagrams use case class statechart sequence diagram:View diagram:View diagram:View diagram:View functional object dynamic model:Model model:Model model:Model analysis model:Model Software Engineering
Software Engineering 2.5 Analysis Model It is composed of three individual models: • Functional model: user cases and scenarios • Analysis object model: class and object diagrams • Dynamic model: state machine and sequence diagrams analysis model:Model dynamic model:Model object model:Model functional model:Model use case diagram:View class diagram:View statechart diagram:View sequence diagram:View
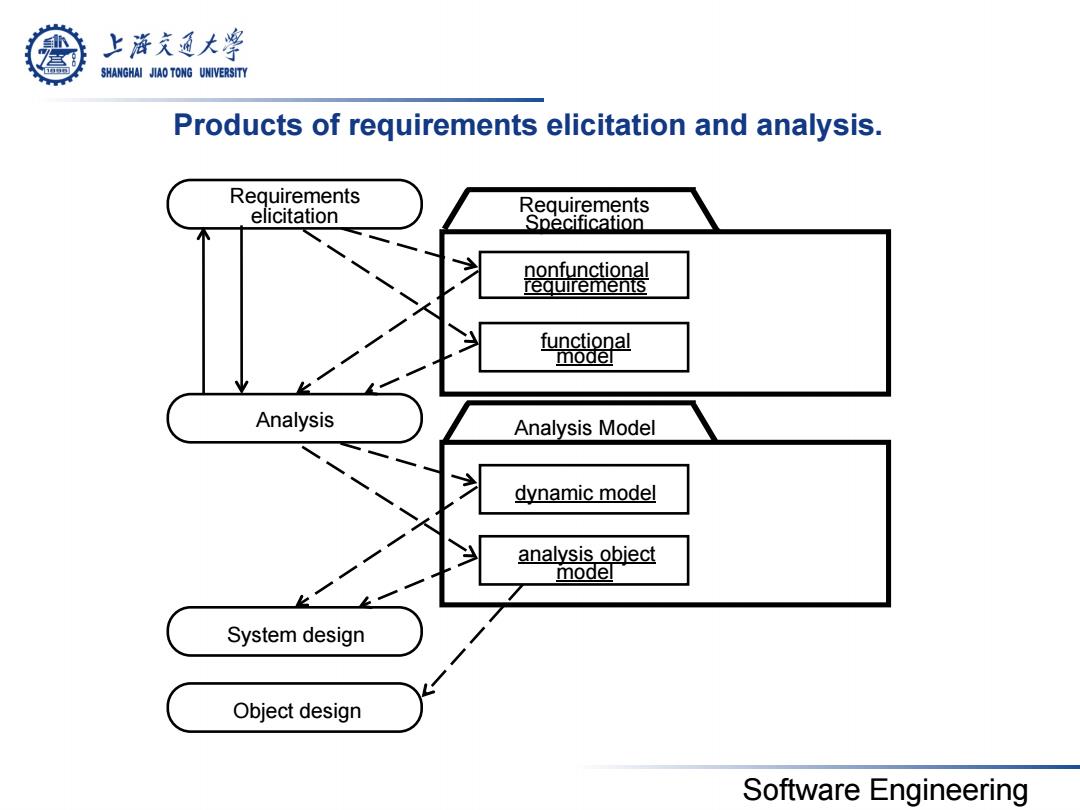
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Products of requirements elicitation and analysis. Requirements elicitation Requirements Specification nonfunctional requirements functional model Analysis Analysis Model dynamic model analysis object model System design Object design Software Engineering
Software Engineering Products of requirements elicitation and analysis. Analysis functional model nonfunctional requirements analysis object model Requirements elicitation dynamic model Requirements Analysis Model Specification System design Object design