正在加载图片...
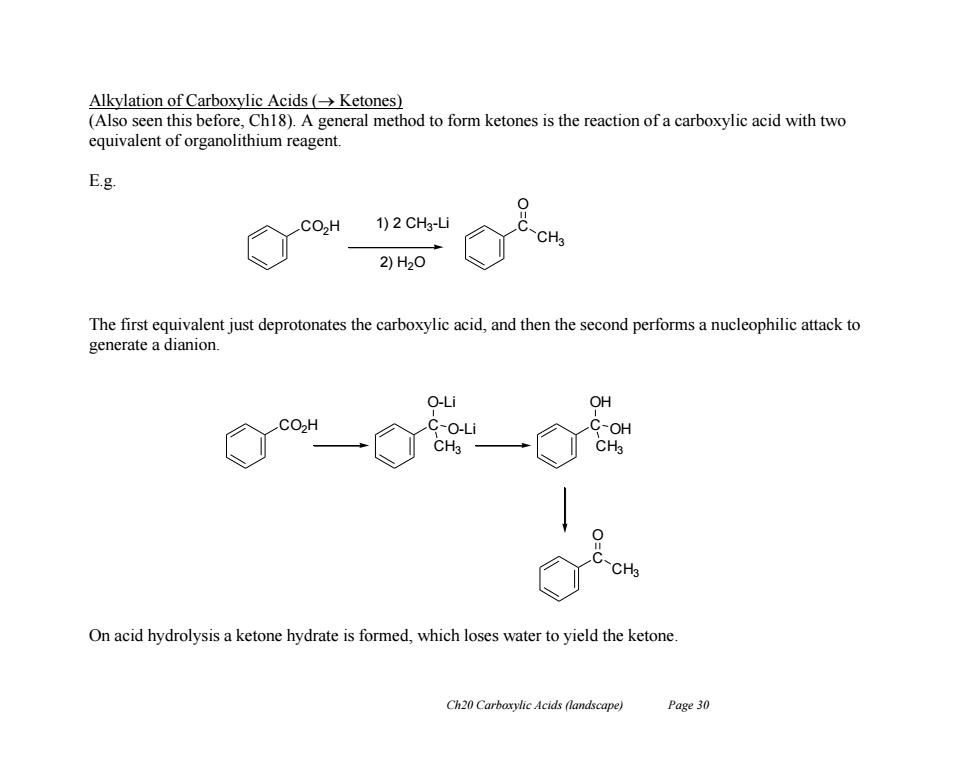
Alkylation of Carboxylic Acids (Ketones) (Also seen this before,Ch18).A general method to form ketones is the reaction of a carboxylic acid with two equivalent of organolithium reagent. E.g. 0 CO,H 1)2CH3-L CH3 2)H2O The first equivalent just deprotonates the carboxylic acid,and then the second performs a nucleophilic attack to generate a dianion. O-Li OH CO>H C-O-Li OH CH3 C On acid hydrolysis a ketone hydrate is formed,which loses water to yield the ketone. Ch20 Carboxylic Acids (landscape) Page 30 Ch20 Carboxylic Acids (landscape) Page 30 Alkylation of Carboxylic Acids ( Ketones) (Also seen this before, Ch18). A general method to form ketones is the reaction of a carboxylic acid with two equivalent of organolithium reagent. E.g. The first equivalent just deprotonates the carboxylic acid, and then the second performs a nucleophilic attack to generate a dianion. On acid hydrolysis a ketone hydrate is formed, which loses water to yield the ketone. CO2H 1) 2 CH3 -Li 2) H2O C O CH3 CO2H C O-Li O-Li CH3 C OH OH CH3 C O CH3