正在加载图片...
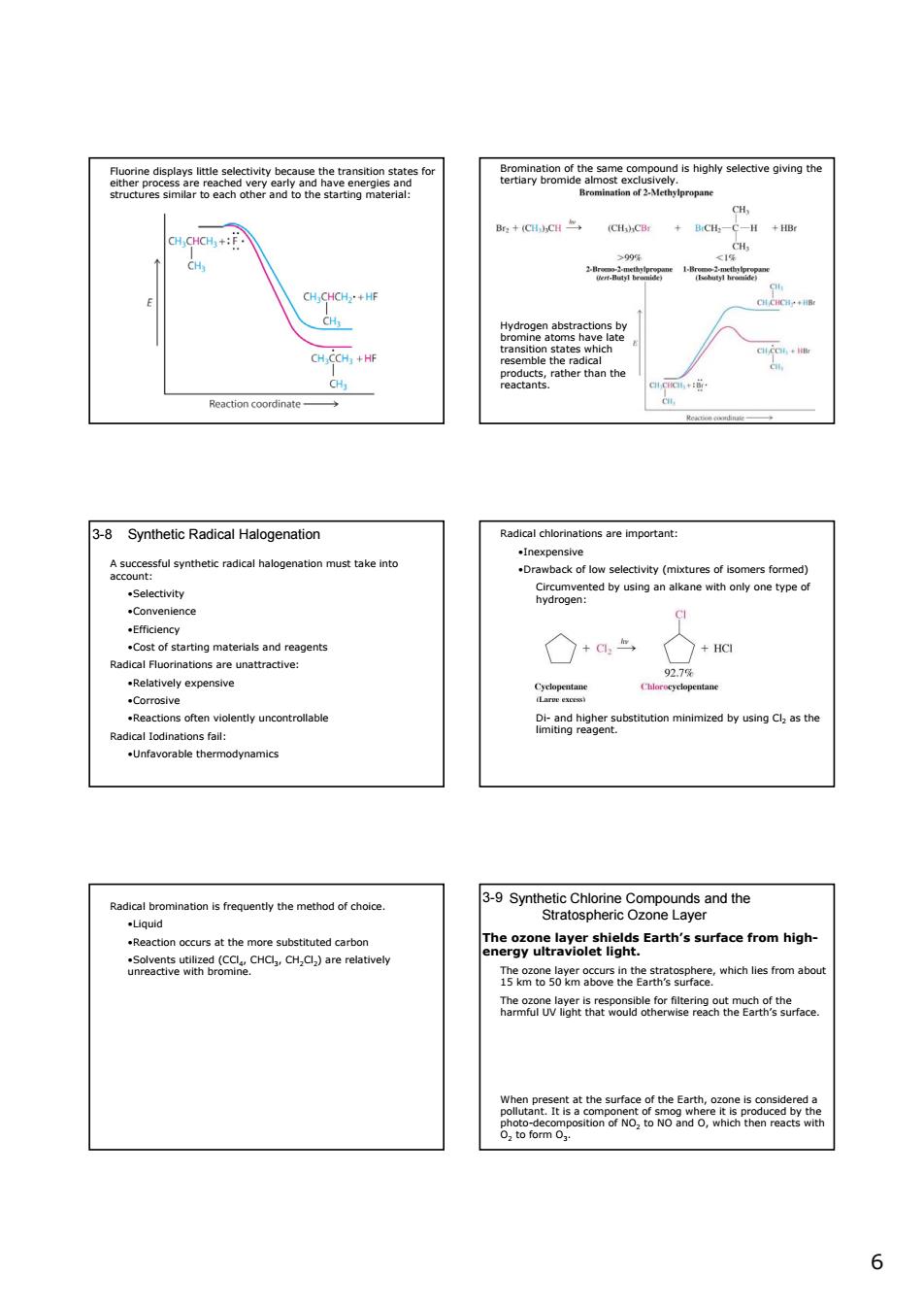
H CH CH CCH+HF nble the radica products,rat Reaction coordinate 3-8 Synthetic Radical Halogenation vely expensiv nd ragen .Unfavorable thermodynamics nty the method of choic 3-Symheti Cndhe Reaction occurs at the mo Earth's surface from high veec le rom abo 6 6 Fluorine displays little selectivity because the transition states for either process are reached very early and have energies and structures similar to each other and to the starting material: Bromination of the same compound is highly selective giving the tertiary bromide almost exclusively. Hydrogen abstractions by bromine atoms have late transition states which resemble the radical products, rather than the reactants. 3-8 Synthetic Radical Halogenation A successful synthetic radical halogenation must take into account: •Selectivity •Convenience •Efficiency •Cost of starting materials and reagents Radical Fluorinations are unattractive: •Relatively expensive •Corrosive •Reactions often violently uncontrollable Radical Iodinations fail: •Unfavorable thermodynamics Radical chlorinations are important: •Inexpensive •Drawback of low selectivity (mixtures of isomers formed) Circumvented by using an alkane with only one type of hydrogen: Di- and higher substitution minimized by using Cl2 as the limiting reagent. Radical bromination is frequently the method of choice. •Liquid •Reaction occurs at the more substituted carbon •Solvents utilized (CCl4, CHCl3, CH2Cl2) are relatively unreactive with bromine. Synthetic Chlorine Compounds and the Stratospheric Ozone Layer 3-9 The ozone layer shields Earth’s surface from highenergy ultraviolet light. The ozone layer occurs in the stratosphere, which lies from about 15 km to 50 km above the Earth’s surface. The ozone layer is responsible for filtering out much of the harmful UV light that would otherwise reach the Earth’s surface. hν 2 2 3 hν 3 2 O 2O 1) O + O O 2) O O + O 3) ⎯⎯→ ⎯⎯→ ⎯⎯→ When present at the surface of the Earth, ozone is considered a pollutant. It is a component of smog where it is produced by the photo-decomposition of NO2 to NO and O, which then reacts with O2 to form O3