正在加载图片...
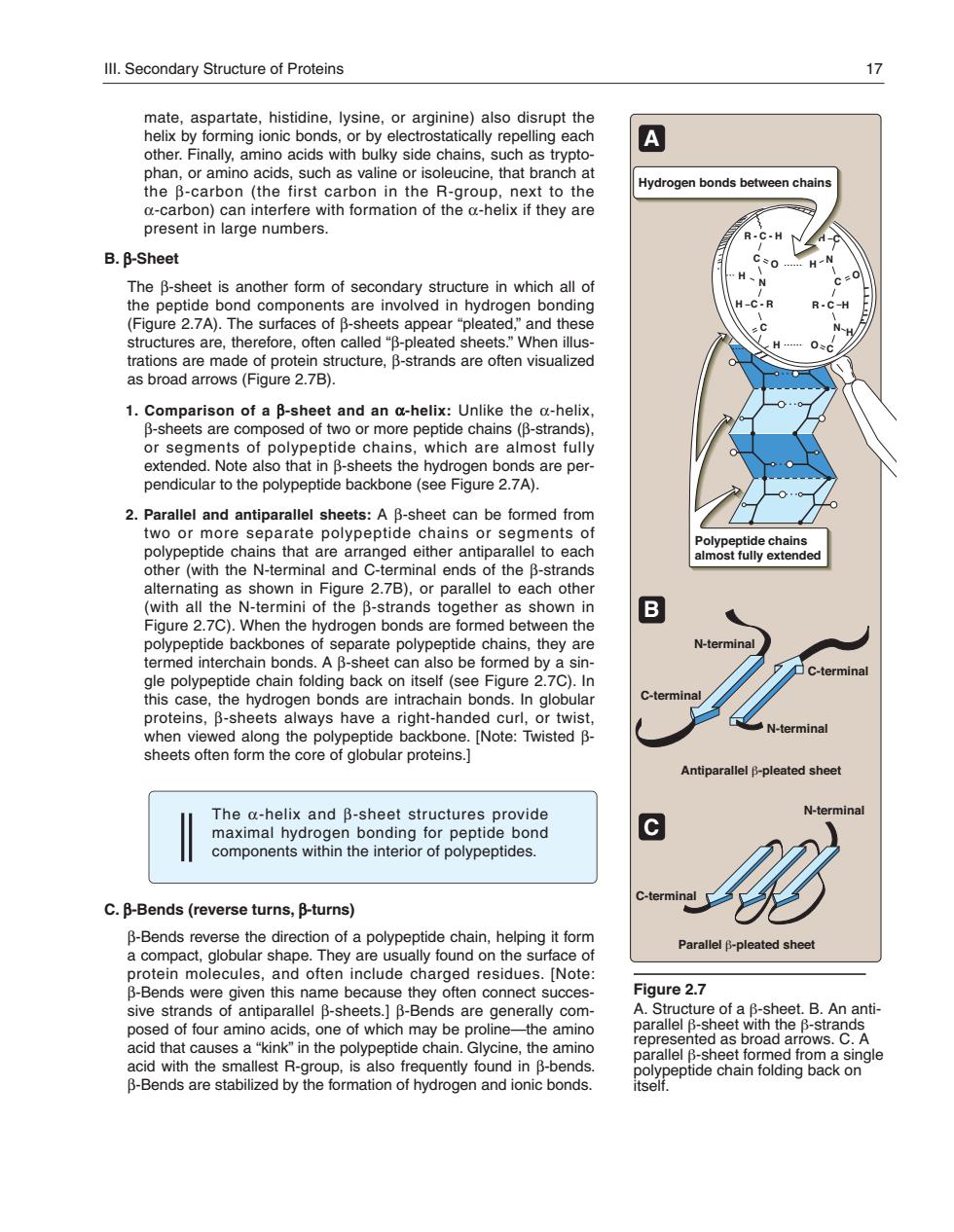
Ill.Secondary Structure of Proteins other.Finally,amino acids with bulky side chains,such as trypto A n as valine or is that branch Hydrogen bonds between chain present in large numbers. B.B-Sheet 0 of se re ofen vee d sheets."When illus. of polypeptide chains,which are am roheas s are per polypepti pone (se 盒 that are a eltoeach as 27B1 uel to (with all the N-termini of the B-strands together as shown in Figure 2.7C).When the hydrogen bonds are formed between the A R arate polypeptide chains. they are this case.the hydrogen bonds are intrachain bonds.In globular eets er viwep a bone. The a-helix and B-sheet structures provide maximal hydrogen bonding tor peptide bond n the inte C.B-Bends(reverse turns,B-turns) protein molecules,and often include charged residues.Note B-Bends were given this name because they often connect succes gure 2. sive strands of antiparallel B-sheets. -Benas are generally com ne.the am parallel a fr a single acid with the smallest R-group,is also frequently found in B-bends. B-Bends are stabilized by the formation of hydrogen and ionic bonds.mate, aspartate, histidine, lysine, or arginine) also disrupt the helix by forming ionic bonds, or by electrostatically repelling each other. Finally, amino acids with bulky side chains, such as tryptophan, or amino acids, such as valine or isoleucine, that branch at the β-carbon (the first carbon in the R-group, next to the α-carbon) can interfere with formation of the α-helix if they are present in large numbers. B. β-Sheet The β-sheet is another form of secondary structure in which all of the peptide bond components are involved in hydrogen bonding (Figure 2.7A). The surfaces of β-sheets appear “pleated,” and these structures are, therefore, often called “β-pleated sheets.” When illustrations are made of protein structure, β-strands are often visualized as broad arrows (Figure 2.7B). 1. Comparison of a β-sheet and an α-helix: Unlike the α-helix, β-sheets are composed of two or more peptide chains (β-strands), or segments of polypeptide chains, which are almost fully extended. Note also that in β-sheets the hydrogen bonds are perpendicular to the polypeptide backbone (see Figure 2.7A). 2. Parallel and antiparallel sheets: A β-sheet can be formed from two or more separate polypeptide chains or segments of polypeptide chains that are arranged either antiparallel to each other (with the N-terminal and C-terminal ends of the β-strands alternating as shown in Figure 2.7B), or parallel to each other (with all the N-termini of the β-strands together as shown in Figure 2.7C). When the hydrogen bonds are formed between the polypeptide backbones of separate polypeptide chains, they are termed interchain bonds. A β-sheet can also be formed by a single polypeptide chain folding back on itself (see Figure 2.7C). In this case, the hydrogen bonds are intrachain bonds. In globular proteins, β-sheets always have a right-handed curl, or twist, when viewed along the polypeptide backbone. [Note: Twisted β- sheets often form the core of globular proteins.] The α-helix and β-sheet structures provide maximal hydrogen bonding for peptide bond components within the interior of polypeptides. C. β-Bends (reverse turns, β-turns) β-Bends reverse the direction of a polypeptide chain, helping it form a compact, globular shape. They are usually found on the surface of protein molecules, and often include charged residues. [Note: β-Bends were given this name because they often connect successive strands of antiparallel β-sheets.] β-Bends are generally composed of four amino acids, one of which may be proline—the amino acid that causes a “kink” in the polypeptide chain. Glycine, the amino acid with the smallest R-group, is also frequently found in β-bends. β-Bends are stabilized by the formation of hydrogen and ionic bonds. Figure 2.7 A. Structure of a β-sheet. B. An antiparallel β-sheet with the β-strands represented as broad arrows. C. A parallel β-sheet formed from a single polypeptide chain folding back on itself. Polypeptide chains almost fully extended Antiparallel β-pleated sheet Parallel β-pleated sheet C-terminal N-terminal N-terminal C-terminal N-terminal C-terminal O R - C - H H N N C C N C C - R H C H O R - C H O H H H C A B C Hydrogen bonds between chains III. Secondary Structure of Proteins 17 168397_P013-024.qxd7.0:02 Protein structure 5-20-04 2010.4.4 11:31 AM Page 17