
Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling OOK(On-Off Keying) Or ASK(Amplitude Shift Keying) BPSK(Binary Phase Shift Keying) FSK(Frequency Shift Keying)
Binary Modulated Bandpass Signaling OOK(On-Off Keying) Or ASK(Amplitude Shift Keying) BPSK(Binary Phase Shift Keying) FSK(Frequency Shift Keying)
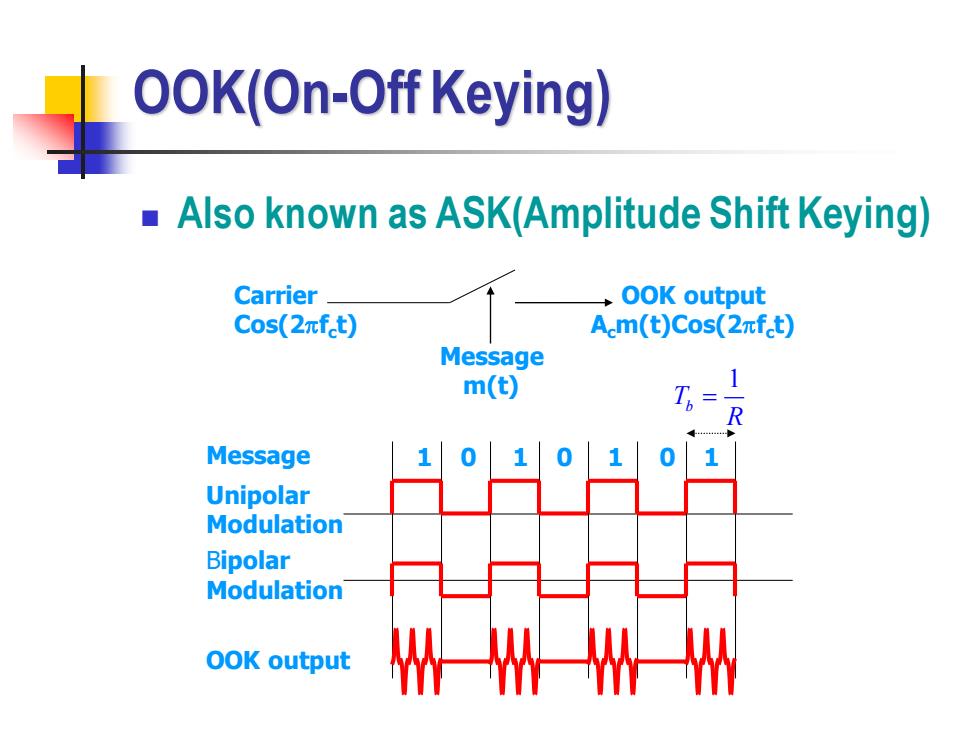
OOK(On-Off Keying) Also known as ASK(Amplitude Shift Keying) Carrier OOK output Cos(2πft) A.m(t)Cos(2πft) Message m(t) Message 1 Unipolar Modulation Bipolar Modulation OOK output W MWW
OOK(On-Off Keying) ◼ Also known as ASK(Amplitude Shift Keying) Carrier Cos(2fc t) Message m(t) OOK output Acm(t)Cos(2fc t) Message 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Unipolar Modulation Bipolar Modulation OOK output 1 Tb R =

OOK(On-Off Keying) OOK signal in time domain ■s(t)=Am(t)cos(2πf) PSD(Power Spectral Density) Conventional AM type ■ A 8 A sin(π(f-f)/R 8R π(f-f)/R fc 2R 2/Th
OOK(On-Off Keying) ◼ OOK signal in time domain ◼ ◼ PSD(Power Spectral Density) ◼ Conventional AM type ( ) ( )cos(2 ) c c s t A m t f t = fc 2R = 2/Tb 2 8 Ac 2 2 sin( ( ) / ) ( ) 8 ( ) / c c c A f f R R f f R − −
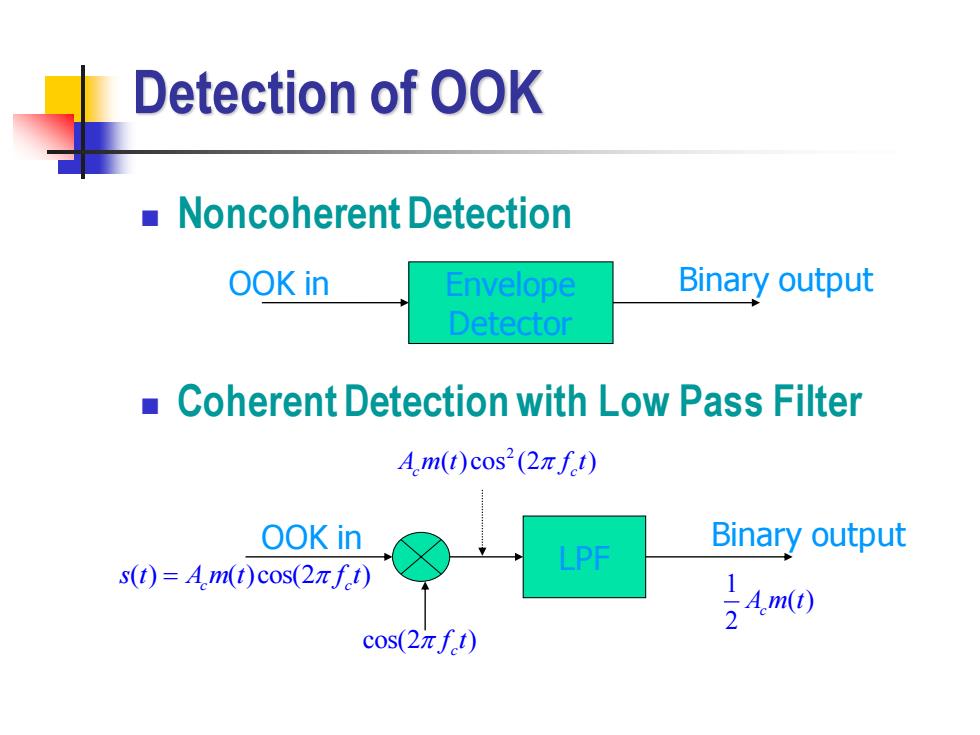
Detection of OOK Noncoherent Detection OOK in Envelope Binary output Detector Coherent Detection with Low Pass Filter Am(t)cos2(2πft) OOK in Binary output LPF s(t)=Am(t)cos(2πft) 3n0 cos(2πft)
Detection of OOK ◼ Noncoherent Detection ◼ Coherent Detection with Low Pass Filter Envelope Detector OOK in Binary output LPF OOK in Binary output cos(2 ) c f t ( ) ( )cos(2 ) c c s t A m t f t = 2 ( ) cos (2 ) A m t f t c c 1 ( ) 2 A m t c

Detection of OOK Coherent Detection with Correlator Optimum Receiver OOK in Sample Am(t)cos(2πft) & Binary Hold Out +n(t) cos(2πft) Clock From PLL From Bit sync logic Correlator output Comparator input Binary output
Detection of OOK ◼ Coherent Detection with Correlator ◼ Optimum Receiver Sample & Hold OOK in cos(2 ) c f t ( ) cos(2 ) ( ) A m t f t c c n t + From PLL 0 ( ) t d Clock From Bit sync logic VT Binary Out VT Correlator output Binary output Comparator input

Detection of OOK ■ Choosing the detector Optimum coherent detector Best noise performance More costly Noncoherent detector ▣More error rate ■Less costly ■Trade-off between Cost/Noise Performance
Detection of OOK ◼ Choosing the detector ◼ Optimum coherent detector ◼ Best noise performance ◼ More costly ◼ Noncoherent detector ◼ More error rate ◼ Less costly ◼ Trade-off between ◼ Cost / Noise Performance
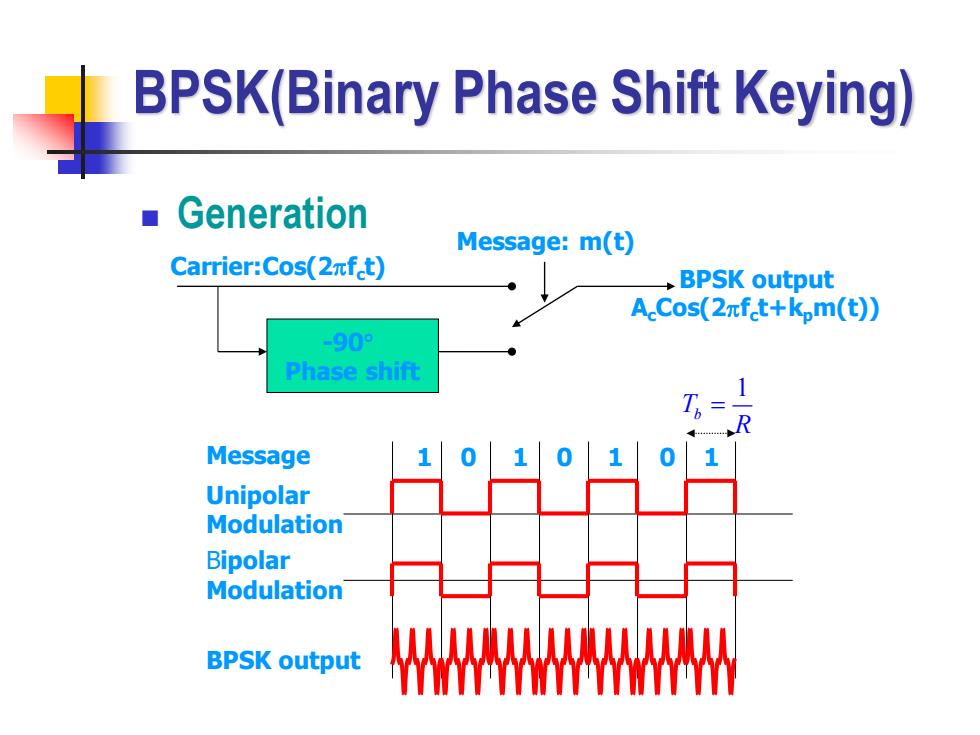
BPSK(Binary Phase Shift Keying) Generation Message:m(t) Carrier:Cos(2πft) BPSK output A.Cos(2πft+k,m(t)) -909 Phase shift Message 1 10 Unipolar Modulation Bipolar Modulation BPSK output
BPSK(Binary Phase Shift Keying) ◼ Generation Carrier:Cos(2fc t) Message: m(t) BPSK output AcCos(2fc t+kpm(t)) -90 Phase shift Message 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 Unipolar Modulation Bipolar Modulation BPSK output 1 Tb R =

BPSK Signals in time domain Since m(t)=±1 s(t)=A.cos(2zft+km(t)) =A cos(k,m(t))cos(2ft)-A sin(k m(t))sin(2zft) =A.cos(kn)cos(2πf)-A.sin(k,)m)sin(2πf) Pilot term ▣fk.is small Data term Then little power in data term,most power in pilot term To maximized performance(low Pe) =Optimum case:k,=π/2 ■s(t)=-Am(t)sin(2πft)
BPSK ◼ Signals in time domain ◼ Since m(t) = 1 ◼ If kp is small ◼ Then little power in data term, most power in pilot term ◼ To maximized performance (low Pe) ◼ Optimum case : kp = /2 ◼ ( ) cos(2 ( )) cos( ( ))cos(2 ) sin( ( ))sin(2 ) cos( )cos(2 ) sin( ) ( )sin(2 ) c c p c p c c p c c p c c p c s t A f t k m t A k m t f t A k m t f t A k f t A k m t f t = + = − = − Pilot term Data term ( ) ( )sin(2 ) c c s t A m t f t = −

BPSK PSD of optimum BPSK Equivalent to DSB Ifkp≠元/2 Pilot exists sin(π(f-f)/R 4R π(f-f)/R fe 2R=2T
BPSK ◼ PSD of optimum BPSK ◼ Equivalent to DSB fc 2R = 2/Tb 2 2 sin( ( ) / ) ( ) 4 ( ) / c c c A f f R R f f R − − If kp /2 Pilot exists

Detection of BPSK ■ Coherent Detector with Low Pass Filter BPSK in Binary output LPF s(t)=-A.m(t)sin(2uft) 0 cos(2πft) From PLL if pilot exist Costas Loop or Squaring Loop if no pilot exist To remove Half cycle(180 phase)ambiguity DPSK(Differential PSK)is used
Detection of BPSK ◼ Coherent Detector with Low Pass Filter ◼ To remove Half cycle (180 phase) ambiguity ◼ DPSK(Differential PSK) is used LPF BPSK in Binary output cos(2 ) c f t ( ) ( )sin(2 ) c c s t A m t f t = − 1 ( ) 2 A m t c From PLL if pilot exist Costas Loop or Squaring Loop if no pilot exist