正在加载图片...
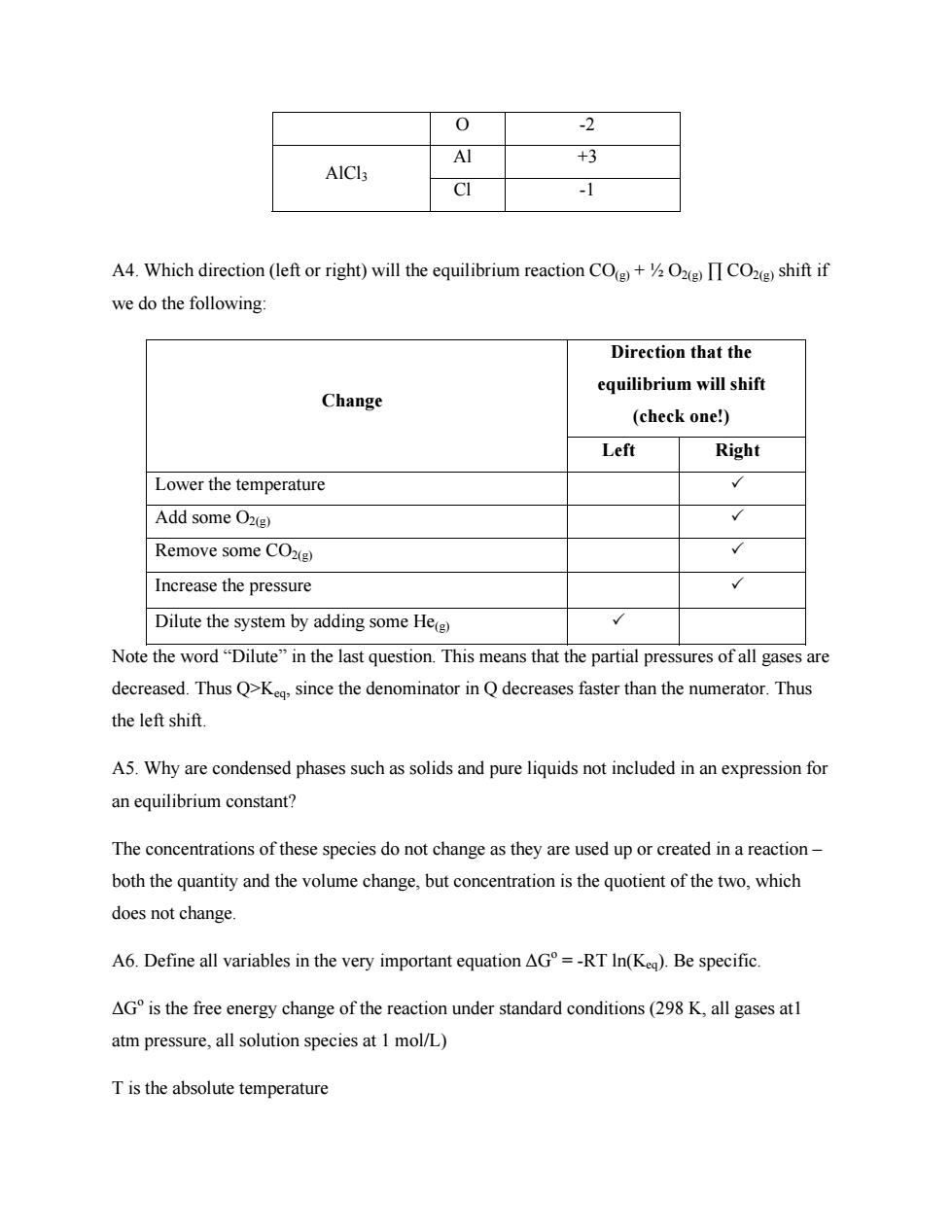
0 -2 Al +3 -1 A4.Which direction(left or right)will the equilibrium reaction CO+CO)shift if we do the following: Direction that the Change equilibrium will shift (check one!) Left Right Lower the temperature Add some O2() Remove some COxg) Increase the pressure Dilute the system by adding some Heg Note the word"Dilute"in the last question.This means that the partial pressures of all gases are decreased.Thus Q>K,since the denominator in Q decreases faster than the numerator.Thus the left shift. A5.Why are condensed phases such as solids and pure liquids not included in an expression for an equilibrium constant? The concentrations of these species do not change as they are used up or created in a reaction both the quantity and the volume change,but concentration is the quotient of the two,which does not change A6.Define all variables in the very important equation AG=-RT In(Keq).Be specific. AGis the free energy change of the reaction under standard conditions(29 K,all gases at atm pressure,all solution species at 1 mol/L) Tis the absolute temperatureO -2 Al +3 AlCl3 Cl -1 A4. Which direction (left or right) will the equilibrium reaction CO(g) + ½ O2(g) ∏ CO2(g) shift if we do the following: Direction that the equilibrium will shift (check one!) Change Left Right Lower the temperature 3 Add some O2(g) 3 Remove some CO2(g) 3 Increase the pressure 3 Dilute the system by adding some He(g) 3 Note the word “Dilute” in the last question. This means that the partial pressures of all gases are decreased. Thus Q>Keq, since the denominator in Q decreases faster than the numerator. Thus the left shift. A5. Why are condensed phases such as solids and pure liquids not included in an expression for an equilibrium constant? The concentrations of these species do not change as they are used up or created in a reaction – both the quantity and the volume change, but concentration is the quotient of the two, which does not change. A6. Define all variables in the very important equation ΔGo = -RT ln(Keq). Be specific. ΔGo is the free energy change of the reaction under standard conditions (298 K, all gases at1 atm pressure, all solution species at 1 mol/L) T is the absolute temperature