正在加载图片...
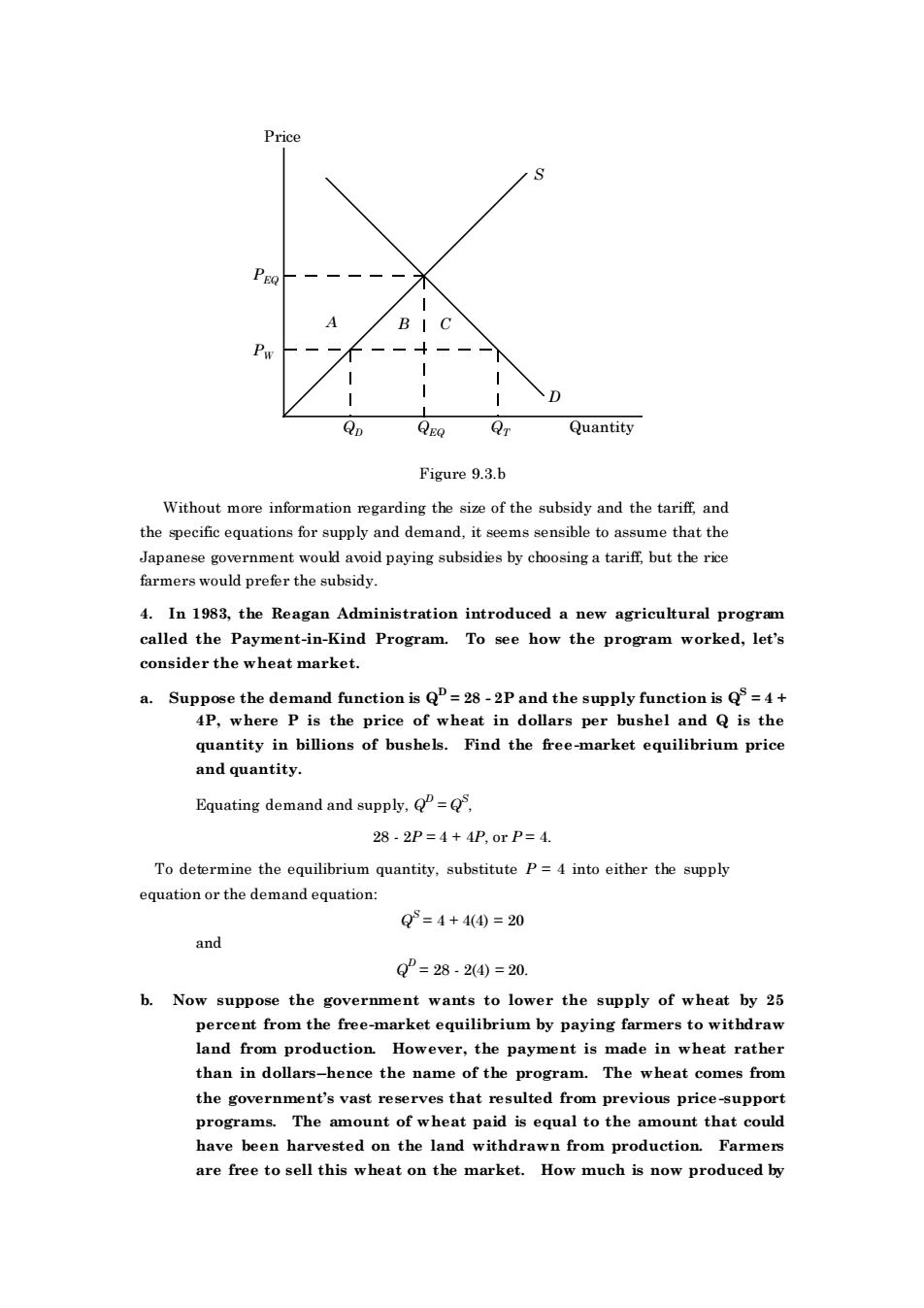
C D Quantity Figure 9.3.b Without more information egarding thesize of the subsidy and the tarif,and the specific equations for supply and demand,it seems sensible to assume that the Japanese government would avoid paying subsidies by choosing a tariff,but the rice farmers would prefer the subsidy 4.In 1983,the Reagan Administration introduced a new agricultural program called the Payment-in-Kind Program. To see how the program worked,let's consider the wheat market. a.Suppose the demand function is =28-2P and the supply function is=4+ 4P,where P is the price of wheat in dollars per bushel and Q is the quantity in billions of bushels.Find the free-market equilibrium price and quantitv. Equating demand and supply,= 28.2P=4+4P,orP=4 To determine the equilibrium quantity,substitute P=4 into either the supply equation or the demand equation Q=4+44)=20 and Q°=28-2④=20. b.Now suppose the government wants to lower the supply of wheat by 25 percent from the free-market equilibrium by paying farmers to withdraw land from production.However,the payment is made in wheat rather than in dollars-hence the name of the program.The wheat comes from the government's vast reserves that resulted from previous price-support programs.The amount of wheat paid is equal to the amount that could have been harvested on the land withdrawn from production.Farmers are free to sell this wheat on the market.How much is now produced by Price S D PEQ PW A B C QD QEQ QT Quantity Figure 9.3.b Without more information regarding the size of the subsidy and the tariff, and the specific equations for supply and demand, it seems sensible to assume that the Japanese government would avoid paying subsidies by choosing a tariff, but the rice farmers would prefer the subsidy. 4. In 1983, the Reagan Administration introduced a new agricultural program called the Payment-in-Kind Program. To see how the program worked, let’s consider the wheat market. a. Suppose the demand function is QD = 28 - 2P and the supply function is QS = 4 + 4P, where P is the price of wheat in dollars per bushel and Q is the quantity in billions of bushels. Find the free-market equilibrium price and quantity. Equating demand and supply, Q D = QS , 28 - 2P = 4 + 4P, or P = 4. To determine the equilibrium quantity, substitute P = 4 into either the supply equation or the demand equation: Q S = 4 + 4(4) = 20 and Q D = 28 - 2(4) = 20. b. Now suppose the government wants to lower the supply of wheat by 25 percent from the free-market equilibrium by paying farmers to withdraw land from production. However, the payment is made in wheat rather than in dollars-hence the name of the program. The wheat comes from the government’s vast reserves that resulted from previous price-support programs. The amount of wheat paid is equal to the amount that could have been harvested on the land withdrawn from production. Farmers are free to sell this wheat on the market. How much is now produced by