正在加载图片...
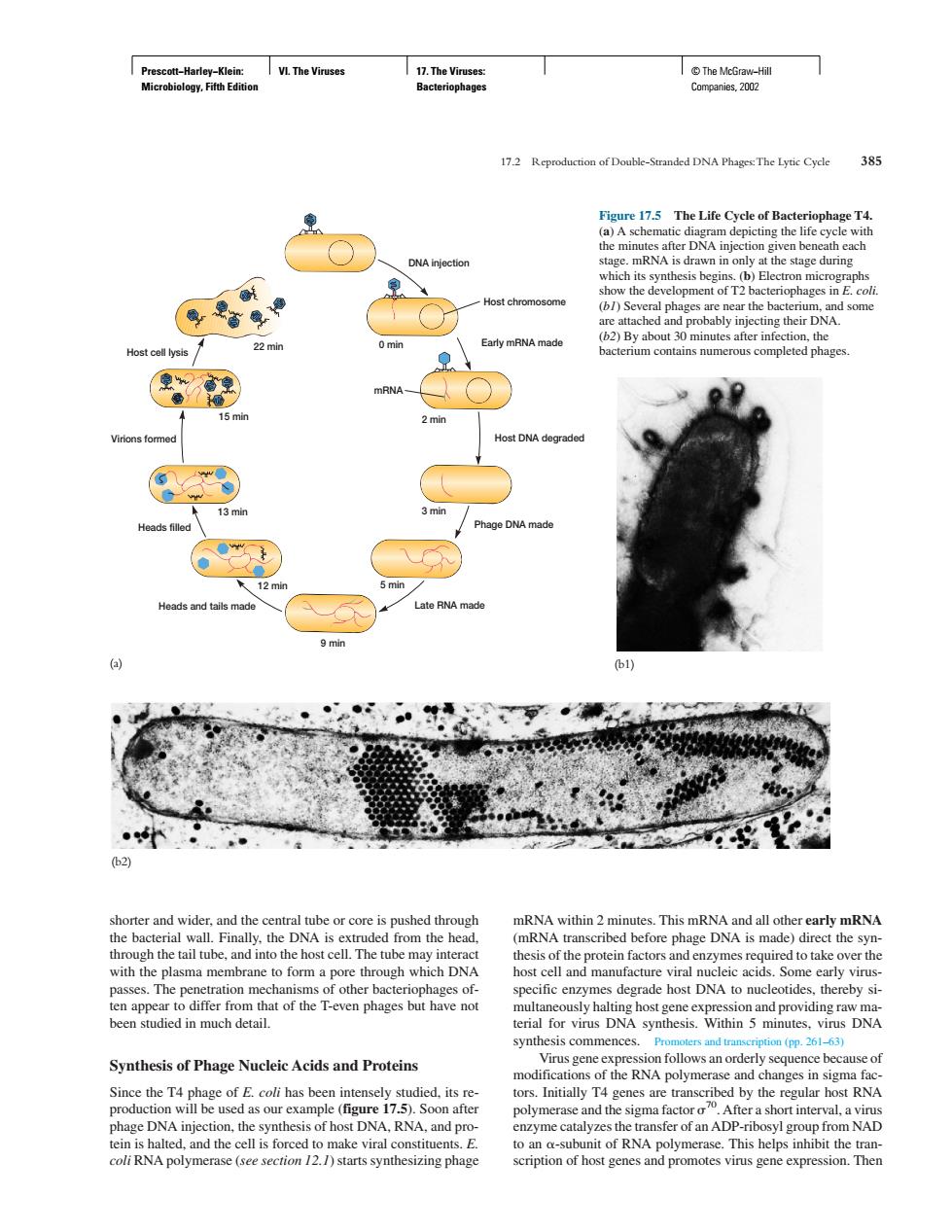
n 172 Reproduction of Double-Standed DNA Phages The Lytic Cyde 385 he Life Cvele of E ONA ini es an h protein Synthesis of Phage Nucleic Acids and Proteins anges ed hy polymerase and the sigma factor coli RNA polymerase (see section /2.1)starts synthesizing phage scription of host genes and promotes virus gene expression.Then Prescott−Harley−Klein: Microbiology, Fifth Edition VI. The Viruses 17. The Viruses: Bacteriophages © The McGraw−Hill Companies, 2002 shorter and wider, and the central tube or core is pushed through the bacterial wall. Finally, the DNA is extruded from the head, through the tail tube, and into the host cell. The tube may interact with the plasma membrane to form a pore through which DNA passes. The penetration mechanisms of other bacteriophages often appear to differ from that of the T-even phages but have not been studied in much detail. Synthesis of Phage Nucleic Acids and Proteins Since the T4 phage of E. coli has been intensely studied, its reproduction will be used as our example (figure 17.5). Soon after phage DNA injection, the synthesis of host DNA, RNA, and protein is halted, and the cell is forced to make viral constituents. E. coli RNA polymerase (see section 12.1) starts synthesizing phage mRNA within 2 minutes. This mRNA and all other early mRNA (mRNA transcribed before phage DNA is made) direct the synthesis of the protein factors and enzymes required to take over the host cell and manufacture viral nucleic acids. Some early virusspecific enzymes degrade host DNA to nucleotides, thereby simultaneously halting host gene expression and providing raw material for virus DNA synthesis. Within 5 minutes, virus DNA synthesis commences. Promoters and transcription (pp. 261–63) Virus gene expression follows an orderly sequence because of modifications of the RNA polymerase and changes in sigma factors. Initially T4 genes are transcribed by the regular host RNA polymerase and the sigma factor 70. After a short interval, a virus enzyme catalyzes the transfer of an ADP-ribosyl group from NAD to an -subunit of RNA polymerase. This helps inhibit the transcription of host genes and promotes virus gene expression. Then 17.2 Reproduction of Double-Stranded DNA Phages:The Lytic Cycle 385 DNA injection 0 min Early mRNA made 2 min Host DNA degraded mRNA 3 min Phage DNA made 5 min Late RNA made 9 min Heads and tails made 12 min 13 min Heads filled 15 min Virions formed 22 min Host cell lysis Host chromosome Figure 17.5 The Life Cycle of Bacteriophage T4. (a) A schematic diagram depicting the life cycle with the minutes after DNA injection given beneath each stage. mRNA is drawn in only at the stage during which its synthesis begins. (b) Electron micrographs show the development of T2 bacteriophages in E. coli. (b1) Several phages are near the bacterium, and some are attached and probably injecting their DNA. (b2) By about 30 minutes after infection, the bacterium contains numerous completed phages. (a) (b1) (b2)�