正在加载图片...
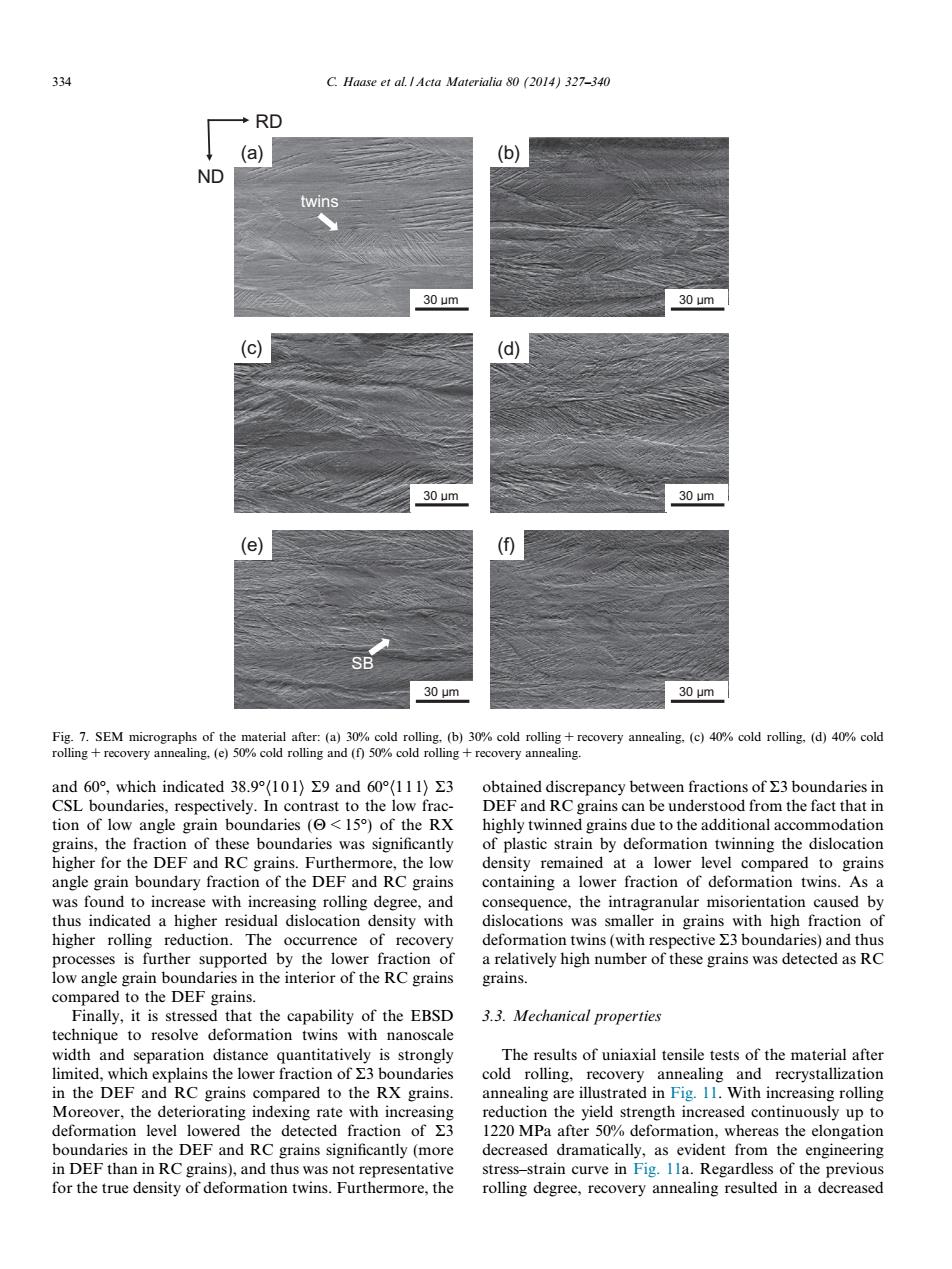
334 C.Haase et al.Acta Materialia 80 (2014)327-340 RD (a) (b) ND twins 30 um 30 um 30 um 30 um (e) (⑤ SB 30μm 30μm Fig.7.SEM micrographs of the material after:(a)30%cold rolling,(b)30%cold rolling recovery annealing,(c)40%cold rolling,(d)40%cold rolling recovery annealing,(e)50%cold rolling and (f)50%cold rolling recovery annealing. and60°,which indicated38.9(10l)Σ9and60°(111)3 obtained discrepancy between fractions of 3 boundaries in CSL boundaries,respectively.In contrast to the low frac- DEF and RC grains can be understood from the fact that in tion of low angle grain boundaries (<15)of the RX highly twinned grains due to the additional accommodation grains,the fraction of these boundaries was significantly of plastic strain by deformation twinning the dislocation higher for the DEF and RC grains.Furthermore,the low density remained at a lower level compared to grains angle grain boundary fraction of the DEF and RC grains containing a lower fraction of deformation twins.As a was found to increase with increasing rolling degree,and consequence,the intragranular misorientation caused by thus indicated a higher residual dislocation density with dislocations was smaller in grains with high fraction of higher rolling reduction.The occurrence of recovery deformation twins(with respective E3 boundaries)and thus processes is further supported by the lower fraction of a relatively high number of these grains was detected as RC low angle grain boundaries in the interior of the RC grains grains. compared to the DEF grains. Finally,it is stressed that the capability of the EBSD 3.3.Mechanical properties technique to resolve deformation twins with nanoscale width and separation distance quantitatively is strongly The results of uniaxial tensile tests of the material after limited.which explains the lower fraction of X3 boundaries cold rolling,recovery annealing and recrystallization in the DEF and RC grains compared to the RX grains. annealing are illustrated in Fig.11.With increasing rolling Moreover,the deteriorating indexing rate with increasing reduction the yield strength increased continuously up to deformation level lowered the detected fraction of E3 1220 MPa after 50%deformation,whereas the elongation boundaries in the DEF and RC grains significantly(more decreased dramatically,as evident from the engineering in DEF than in RC grains),and thus was not representative stress-strain curve in Fig.Ila.Regardless of the previous for the true density of deformation twins.Furthermore,the rolling degree,recovery annealing resulted in a decreasedand 60, which indicated 38.9h101i R9 and 60h111i R3 CSL boundaries, respectively. In contrast to the low fraction of low angle grain boundaries (H < 15) of the RX grains, the fraction of these boundaries was significantly higher for the DEF and RC grains. Furthermore, the low angle grain boundary fraction of the DEF and RC grains was found to increase with increasing rolling degree, and thus indicated a higher residual dislocation density with higher rolling reduction. The occurrence of recovery processes is further supported by the lower fraction of low angle grain boundaries in the interior of the RC grains compared to the DEF grains. Finally, it is stressed that the capability of the EBSD technique to resolve deformation twins with nanoscale width and separation distance quantitatively is strongly limited, which explains the lower fraction of R3 boundaries in the DEF and RC grains compared to the RX grains. Moreover, the deteriorating indexing rate with increasing deformation level lowered the detected fraction of R3 boundaries in the DEF and RC grains significantly (more in DEF than in RC grains), and thus was not representative for the true density of deformation twins. Furthermore, the obtained discrepancy between fractions of R3 boundaries in DEF and RC grains can be understood from the fact that in highly twinned grains due to the additional accommodation of plastic strain by deformation twinning the dislocation density remained at a lower level compared to grains containing a lower fraction of deformation twins. As a consequence, the intragranular misorientation caused by dislocations was smaller in grains with high fraction of deformation twins (with respective R3 boundaries) and thus a relatively high number of these grains was detected as RC grains. 3.3. Mechanical properties The results of uniaxial tensile tests of the material after cold rolling, recovery annealing and recrystallization annealing are illustrated in Fig. 11. With increasing rolling reduction the yield strength increased continuously up to 1220 MPa after 50% deformation, whereas the elongation decreased dramatically, as evident from the engineering stress–strain curve in Fig. 11a. Regardless of the previous rolling degree, recovery annealing resulted in a decreased RD ND (a) 30 µm 30 µm (f) 30 µm (e) 30 µm (d) 30 µm (c) 30 µm (b) twins SB Fig. 7. SEM micrographs of the material after: (a) 30% cold rolling, (b) 30% cold rolling + recovery annealing, (c) 40% cold rolling, (d) 40% cold rolling + recovery annealing, (e) 50% cold rolling and (f) 50% cold rolling + recovery annealing. 334 C. Haase et al. / Acta Materialia 80 (2014) 327–340����