正在加载图片...
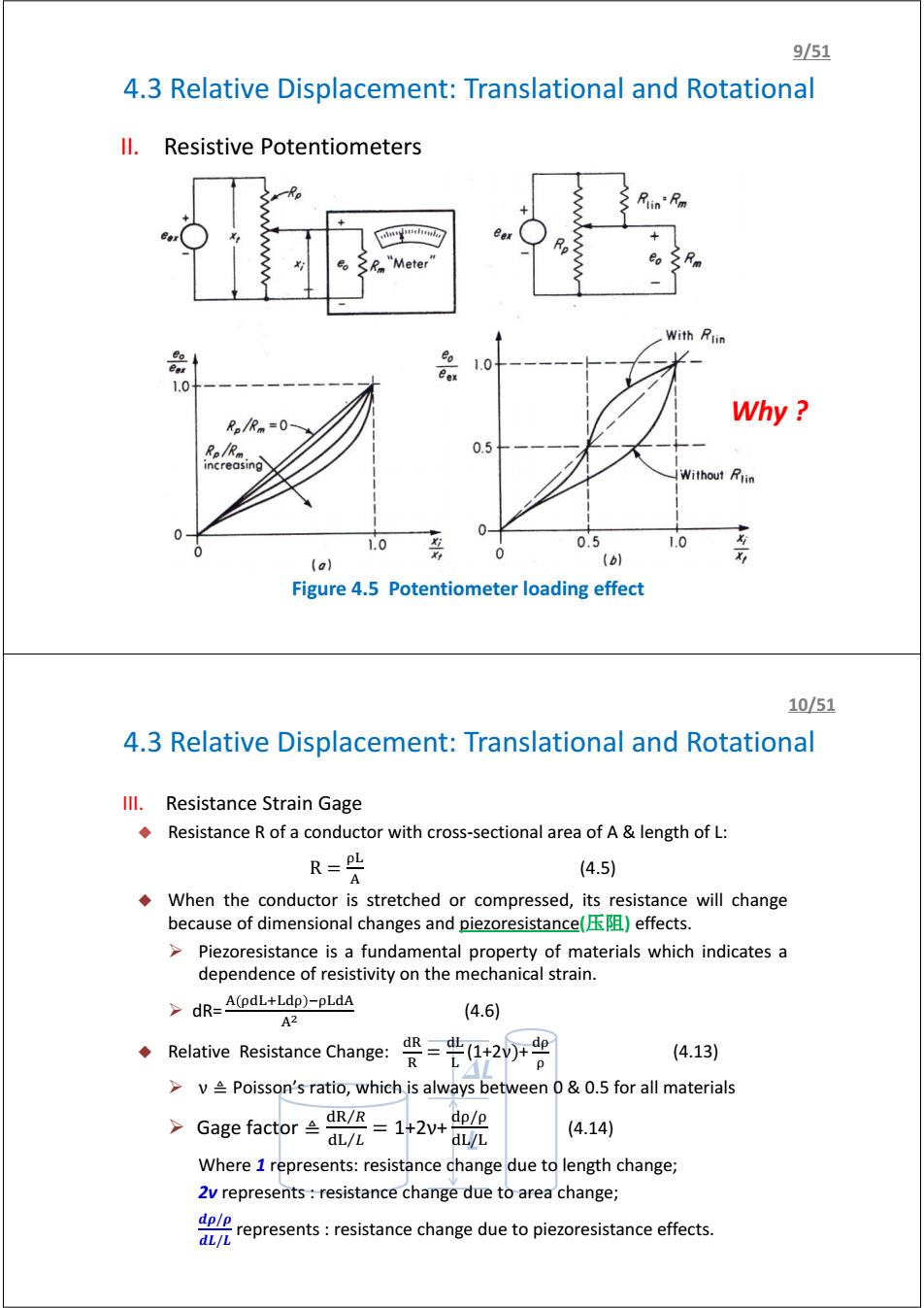
951 4.3 Relative Displacement:Translational and Rotational ll.Resistive Potentiometers Rlin'Fm "Meter With Rtin 品 Bex 1.0 1.0 Why Re/Rm=0- R。R。 0.5 increasing Without Rlin 1.0 0.5 1.0 0 (a) (b) Figure 4.5 Potentiometer loading effect 10/51 4.3 Relative Displacement:Translational and Rotational Ill.Resistance Strain Gage Resistance R of a conductor with cross-sectional area of A length of L: R=PL (4.5) A When the conductor is stretched or compressed,its resistance will change because of dimensional changes and piezoresistance()effects. >Piezoresistance is a fundamental property of materials which indicates a dependence of resistivity on the mechanical strain. >dR=A(pdL+Ldp)-pLdA A2 (4.6) Relative Resistance Change: =20r号 (4.13) p >v Poisson's ratio,which is always between 0&0.5 for all materials >Ga8 efactor2=142+鼢 dL/L (4.14) Where 1 represents:resistance change due to length change; 2v represents resistance change due to area change; represets:resistance change due to piezoresistance effects. dL/LII. Resistive Potentiometers Figure 4.5 Potentiometer loading effect 4.3 Relative Displacement: Translational and Rotational 9/51 www.vishay.com www.bourns.com Why ? 4.3 Relative Displacement: Translational and Rotational L DL III. Resistance Strain Gage Resistance R of a conductor with cross-sectional area of A & length of L: R = (4.5) When the conductor is stretched or compressed, its resistance will change because of dimensional changes and piezoresistance(压阻) effects. ¾ Piezoresistance is a fundamental property of materials which indicates a dependence of resistivity on the mechanical strain. ¾ dR= ୢାୢ ିୢ మ (4.6) Relative Resistance Change: ୢୖ ୖ = ୢ (1+2ν)+ ୢ (4.13) ¾ ν ≜ Poisson’s ratio, which is always between 0 & 0.5 for all materials ¾ Gage factor ≜ ୢୖ ோ⁄ ୢ ⁄ = 1+2ν+ ୢ/ ୢ/ (4.14) Where 1 represents: resistance change due to length change; 2ν represents : resistance change due to area change; ࣋/࣋ࢊ ࡸࢊ/ࡸ represents : resistance change due to piezoresistance effects. 10/51