
Hypertensive states of pregnancy Xiaojing Dong E-mail:xffdoctor@163.com Mobile:13648437247
Hypertensive states of pregnancy Xiaojing Dong E-mail: xffdoctor@163.com Mobile: 13648437247

Definition One of the common complications met with in pregnancy,it is a sign of an underlying pathology which may be pre-existing or appears for the first time during pregnancy. The etiology is unknown BP>140/90 mmHg,at least 2 separate occasions,6 hours or more
Definition • One of the common complications met with in pregnancy, it is a sign of an underlying pathology which may be pre-existing or appears for the first time during pregnancy. • The etiology is unknown • BP>140/90 mmHg, at least 2 separate occasions, 6 hours or more

Classification Pregnancy induced hypertension(PIH) Preeclampsia(mild and severe) Eclampsia 。 Chronic hypertension preceding pregnancy Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia Transient hypertension
Classification • Pregnancy induced hypertension(PIH) – Preeclampsia (mild and severe) – Eclampsia • Chronic hypertension preceding pregnancy • Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia • Transient hypertension

Pregnancy induced hypertension(PIH) Definition PIH is a condition occuring after the 20th week of pregnancy,usually in the third tremester,in which at least two of the three signs (hypertension,proteinuria and edema) are present. Clinical type:preeclampsia and eclampsia
Pregnancy induced hypertension(PIH) • Definition – PIH is a condition occuring after the 20th week of pregnancy, usually in the third tremester, in which at least two of the three signs (hypertension, proteinuria and edema) are present. • Clinical type: preeclampsia and eclampsia

Preeclampsia ·Edema 。 Hypertension ·Proteinuria occurring primarily in nulliparas after the 20th gestational week,most frequently near term 。·Incidence:6%of the general population ·In our country9.4%
Preeclampsia • Edema • Hypertension • Proteinuria • occurring primarily in nulliparas after the 20th gestational week, most frequently near term • Incidence: 6% of the general population • In our country 9.4%

1.Pathogenesis Endothelial cell injury Imbalance between prostacyclin and thromboxane Rejection phenomenon:allograft Compromised placental perfusion Altered vascular reactivity Decreased glomerular filtration rate with retention of salt and water
1. Pathogenesis • Endothelial cell injury • Imbalance between prostacyclin and thromboxane • Rejection phenomenon: allograft • Compromised placental perfusion • Altered vascular reactivity • Decreased glomerular filtration rate with retention of salt and water

Decreased intravascular volume Increased central nervous system irritability Disseminated intravascular coagulation Uterine muscle stretch Dietary factors:calcium deficiency Genetic factors
• Decreased intravascular volume • Increased central nervous system irritability • Disseminated intravascular coagulation • Uterine muscle stretch • Dietary factors: calcium deficiency • Genetic factors

pathogenesis Immunologic disturbance 1 abnormal placental implantation decreased placental perfusion ↓ Production of substances Injure or activate endothelial cell
pathogenesis Immunologic disturbance abnormal placental implantation decreased placental perfusion Production of substances Injure or activate endothelial cell
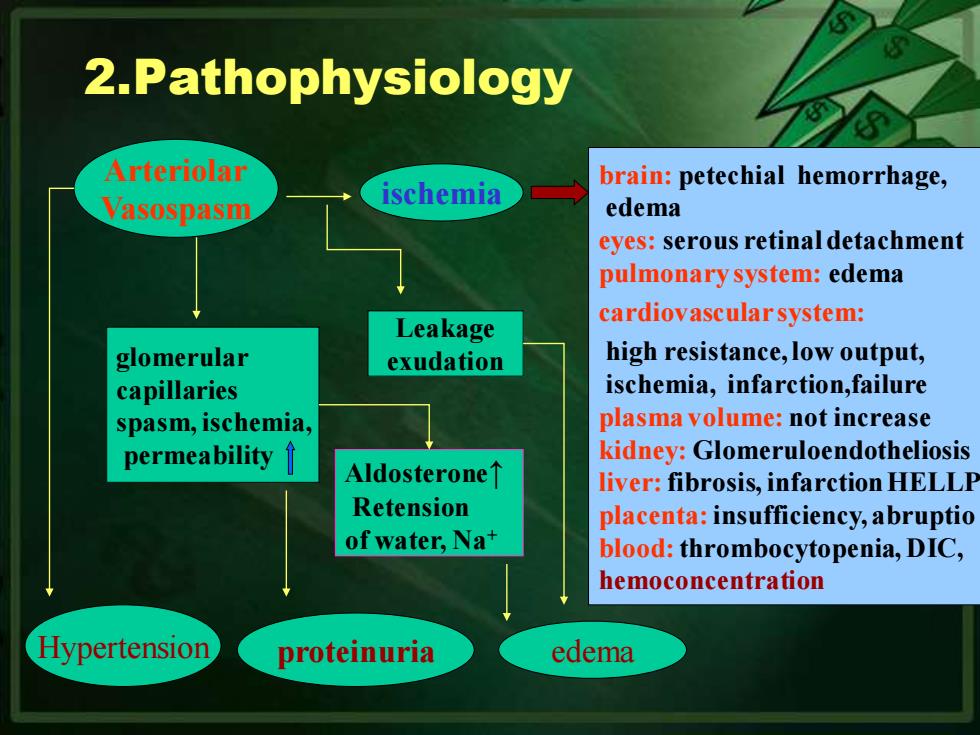
2.Pathophysiology Arteriolar brain:petechial hemorrhage, Vasospasm ischemia edema eyes:serous retinal detachment pulmonary system:edema Leakage cardiovascular system: glomerular exudation high resistance,low output, capillaries ischemia,infarction,failure spasm,ischemia, plasma volume:not increase permeability kidney:Glomeruloendotheliosis AldosteroneT liver:fibrosis,infarction HELLP Retension placenta:insufficiency,abruptio of water,Na+ blood:thrombocytopenia,DIC, hemoconcentration Hypertension proteinuria edema
2.Pathophysiology glomerular capillaries spasm, ischemia, permeability ischemia brain: petechial hemorrhage, edema eyes: serous retinal detachment pulmonary system: edema cardiovascular system: high resistance, low output, ischemia, infarction,failure plasma volume: not increase kidney: Glomeruloendotheliosis liver:fibrosis, infarction HELLP placenta:insufficiency, abruptio blood:thrombocytopenia, DIC, hemoconcentration Aldosterone↑ Retension of water, Na+ Hypertension proteinuria edema Leakage exudation Arteriolar Vasospasm

3.Predisposing factors: Nulliparity Black race Maternal age 35 Low socioeconomic status Multiple gestation Hydatidiform mole Polyhydramnios Nonimmune fetal hydrops Diabetes Chronic hypertension Underlying renal disease Family history
3. Predisposing factors: – Nulliparity – Black race – Maternal age 35 – Low socioeconomic status – Multiple gestation – Hydatidiform mole – Polyhydramnios – Nonimmune fetal hydrops – Diabetes – Chronic hypertension – Underlying renal disease – Family history