正在加载图片...
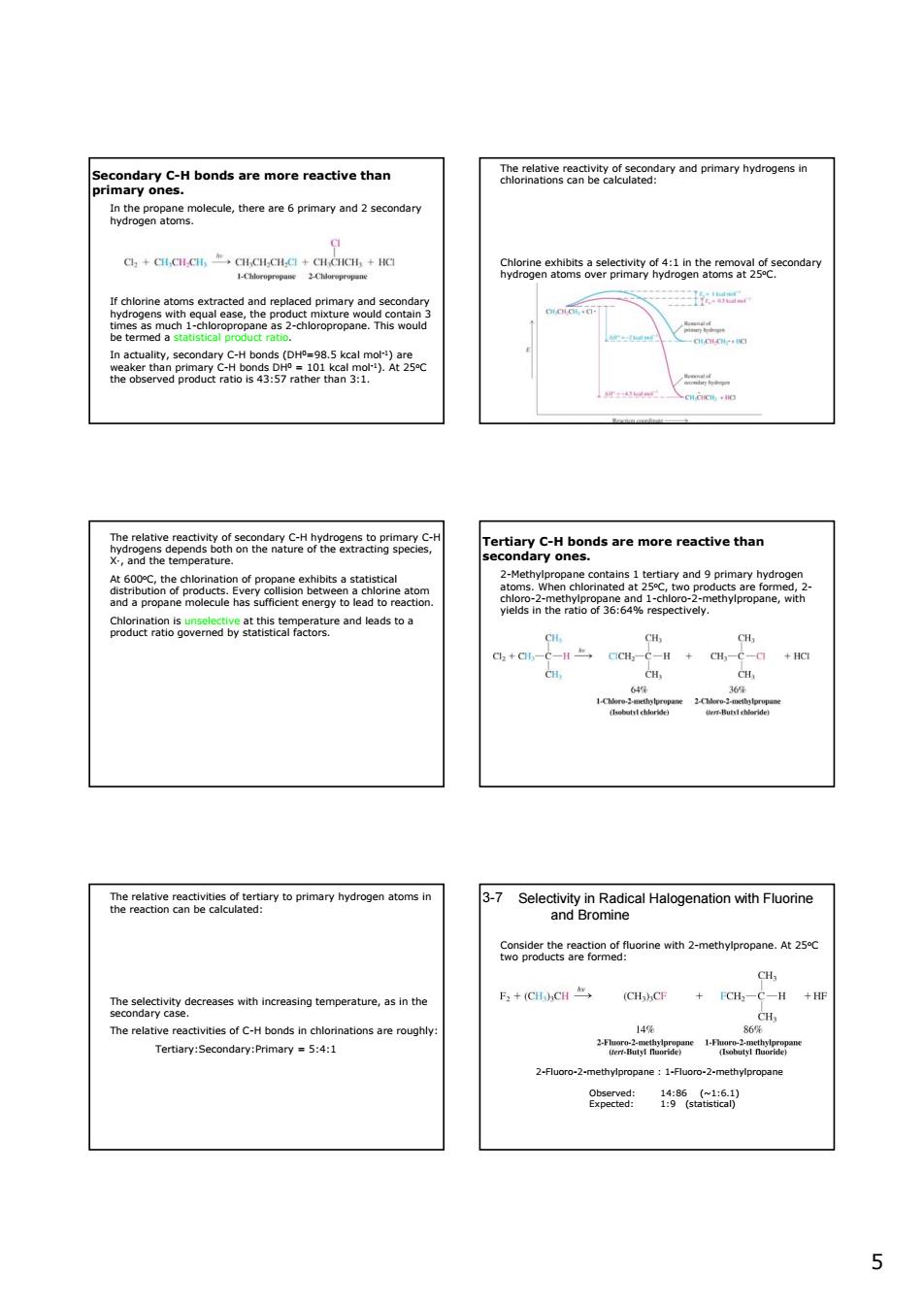
hiegaeoeae,heen6myand2saconaen gg9ogeneatosa2eetmc4anhega2gEecondan 学学 2 wwww Caaaioeadyaendwaoa heeioCnteteioftaayoprimayhydroegmatomsth 37seeananRatgalHaogenaiontwhFuoine easUtsreioemcetnomnewmtn2-methyheropane.kt25c 一H+H rd) 55 If chlorine atoms extracted and replaced primary and secondary hydrogens with equal ease, the product mixture would contain 3 times as much 1-chloropropane as 2-chloropropane. This would be termed a statistical product ratio. In actuality, secondary C-H bonds (DH0=98.5 kcal mol-1) are weaker than primary C-H bonds DH0 = 101 kcal mol-1). At 25oC the observed product ratio is 43:57 rather than 3:1. Secondary C-H bonds are more reactive than primary ones. In the propane molecule, there are 6 primary and 2 secondary hydrogen atoms. The relative reactivity of secondary and primary hydrogens in chlorinations can be calculated: relative reactivity of yield of product from number of / a secondary hydrogen secondary hydrogen abstraction secondary hydrogens = Relative reactivity of yield of product from a primary hydrogen prim ⎛ ⎞⎛ ⎞ ⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠⎝ ⎠ 57/2 = 4 number of 43/6 / ary hydrogen abstraction primary hydrogens ≈ ⎛ ⎞⎛ ⎞ ⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠⎝ ⎠ Chlorine exhibits a selectivity of 4:1 in the removal of secondary hydrogen atoms over primary hydrogen atoms at 25oC. The relative reactivity of secondary C-H hydrogens to primary C-H hydrogens depends both on the nature of the extracting species, X·, and the temperature. At 600oC, the chlorination of propane exhibits a statistical distribution of products. Every collision between a chlorine atom and a propane molecule has sufficient energy to lead to reaction. Chlorination is unselective at this temperature and leads to a product ratio governed by statistical factors. Tertiary C-H bonds are more reactive than secondary ones. 2-Methylpropane contains 1 tertiary and 9 primary hydrogen atoms. When chlorinated at 25oC, two products are formed, 2- chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane, with yields in the ratio of 36:64% respectively. The relative reactivities of tertiary to primary hydrogen atoms in the reaction can be calculated: relative reactivity of yield of product from number of / a tertiary hydrogen tertiary hydrogen abstraction tertiary hydrogens = Relative reactivity of yield of product from a primary hydrogen primary ⎛ ⎞⎛ ⎞ ⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠⎝ ⎠ 36/1 = 5 number of 64/9 / hydrogen abstraction primary hydrogens ≈ ⎛ ⎞⎛ ⎞ ⎜ ⎟⎜ ⎟ ⎝ ⎠⎝ ⎠ The selectivity decreases with increasing temperature, as in the secondary case. The relative reactivities of C-H bonds in chlorinations are roughly: Tertiary:Secondary:Primary = 5:4:1 Selectivity in Radical Halogenation with Fluorine and Bromine 3-7 Consider the reaction of fluorine with 2-methylpropane. At 25oC two products are formed: 2-Fluoro-2-methylpropane : 1-Fluoro-2-methylpropane Observed: 14:86 (~1:6.1) Expected: 1:9 (statistical)