正在加载图片...
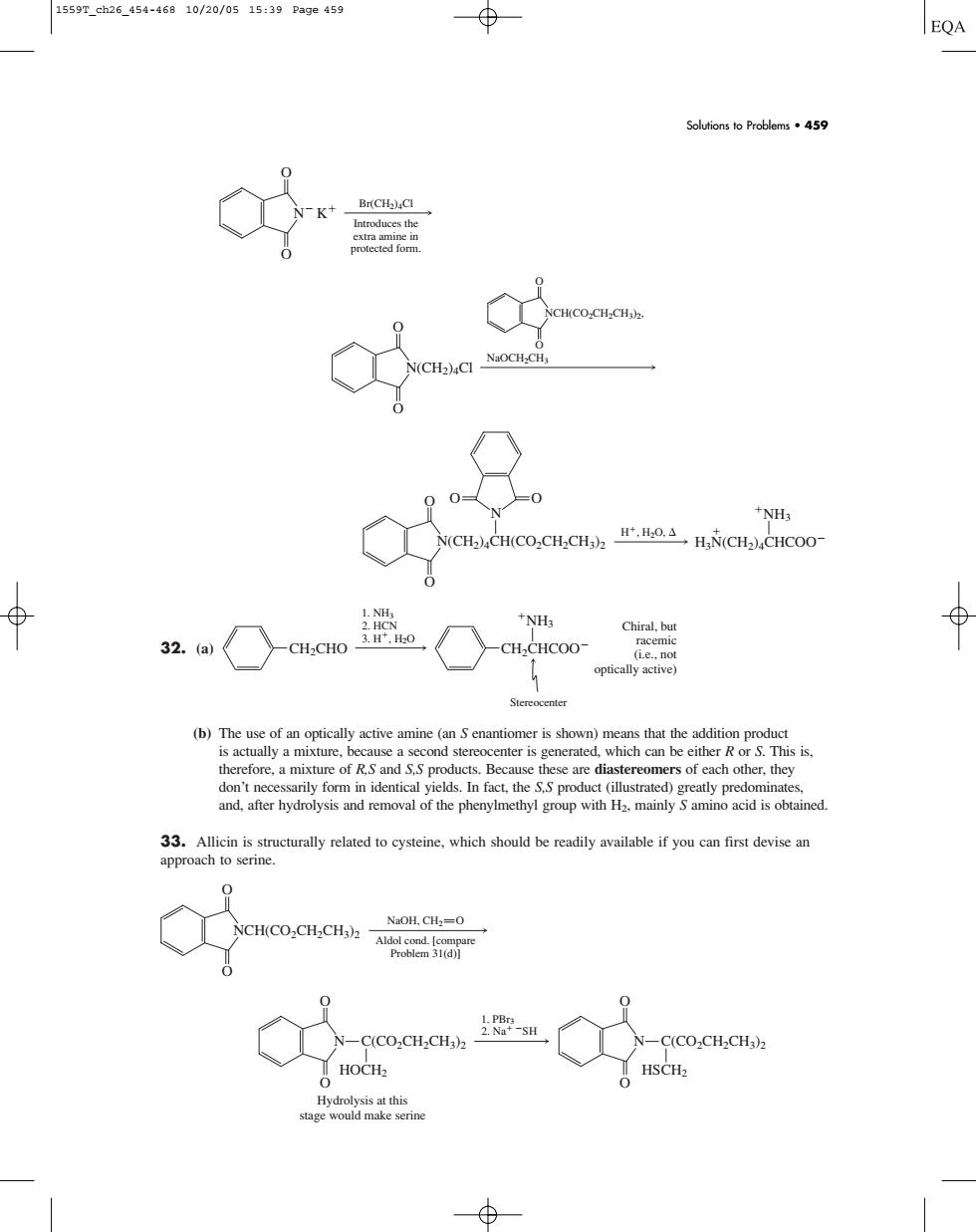
1559T_ch26_454-46810/20/0515:39Pa9e459 EQA Soutions o Problems59 人oa兰e NH. (b)The use of an opically active amine (is shown)means that the addition product s actually a mixture ond stereocenter is generated,which can be e don't necess reatly predominate and,after hydrolysis and removal of the phenylmethyl group with H2,mainly Samino acid is obtained. 33.Allicin is structurally related to cysteine,which should be readily available if you can first devise an approach to serine. NCH(CO-CHCH3)- NaOH.CH:-0 C(CO.CH2CHa2 SH C(CO-CH2CHa2 HOCH2 HSCH2 32. (a) (b) The use of an optically active amine (an S enantiomer is shown) means that the addition product is actually a mixture, because a second stereocenter is generated, which can be either R or S. This is, therefore, a mixture of R,S and S,S products. Because these are diastereomers of each other, they don’t necessarily form in identical yields. In fact, the S,S product (illustrated) greatly predominates, and, after hydrolysis and removal of the phenylmethyl group with H2, mainly S amino acid is obtained. 33. Allicin is structurally related to cysteine, which should be readily available if you can first devise an approach to serine. 1. PBr3 2. Na SH N O O C(CO2CH2CH3)2 HOCH2 Hydrolysis at this stage would make serine N O O C(CO2CH2CH3)2 HSCH2 O O NCH(CO2CH2CH3)2 NaOH, CH2 O Aldol cond. [compare Problem 31(d)] CH2CHO 3. H, H2O 1. NH3 2. HCN NH3 CH2CHCOO Stereocenter Chiral, but racemic (i.e., not optically active) O O O N O N(CH2)4CH(CO2CH2CH3)2 H, H2O, NH3 H3N(CH2)4CHCOO NaOCH2CH3 O O N(CH2)4Cl O O NCH(CO2CH2CH3)2, Br(CH2)4Cl Introduces the extra amine in protected form. N K O O Solutions to Problems • 459 1559T_ch26_454-468 10/20/05 15:39 Page 459�����������