正在加载图片...
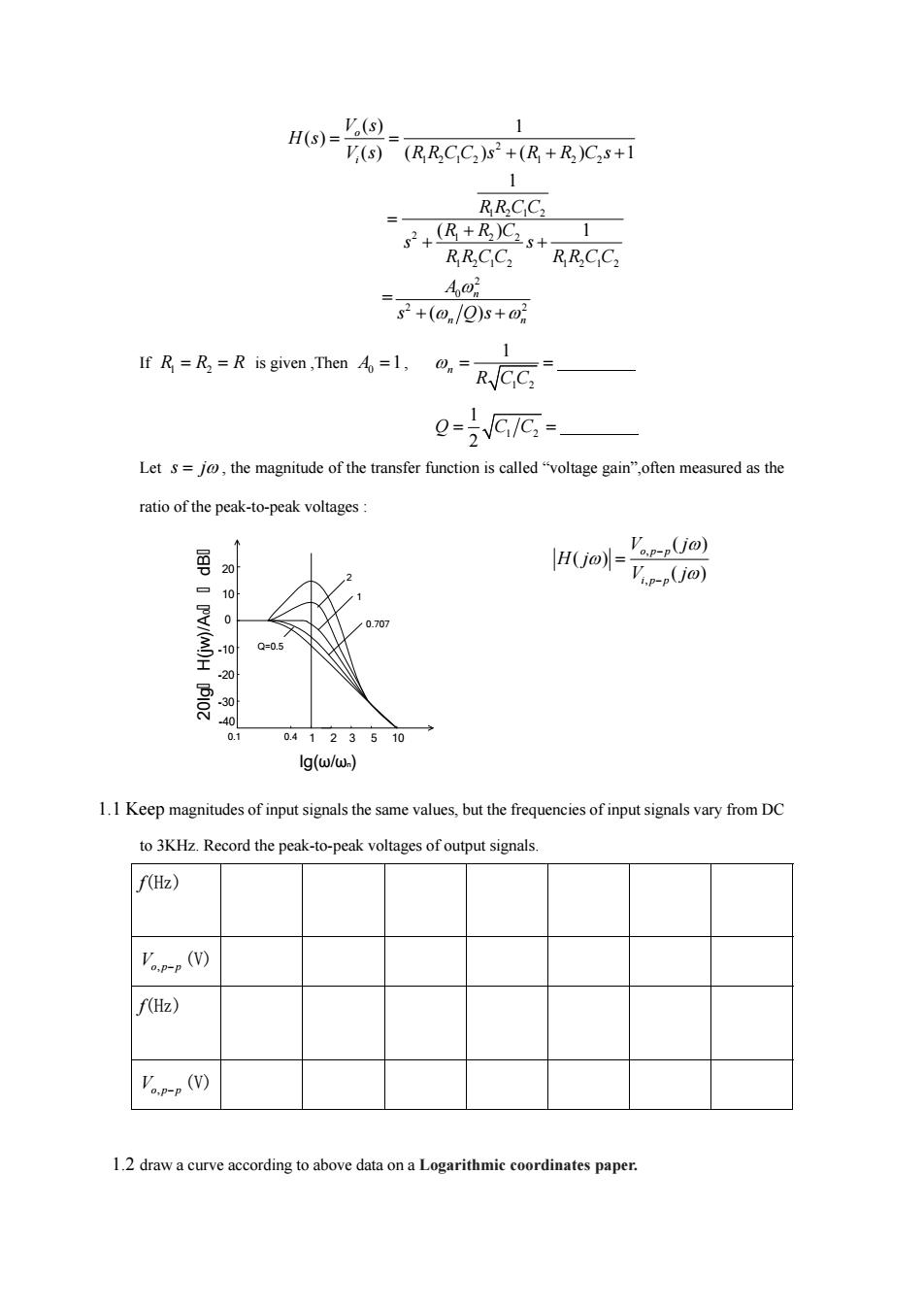
H(s)= '(s) V(s)(RRCC)s2+(R+R)C2s+1 1 RRCC2 (R+R)C.s+ 1 RRCC2 RCC2 Ao斤 s2+(@/Q)s+0 IR=R is given,Then1RCC 0- Let s=jo,the magnitude of the transfer function is called"voltage gain",often measured as the ratio of the peak-to-peak voltages 'op-pUo) H(jo-Tp-pOo) 10 0 0.707 -10 Q=0.5 20 -30 40 0.1 0.4123510 Ig(w/w.) 1.1 Keep magnitudes of input signals the same values,but the frequencies of input signals vary from DC to 3KHz.Record the peak-to-peak voltages of output signals. f(Hz) p-p(W f(Hz) Vp-p() 1.2 draw a curve according to above data on a Logarithmic coordinates paper.2 1212 1 2 2 1212 2 1 22 1212 1212 2 0 2 2 ( ) 1 ( ) () ( ) ( ) 1 1 ( ) 1 = ( ) o i n n n V s H s V s RRCC s R R C s RRCC R RC s s RRCC RRCC A s Qs If R1 2 R R is given ,Then 0 A 1, 1 2 1 n R CC 1 2 1 2 Q CC Let s j , the magnitude of the transfer function is called “voltage gain”,often measured as the ratio of the peak-to-peak voltages : 20 10 0 -10 -20 -30 -40 0.1 0.4 1 2 3 5 10 lg(ω/ωn) 20lg H(jw)/A0 dB 1 2 0.707 Q=0.5 , , ( ) ( ) ( ) op p ip p V j H j V j 1.1 Keep magnitudes of input signals the same values, but the frequencies of input signals vary from DC to 3KHz. Record the peak-to-peak voltages of output signals. f(Hz) Vop p , (V) f(Hz) Vop p , (V) 1.2 draw a curve according to above data on a Logarithmic coordinates paper