正在加载图片...
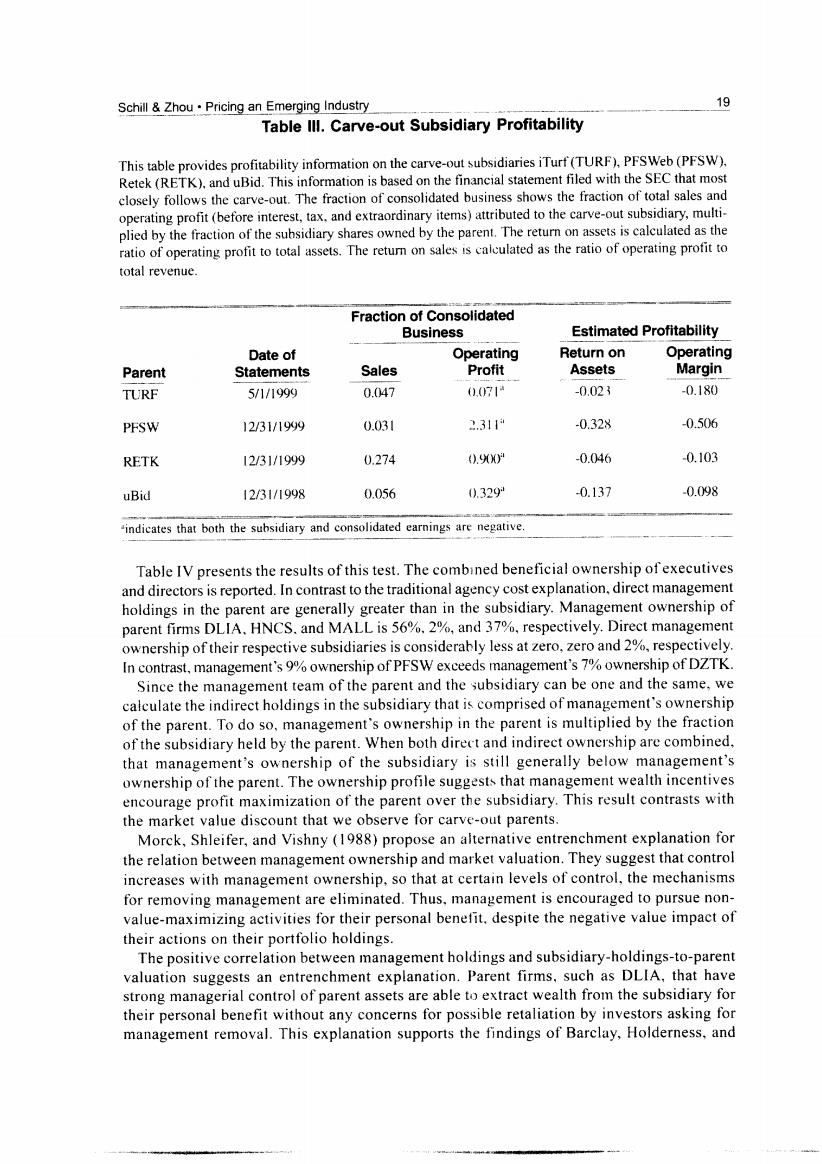
Schill Zhou.Pricing an Emerging Industry 19 Table Ill.Carve-out Subsidiary Profitability This table provides profitability information on the carve-out subsidiaries iTurf(TURF),PFSWeb(PFSW), Retek(RETK).and uBid.This information is based on the financial statement filed with the SEC that most closely follows the carve-out.The fraction of consolidated business shows the fraction of total sales and operating profit(before interest,tax,and extraordinary items)attributed to the carve-out subsidiary,multi- plied by the fraction of the subsidiary shares owned by the parent.The return on assets is calculated as the ratio of operating profit to total assets.The return on sales is calculated as the ratio of operating profit to total revenue. Fraction of Consolidated Business Estimated Profitability Date of Operating Return on Operating Parent Statements Sales Profit Assets Margin TURF 5/1/1999 0.047 (0.071 -0.023 -0.180 PFSW 12/31/1999 0.031 2.311 -0.328 -0.506 RETK 12/31/1999 0.274 .9) -0.046 -0.103 uBid 12/31/1998 0.056 0.329 0.137 -0.098 indicates that both the subsidiary and consolidated earnings are negative Table IV presents the results of this test.The combined beneficial ownership of executives and directors is reported.In contrast to the traditional agency cost explanation,direct management holdings in the parent are generally greater than in the subsidiary.Management ownership of parent firms DLIA.HNCS.and MALL is 56%.2%,and 37%,respectively.Direct management ownership of their respective subsidiaries is considerably less at zero,zero and 2%,respectively. In contrast,management's 9%ownership of PFSW exceeds management's 7%ownership of DZTK. Since the management team of the parent and the subsidiary can be one and the same,we calculate the indirect holdings in the subsidiary that is comprised of management's ownership of the parent.To do so,management's ownership in the parent is multiplied by the fraction of the subsidiary held by the parent.When both direct and indirect ownership are combined, that management's ownership of the subsidiary is still generally below management's ownership of the parent.The ownership profile suggests that management wealth incentives encourage profit maximization of the parent over the subsidiary.This result contrasts with the market value discount that we observe for carve-out parents. Morck,Shleifer,and Vishny (1988)propose an alternative entrenchment explanation for the relation between management ownership and market valuation.They suggest that control increases with management ownership,so that at certain levels of control,the mechanisms for removing management are eliminated.Thus,management is encouraged to pursue non- value-maximizing activities for their personal benefit.despite the negative value impact of their actions on their portfolio holdings. The positive correlation between management holdings and subsidiary-holdings-to-parent valuation suggests an entrenchment explanation.Parent firms,such as DLIA,that have strong managerial control of parent assets are able to extract wealth from the subsidiary for their personal benefit without any concerns for possible retaliation by investors asking for management removal.This explanation supports the findings of Barclay,Holderness,and