正在加载图片...
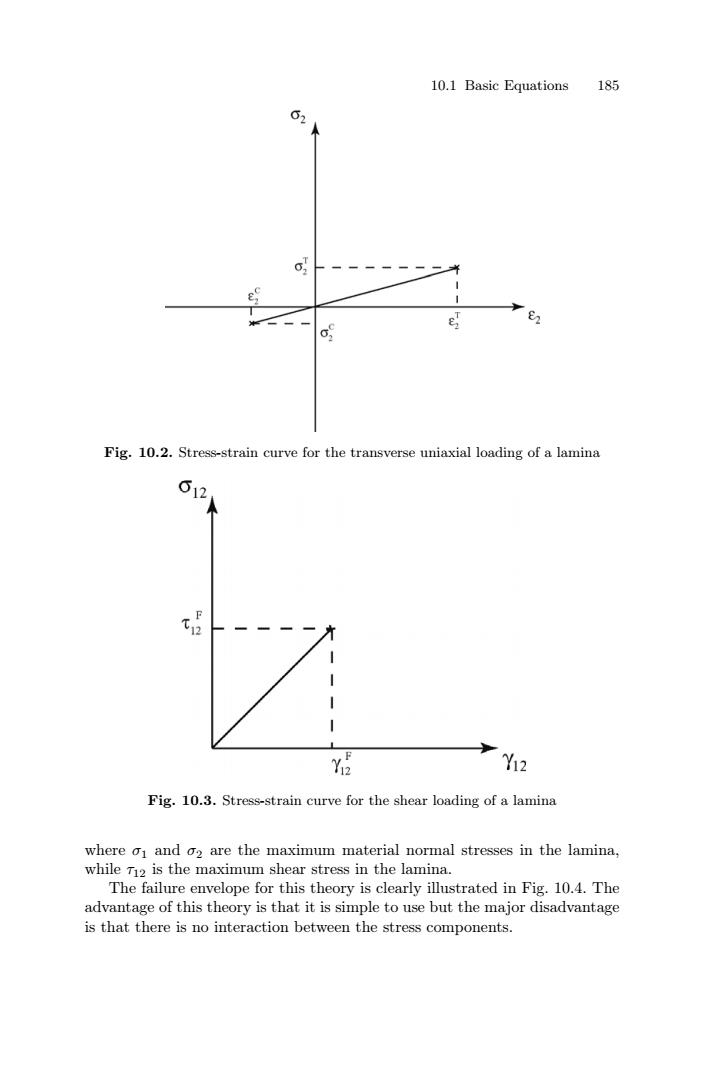
10.1 Basic Equations 185 62 e 6 e Fig.10.2.Stress-strain curve for the transverse uniaxial loading of a lamina 612 I 1 品 Y12 Fig.10.3.Stress-strain curve for the shear loading of a lamina where o1 and o2 are the maximum material normal stresses in the lamina, while T12 is the maximum shear stress in the lamina. The failure envelope for this theory is clearly illustrated in Fig.10.4.The advantage of this theory is that it is simple to use but the major disadvantage is that there is no interaction between the stress components.10.1 Basic Equations 185 Fig. 10.2. Stress-strain curve for the transverse uniaxial loading of a lamina Fig. 10.3. Stress-strain curve for the shear loading of a lamina where σ1 and σ2 are the maximum material normal stresses in the lamina, while τ12 is the maximum shear stress in the lamina. The failure envelope for this theory is clearly illustrated in Fig. 10.4. The advantage of this theory is that it is simple to use but the major disadvantage is that there is no interaction between the stress components