正在加载图片...
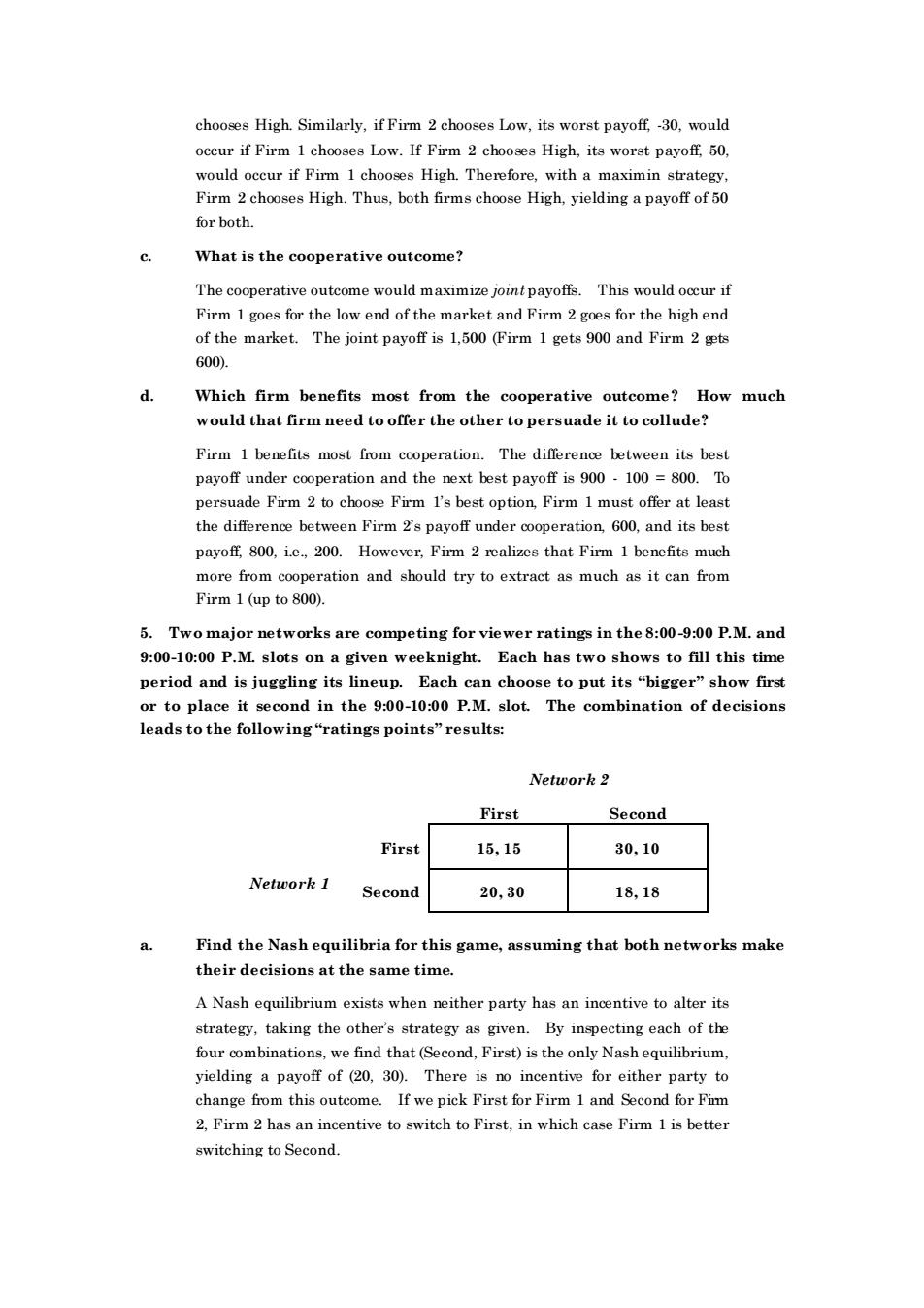
chooses High.Similarly,if Firm 2 chooses Low,its worst payoff,-30,would occur if Firm 1 chooses Low.If Firm 2 chooses High,its worst payoff50. would oceur if Firm I chooses High.Therefore, with a maximin strategy Firm 2 chooses High.Thus,both firms choose High,vielding a payoff of 50 for both. What is the cooperative outcome? The cooperative outcome would maximize joint payoffs.This would occur if Firm 1goes for the low end of the market and Firm 2goes for the highend The payoff is 1.500 (Firm 1gets 90 and Firm 2 gts G00 Which firm benefits most from the cooperative outcome? How much would that firm need to offer the other to persuade it to collude? Firm 1 benefits most from cooperation.The difference between its best payoff under cooperation and the next best payoff is 900.100 =800.To persuade Firm 2 to cboose firm l's best option.Firm 1 must offer at least the differen between Firm2s payof under its best payoff 800.However,Firm 2 realizes that Firm 1 benefits much more from cooperation and should try to extract as much as it can from Firm 1 (up to 800). 5.Two major networks are competing for viewer ratings in the8:00-9:00 P.M.and 9:00-10:00 P.M.slots on a given weeknight.Each has two shows to fill this time period and is juggling its lin Each can choose to put its"bigger"show first or to plac it second in the:0-10:00P.M. slot. The combination of decisions leads to the following"ratings points"results Netuork 2 First Second First 15,15 30,10 Second 20,30 18,18 Find the Nash equilibria for this game,assuming that both networks make their decisions at the same time A Nash equilibrium exists when neither party has an incentive to alter its strategy,taking the other's strategy as given.By inspecting each of the four combinations,we find that(Second,First)is the only Nash equilibrium. yielding a payoff of (20,30).There is no incentive for either party to change from this outcome.If we pick First for Firm 1 and Second for Fim 2.Firm 2 has an incentive to switch to First.in which case Firm 1is better switching to Secondchooses High. Similarly, if Firm 2 chooses Low, its worst payoff, -30, would occur if Firm 1 chooses Low. If Firm 2 chooses High, its worst payoff, 50, would occur if Firm 1 chooses High. Therefore, with a maximin strategy, Firm 2 chooses High. Thus, both firms choose High, yielding a payoff of 50 for both. c. What is the cooperative outcome? The cooperative outcome would maximize joint payoffs. This would occur if Firm 1 goes for the low end of the market and Firm 2 goes for the high end of the market. The joint payoff is 1,500 (Firm 1 gets 900 and Firm 2 gets 600). d. Which firm benefits most from the cooperative outcome? How much would that firm need to offer the other to persuade it to collude? Firm 1 benefits most from cooperation. The difference between its best payoff under cooperation and the next best payoff is 900 - 100 = 800. To persuade Firm 2 to choose Firm 1’s best option, Firm 1 must offer at least the difference between Firm 2’s payoff under cooperation, 600, and its best payoff, 800, i.e., 200. However, Firm 2 realizes that Firm 1 benefits much more from cooperation and should try to extract as much as it can from Firm 1 (up to 800). 5. Two major networks are competing for viewer ratings in the 8:00-9:00 P.M. and 9:00-10:00 P.M. slots on a given weeknight. Each has two shows to fill this time period and is juggling its lineup. Each can choose to put its “bigger” show first or to place it second in the 9:00-10:00 P.M. slot. The combination of decisions leads to the following “ratings points” results: Network 2 First Second First 15, 15 30, 10 Network 1 Second 20, 30 18, 18 a. Find the Nash equilibria for this game, assuming that both networks make their decisions at the same time. A Nash equilibrium exists when neither party has an incentive to alter its strategy, taking the other’s strategy as given. By inspecting each of the four combinations, we find that (Second, First) is the only Nash equilibrium, yielding a payoff of (20, 30). There is no incentive for either party to change from this outcome. If we pick First for Firm 1 and Second for Firm 2, Firm 2 has an incentive to switch to First, in which case Firm 1 is better switching to Second