正在加载图片...
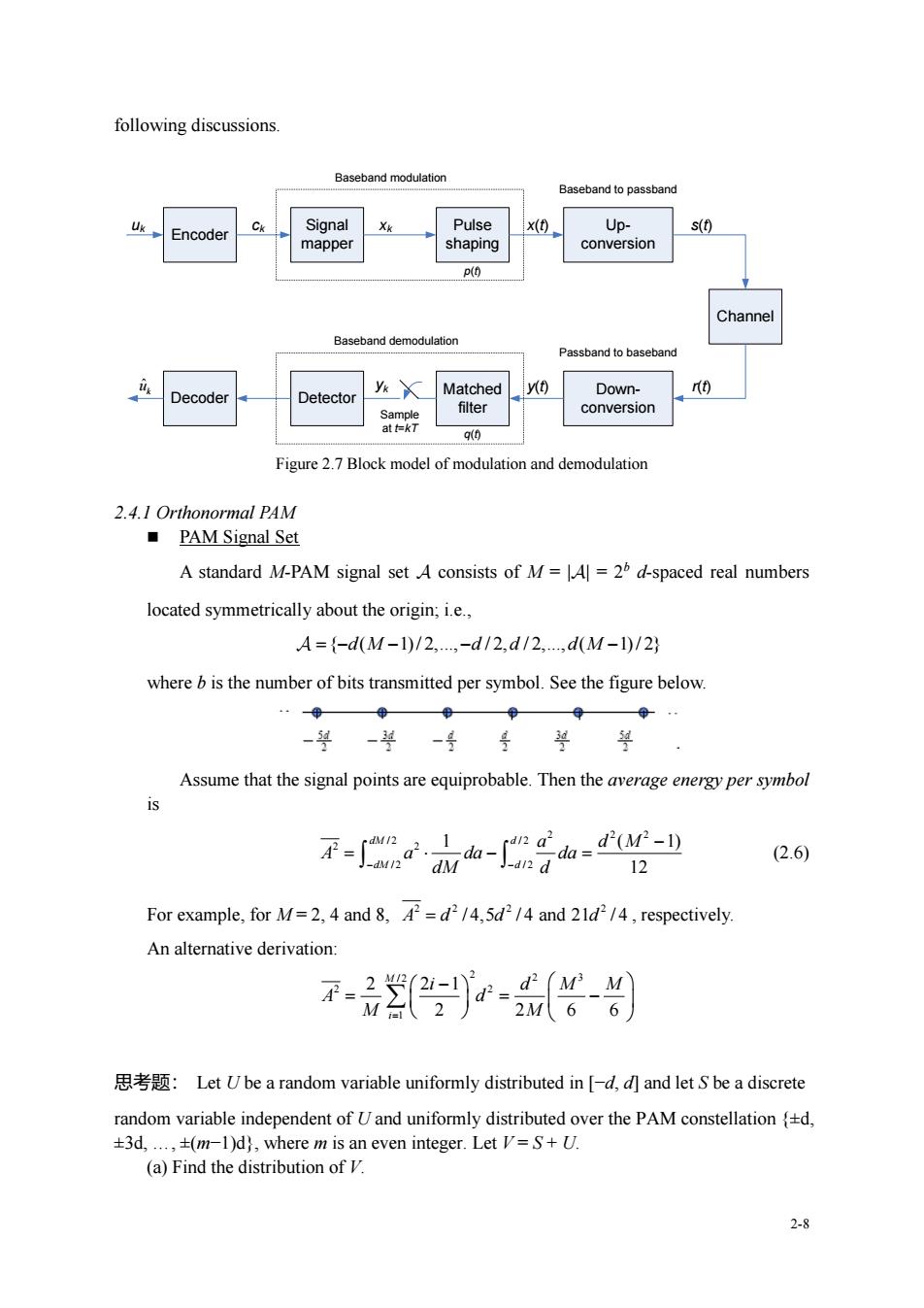
following discussions. Baseband modulation Baseband topassband -Encoder Signal Pulse x(t) Up- s(t) mapper shaping conversion P(O and democ ulation Passband to baseban Decoder etector y Matched yt) Down- conversion 90 Figure 2.7 Block model of modulation and demodulation 2.4.1 Orthonormal PAM ■PAM Signal Set A standard M-PAM signal set A consists of M=A]=2d-spaced real numbers located symmetrically about the origin;i.e., A={-d(M-1)/2,-d/2,d/2,d(M-l0/2} where bis the number of bits transmitted per symbol.See the figure below Assume that the signal points are equiprobable.Then the average energy per symbol 不-小心-音山g- (2.6) 12 For example,for M.4 and/4.5d/4 and /,respectively. An alternative derivation 思考题:Let Ube a random variable uniformly distributed in-d,and letbe adiscrete random variable independent of Uand uniformly distributed over the PAM constellationd, +3d,.,(m-1)d),where m is an even integer.Let V=+U. (a)Find the distribution of 2-8 2-8 following discussions. Encoder Signal mapper Pulse shaping Up- conversion uk ck xk x(t) Baseband modulation Baseband to passband s(t) Channel Down- conversion Passband to baseband Matched filter Decoder Detector y(t) r(t) Sample at t=kT yk Baseband demodulation p(t) q(t) ˆ k u Figure 2.7 Block model of modulation and demodulation 2.4.1 Orthonormal PAM ◼ PAM Signal Set A standard M-PAM signal set consists of M = || = 2b d-spaced real numbers located symmetrically about the origin; i.e., = − − − − { ( 1) / 2,., / 2, / 2,., ( 1) / 2} d M d d d M where b is the number of bits transmitted per symbol. See the figure below. Assume that the signal points are equiprobable. Then the average energy per symbol is 2 2 2 / 2 / 2 2 2 / 2 / 2 1 ( 1) 12 dM d dM d a d M A a da da − − dM d − = − = (2.6) For example, for M = 2, 4 and 8, 2 2 2 2 A d d d = / 4,5 / 4 and 21 / 4 , respectively. An alternative derivation: 2 / 2 2 3 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 6 6 M i i d M M A d M M = − = = − 思考题: Let U be a random variable uniformly distributed in [−d, d] and let S be a discrete random variable independent of U and uniformly distributed over the PAM constellation {±d, ±3d, ., ±(m−1)d}, where m is an even integer. Let V = S + U. (a) Find the distribution of V