正在加载图片...
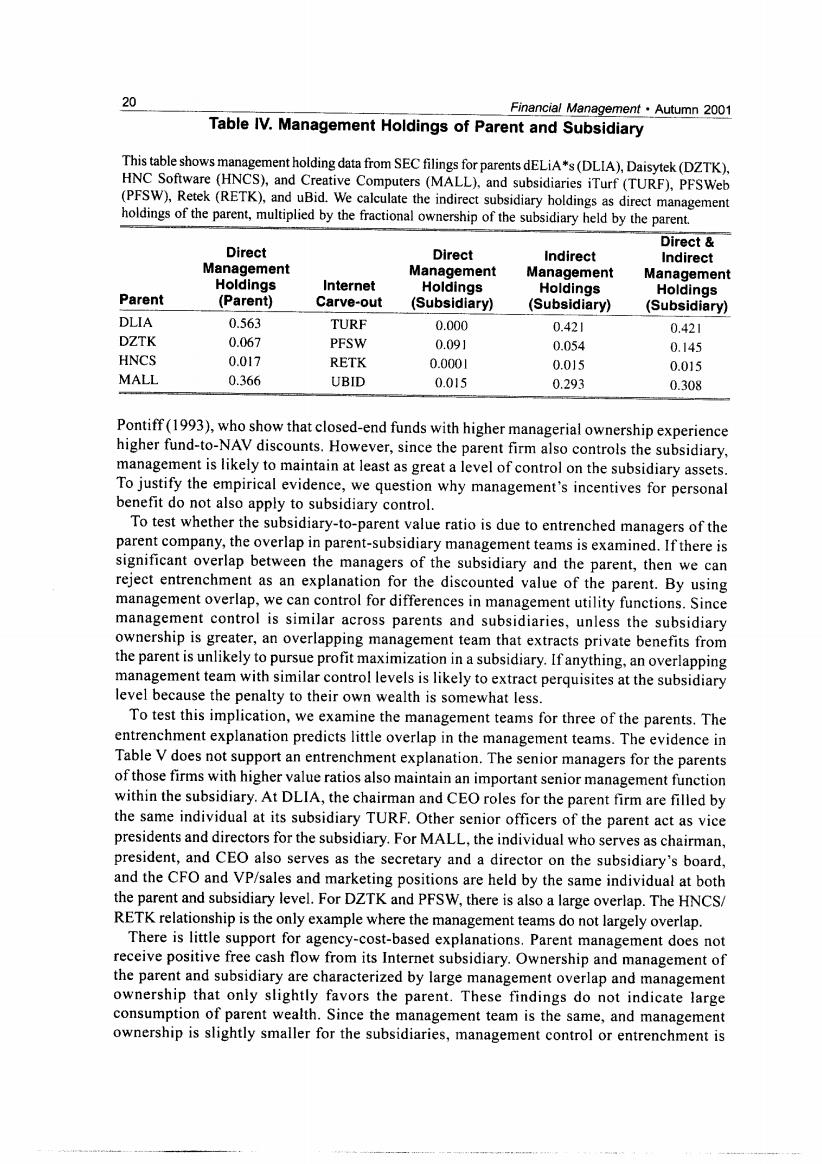
20 Financial Management.Autumn 2001 Table IV.Management Holdings of Parent and Subsidiary This table shows management holding data from SEC filings for parents dELiA*s(DLIA),Daisytek(DZTK), HNC Software (HNCS),and Creative Computers(MALL),and subsidiaries iTurf(TURF),PFSWeb (PFSW),Retek(RETK),and uBid.We calculate the indirect subsidiary holdings as direct management holdings of the parent,multiplied by the fractional ownership of the subsidiary held by the parent. Direct Direct Direct Indirect Indirect Management Management Management Holdings Management Internet Holdings Parent Holdings Holdings (Parent) Carve-out (Subsidiary) (Subsidiary) (Subsidiary) DLIA 0.563 TURF 0.000 0.421 0.421 DZTK 0.067 PFSW 0.091 0.054 0.145 HNCS 0.017 RETK 0.0001 0.015 0.015 MALL 0.366 UBID 0.015 0.293 0.308 Pontiff(1993),who show that closed-end funds with higher managerial ownership experience higher fund-to-NAV discounts.However,since the parent firm also controls the subsidiary. management is likely to maintain at least as great a level of control on the subsidiary assets. To justify the empirical evidence,we question why management's incentives for personal benefit do not also apply to subsidiary control. To test whether the subsidiary-to-parent value ratio is due to entrenched managers of the parent company,the overlap in parent-subsidiary management teams is examined.If there is significant overlap between the managers of the subsidiary and the parent,then we can reject entrenchment as an explanation for the discounted value of the parent.By using management overlap,we can control for differences in management utility functions.Since management control is similar across parents and subsidiaries,unless the subsidiary ownership is greater,an overlapping management team that extracts private benefits from the parent is unlikely to pursue profit maximization in a subsidiary.If anything,an overlapping management team with similar control levels is likely to extract perquisites at the subsidiary level because the penalty to their own wealth is somewhat less. To test this implication,we examine the management teams for three of the parents.The entrenchment explanation predicts little overlap in the management teams.The evidence in Table V does not support an entrenchment explanation.The senior managers for the parents of those firms with higher value ratios also maintain an important senior management function within the subsidiary.At DLIA,the chairman and CEO roles for the parent firm are filled by the same individual at its subsidiary TURF.Other senior officers of the parent act as vice presidents and directors for the subsidiary.For MALL,the individual who serves as chairman, president,and CEO also serves as the secretary and a director on the subsidiary's board, and the CFO and VP/sales and marketing positions are held by the same individual at both the parent and subsidiary level.For DZTK and PFSW,there is also a large overlap.The HNCS/ RETK relationship is the only example where the management teams do not largely overlap. There is little support for agency-cost-based explanations.Parent management does not receive positive free cash flow from its Internet subsidiary.Ownership and management of the parent and subsidiary are characterized by large management overlap and management ownership that only slightly favors the parent.These findings do not indicate large consumption of parent wealth.Since the management team is the same,and management ownership is slightly smaller for the subsidiaries,management control or entrenchment is