正在加载图片...
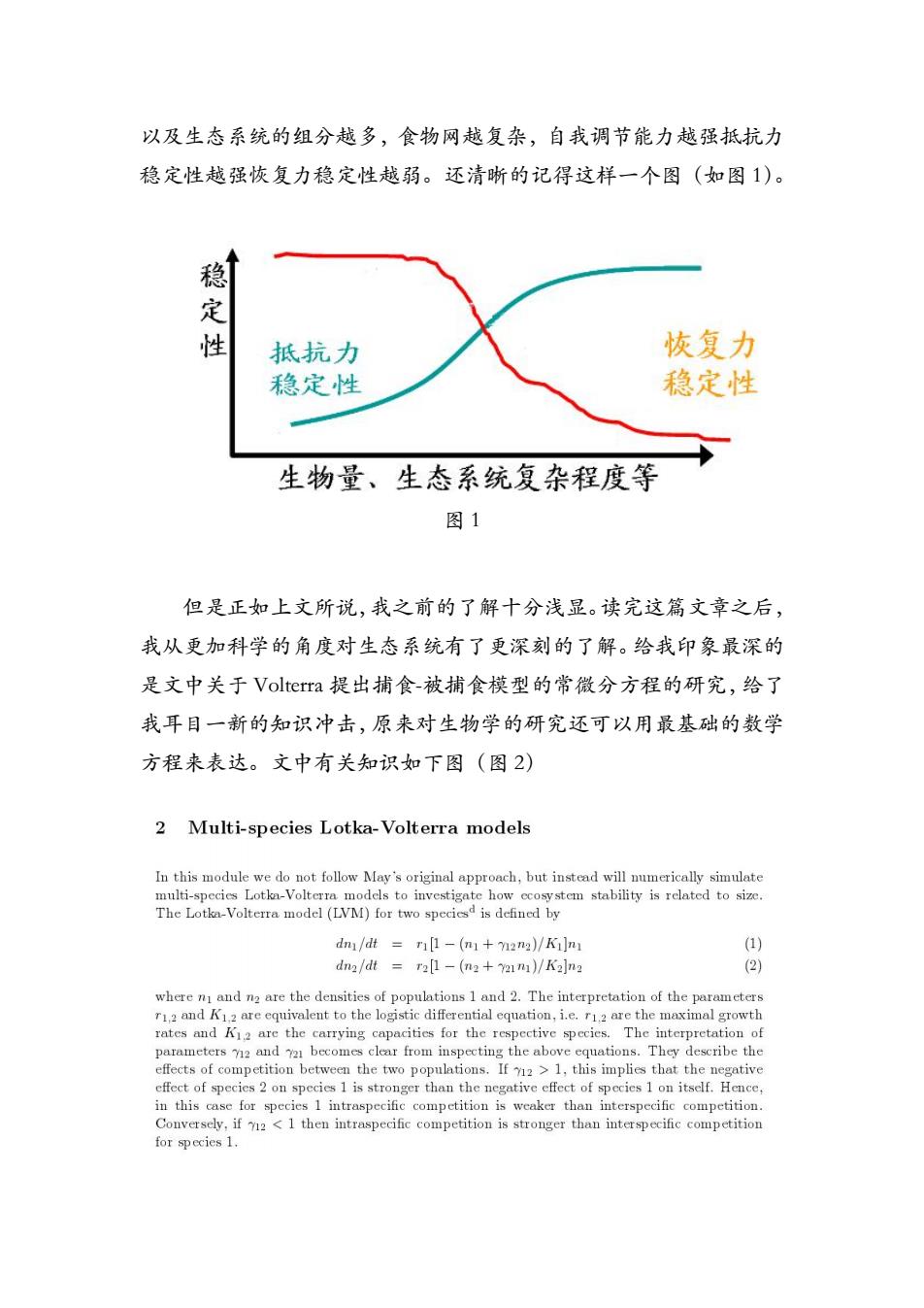
以及生态系统的组分越多,食物网越复杂,自我调节能力越强抵抗力 稳定性越强恢复力稳定性越弱。还清晰的记得这样一个图(如图1)。 稳 定性 抵抗力 恢复力 稳定性 稳定性 生物量、生态系统复杂程度等 图1 但是正如上文所说,我之前的了解十分浅显。读完这篇文章之后, 我从更加科学的角度对生态系统有了更深刻的了解。给我印象最深的 是文中关于Volterra提出捕食-被捕食模型的常微分方程的研究,给了 我耳目一新的知识冲击,原来对生物学的研究还可以用最基础的数学 方程来表达。文中有关知识如下图(图2) 2 Multi-species Lotka-Volterra models In this module we do not follow May's original approach,but instead will numerically simulate multi-specics Lotkn-Volterra models to investigate how ccosystem stability is related to size. The Lotka-Volterra model (LVM)for two speciesd is defined by dmi/dt ri[1-(n1+m2n2)/Ki]n (1) dn2/dt=tr2[1-(2+21n)/K2]n2 (2) where n and n2 are the densities of populations 1 and 2.The interpretation of the parameters r12 and K1.2 are equivalent to the logistic differential equation,i.e.r1.2 are the maximal growth rates and K12 are the carrying capacities for the respective species.The interpretation of parameters 2 and 721 becomes clear from inspecting the above equations.They describe the effects of competition between the two populations.If 712>1,this implies that the negative effect of species 2 on species 1 is stronger than the negative effect of species 1 on itself.Hence, in this case for species 1 intraspecific competition is weaker than interspecific competition. Conversely,if 72<1 then intraspecific competition is stronger than interspecific competition for species 1.以及生态系统的组分越多,食物网越复杂,自我调节能力越强抵抗力 稳定性越强恢复力稳定性越弱。还清晰的记得这样一个图(如图 1)。 图 1 但是正如上文所说,我之前的了解十分浅显。读完这篇文章之后, 我从更加科学的角度对生态系统有了更深刻的了解。给我印象最深的 是文中关于 Volterra 提出捕食-被捕食模型的常微分方程的研究,给了 我耳目一新的知识冲击,原来对生物学的研究还可以用最基础的数学 方程来表达。文中有关知识如下图(图 2)